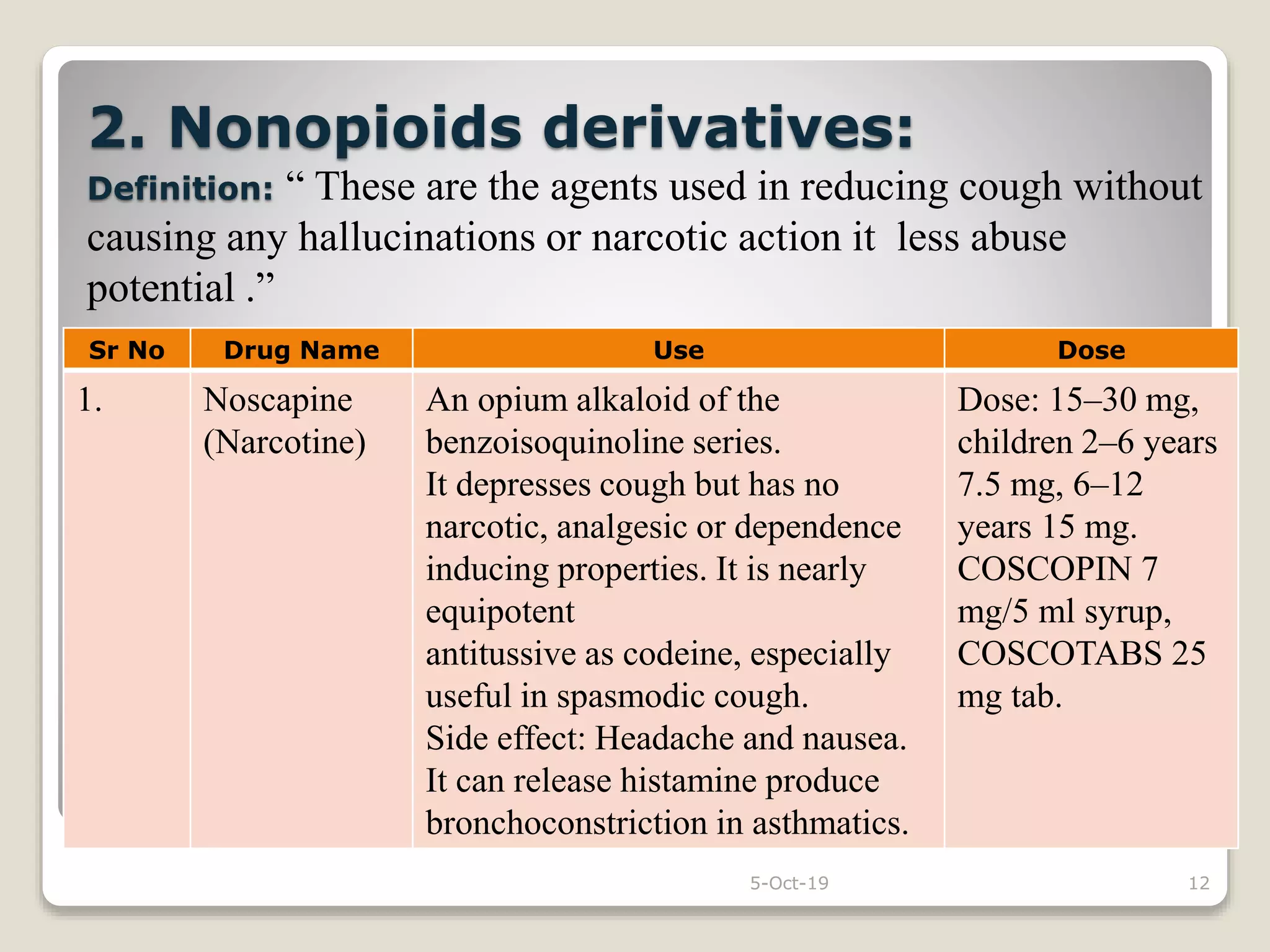
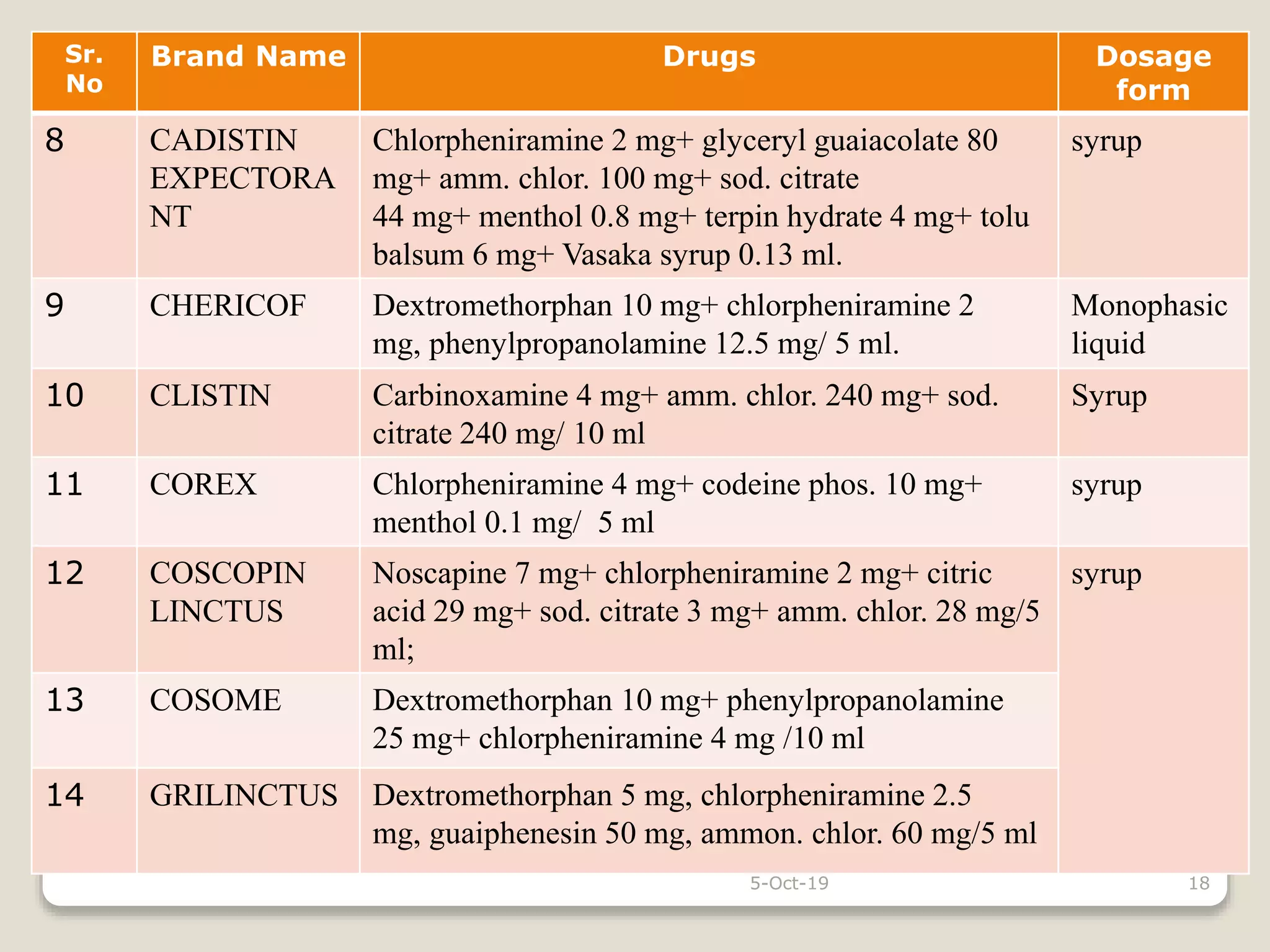
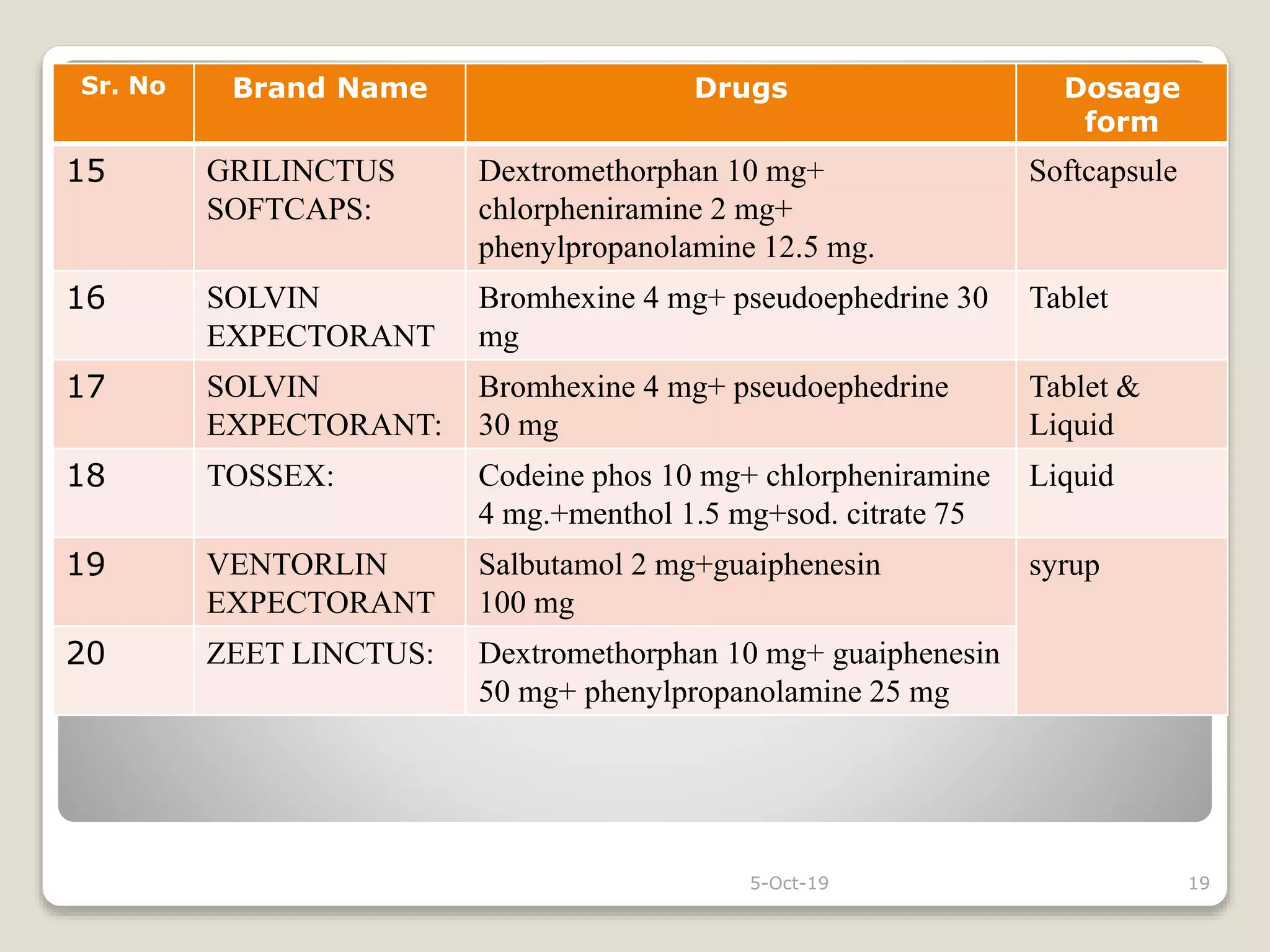
The document discusses expectorants and antitussives. It defines expectorants as drugs that increase bronchial secretion or reduce viscosity, facilitating removal by coughing. Only guaiphenesin is approved as an expectorant in the U.S. Expectorants are classified as bronchial secretion enhancers or mucolytics. Antitussives act in the CNS to suppress cough or act peripherally in the respiratory tract. Antitussives are classified as opioids, nonopioids, antihistamines, or peripherally acting drugs. The document provides examples and doses of expectorants and antitussives and discusses some combination antitussive-expectorant formulations.