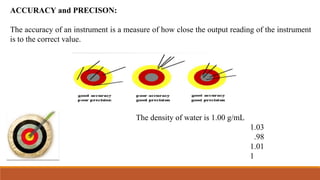
This document discusses errors in measurement and analysis. It defines absolute and relative errors as the difference between experimental and true values. Errors are classified as determinate (systemic) or indeterminate (random). Determinate errors include personal, instrumental, method, additive and proportional errors. Indeterminate errors cannot be avoided and come from unknown causes. Accuracy refers to how close a measurement is to the true value, while precision describes the reproducibility of measurements. Significant figures convey the precision or accuracy of numerical values. The document provides examples and rules for determining significant figures.