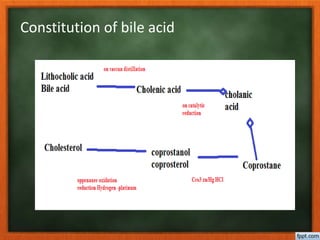
Bile is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder. It consists of bile acids, bile pigments, and other organic and inorganic compounds. Bile acids are conjugated with either glycine or taurine and act to facilitate fat digestion by emulsifying lipids. More than 20 natural bile acids have been characterized that differ in their hydroxyl group positions. Bile acids are synthesized from cholesterol in the liver through a series of modifications including removal of the side chain and introduction of hydroxyl groups. They play an important role in fat digestion by emulsifying lipids to increase their surface area for pancreatic enzymes to act upon.

![• Liver secrete a clear golden
yellow viscous fluid known as
bile.
• It is stored in gall bladder and
mainly used in digestion.
• Bile consist of inorganic ions as
well as organic compound.[ bile
acids, bile pigments, liquids,
fatty acids and cholesterol]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-180305101727/85/5-bileacid-2-320.jpg)



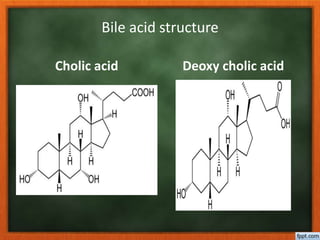


![• Cholic acid [ 3 α,7 α,12α trihydroxy ]
is extracted from ethereal solution
by 15% HCl.
• Dihydroxy acids [ deoxy and cheno
deoxy cholic acid] are extracted
from ethereal solution by 25% HCl.
• Mono hydroxy acid [ litho cholic acid
] is extracted by concentrated HCl.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-180305101727/85/5-bileacid-9-320.jpg)