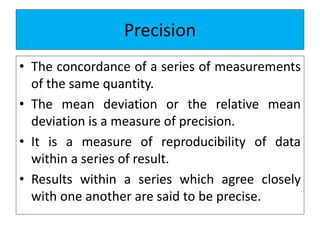
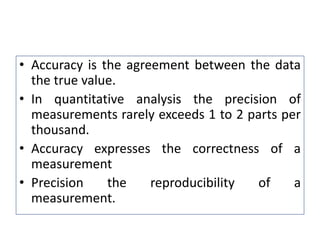
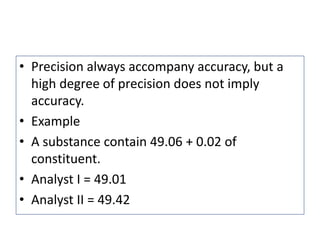
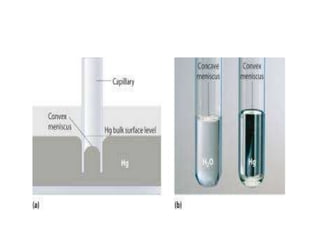
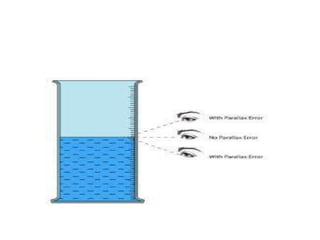
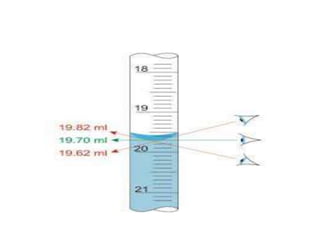
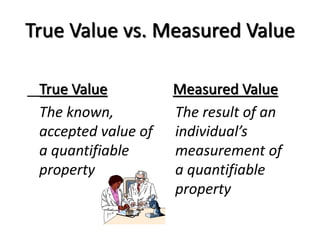
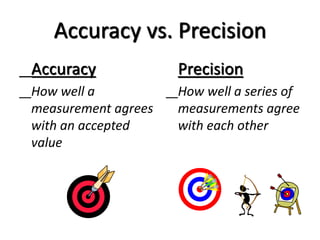
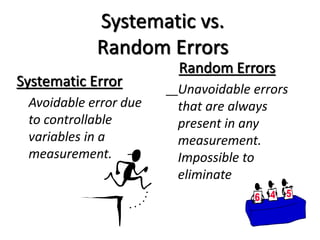
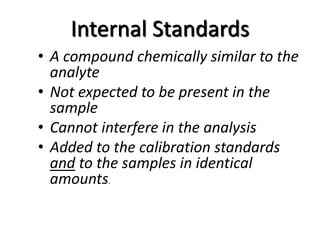
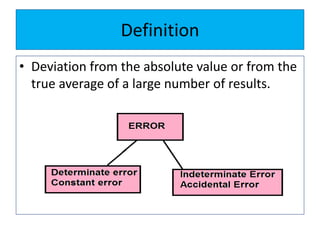
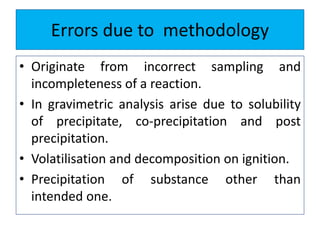
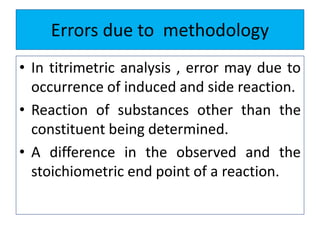
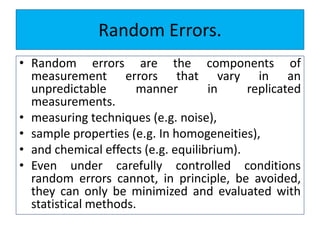
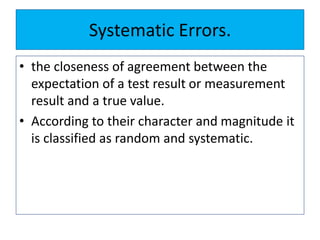
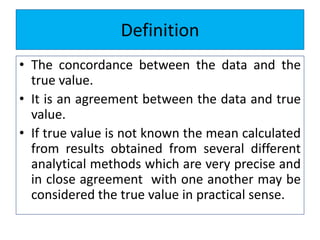
The document discusses various types of errors that can occur in quantitative chemical analysis, including random errors, systematic errors, determinate errors, indeterminate errors, and errors due to faulty instrumentation, impure reagents, or improper methodology. It also describes ways to minimize errors, such as calibrating apparatus, running blanks and controls, using multiple analytical techniques, and performing replicate measurements. Accuracy is defined as how close a measurement is to the true value, while precision refers to the reproducibility of measurements.















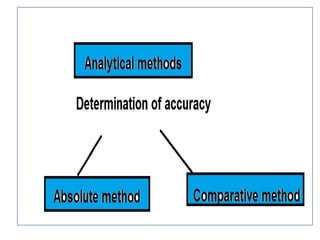


![• It is useful in applied analysis.
• If fundamentally different methods of analysis
for a given constituent [ gravimetric,
titrimetric and spectrometric]. The agreement
between at least two methods of essentially
different character can usually be accepted as
indicating the absence of an appreciable
determinate error .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/errors-180321044425/85/Errors-33-320.jpg)