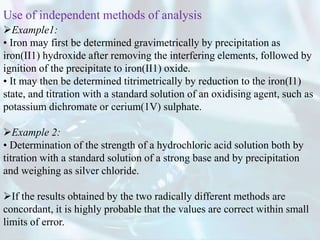
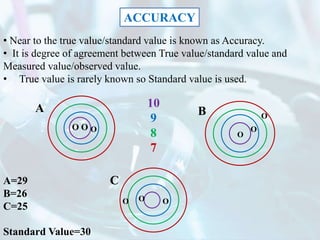
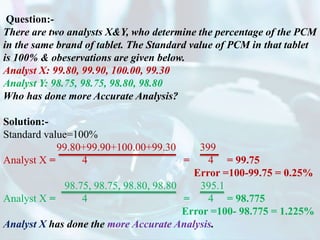
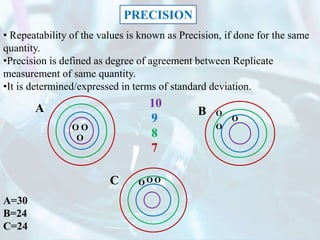
The document explains the concept of error in analytical chemistry, highlighting the importance of reliability and accuracy due to potential serious consequences from errors in laboratory results. It categorizes errors into determinate (systematic) and indeterminate (random) errors, discussing their sources, effects, and examples, as well as methods to minimize these errors. Additionally, it covers procedures for improving accuracy and precision in analyses, such as calibration, blank determinations, and the use of standard additions.