Embed presentation
Downloaded 34 times







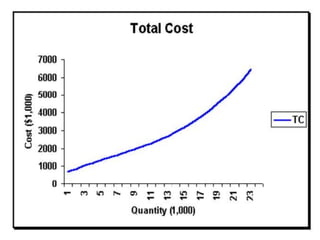

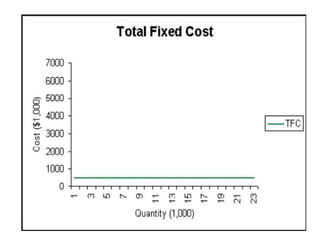

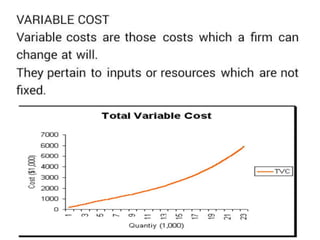


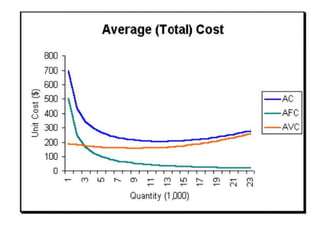



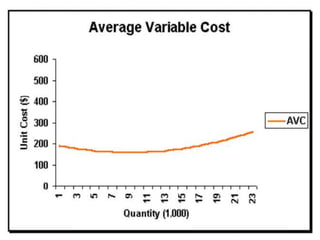



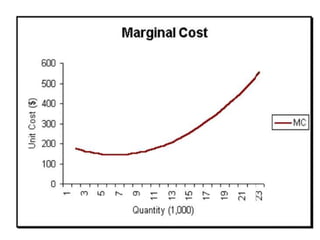

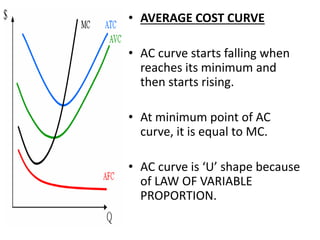
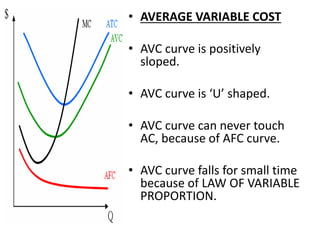
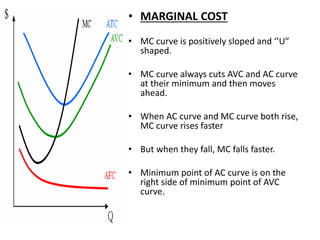

The document discusses various cost curves, including the average cost (AC), average variable cost (AVC), and marginal cost (MC) curves, highlighting their shapes and relationships. AC and AVC are 'U' shaped, with AC starting to rise after reaching its minimum point, which coincides with MC at this point. Additionally, it notes that while AVC is positively sloped and can never touch AC, MC intersects both curves at their minimums and rises and falls at different rates.


























