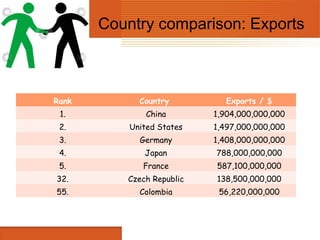
The document provides an overview of export, including its definition as goods produced in one country being shipped to other markets. It discusses the history and process of export, identifying key actors like exporters, banks, and customs agencies. The document outlines reasons for exporting like increasing sales and diversifying sources of revenue. It also examines advantages and disadvantages as well as direct and indirect methods of export. Barriers to export and factors to consider in the export decision-making process are presented. Country-level export data is given to facilitate comparisons.