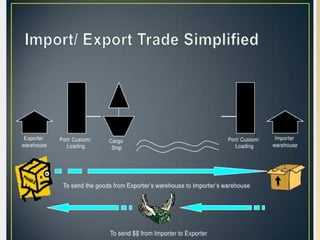
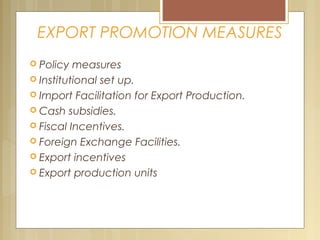
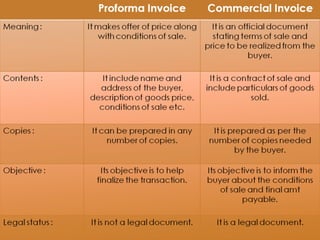
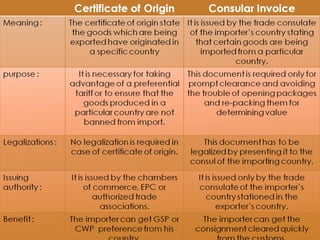
The document discusses India's import-export policy, emphasizing the importance of exports for economic growth and foreign exchange reserve enhancement. It details the Exim policy, which guides foreign trade regulations and promotional measures, along with various standardized export documentation required for international trade. The text also explains the types of shipping documents, including bills of lading and invoices, essential for the smooth functioning of export activities.