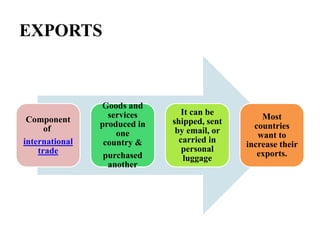
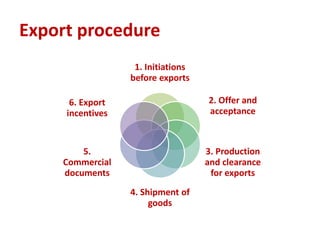
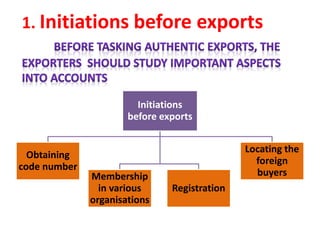
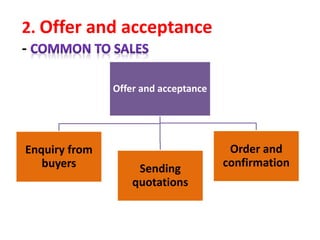
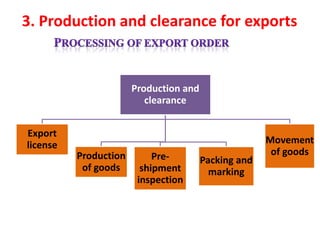
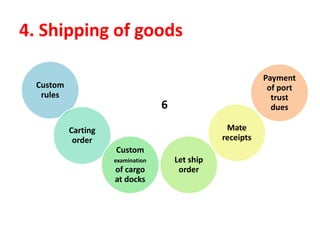
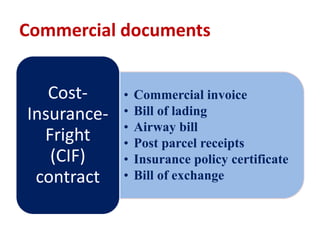
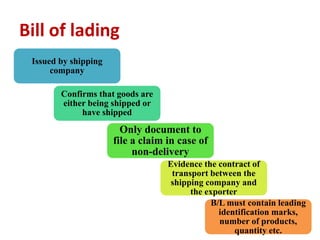
The document discusses export procedures and incentives. It describes 6 key steps: 1) Initiations like obtaining codes and finding buyers. 2) Offer/acceptance involving quotes and orders. 3) Production and clearance involving licenses, inspections, and transport. 4) Shipping using customs, shipping documents, and port procedures. 5) Commercial documents like invoices and bills of lading. 6) Obtaining export incentives like financing. Maintaining proper documentation is essential for exports to follow regulations and receive benefits.