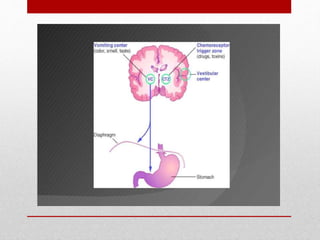
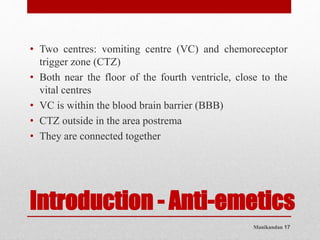
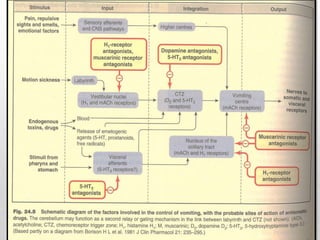
This document discusses emetics, which induce vomiting, and antiemetics, which prevent vomiting. It describes the physiology of vomiting including the vomiting center and chemoreceptor trigger zone in the brain. It explains the mechanisms and sites of action of various classes of antiemetic drugs including antihistamines, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, dopamine antagonists, cannabinoids, glucocorticoids, and others. It provides details on specific antiemetic drugs like metoclopramide, ondansetron, dexamethasone, and their indications, mechanisms, pharmacokinetics and adverse effects.