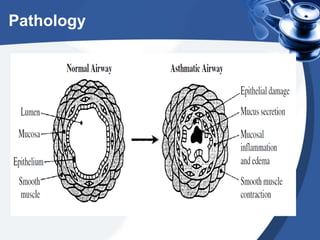
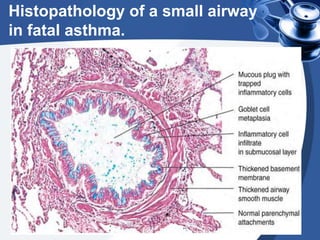
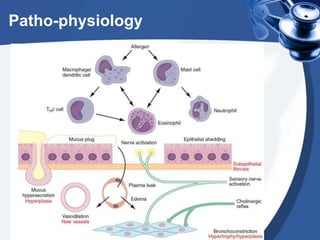
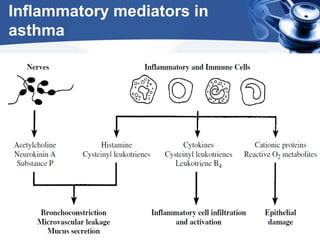
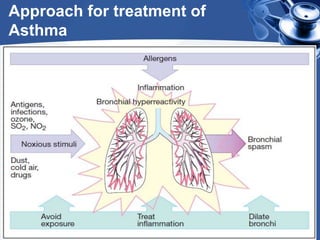
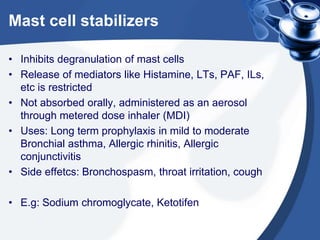
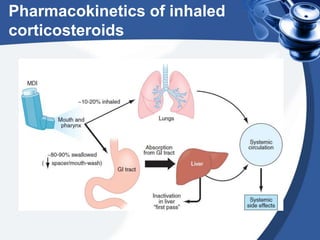
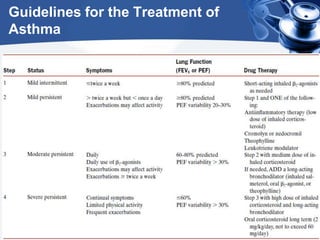
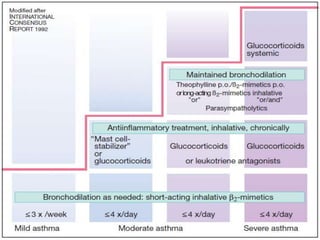
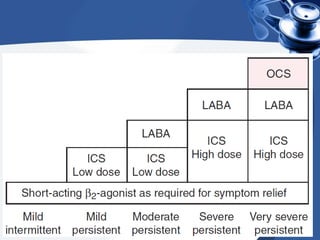
Bronchial asthma is a chronic disease characterized by recurrent episodes of coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath. It has various etiologies and types based on clinical features. The document discusses the pathophysiology and classification of drugs used to treat asthma including bronchodilators, corticosteroids, leukotriene antagonists, mast cell stabilizers and anti-IgE antibody. Treatment approaches for acute severe asthma involving nebulized bronchodilators, systemic corticosteroids and monitoring are also outlined.