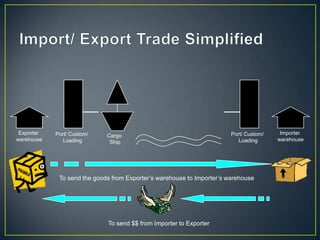
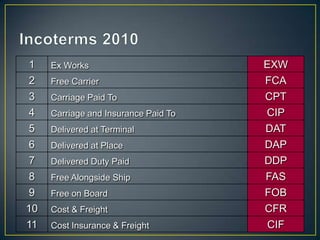
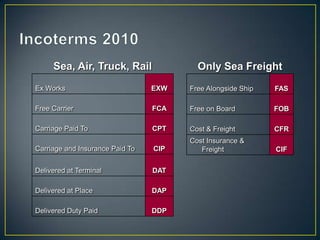
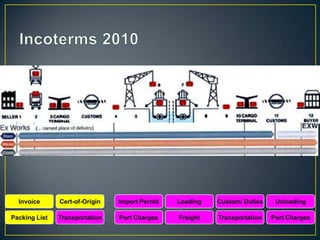
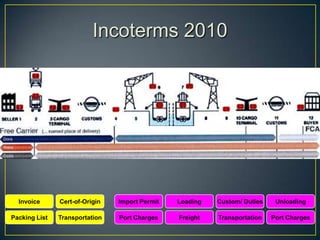
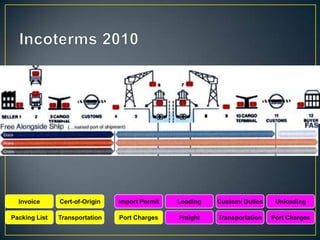
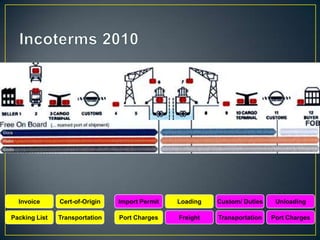
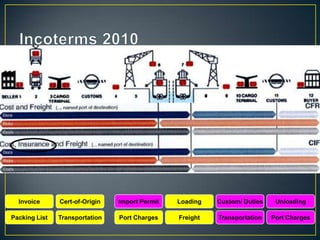
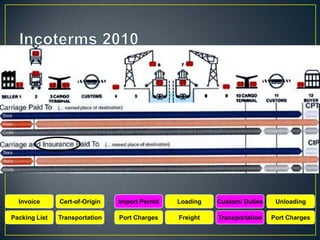
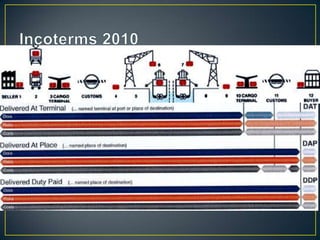
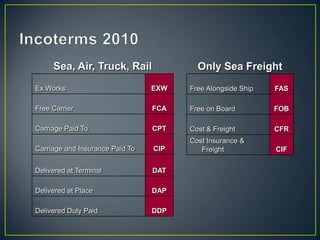
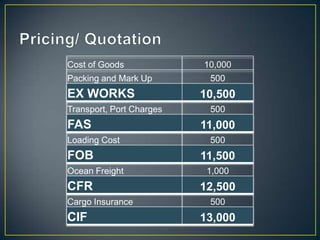
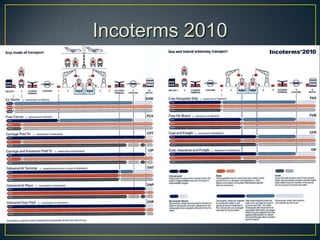
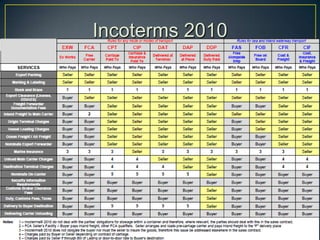
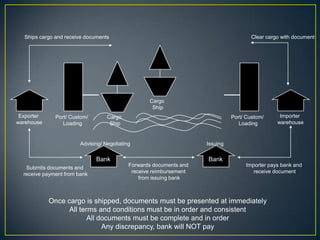
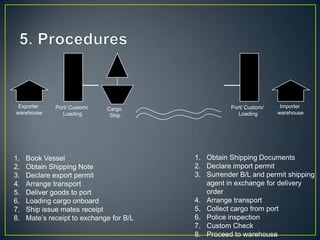
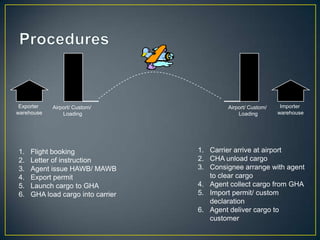
The exporter books an air freight flight, arranges for the cargo to be delivered to the airport and loaded onto the aircraft. The aircraft then flies to the destination airport where the cargo is unloaded and cleared by customs and transportation agents before being delivered to the importer's warehouse. Proper documentation such as the HAWB, export permits, and import permits are required to facilitate the international air freight of goods.