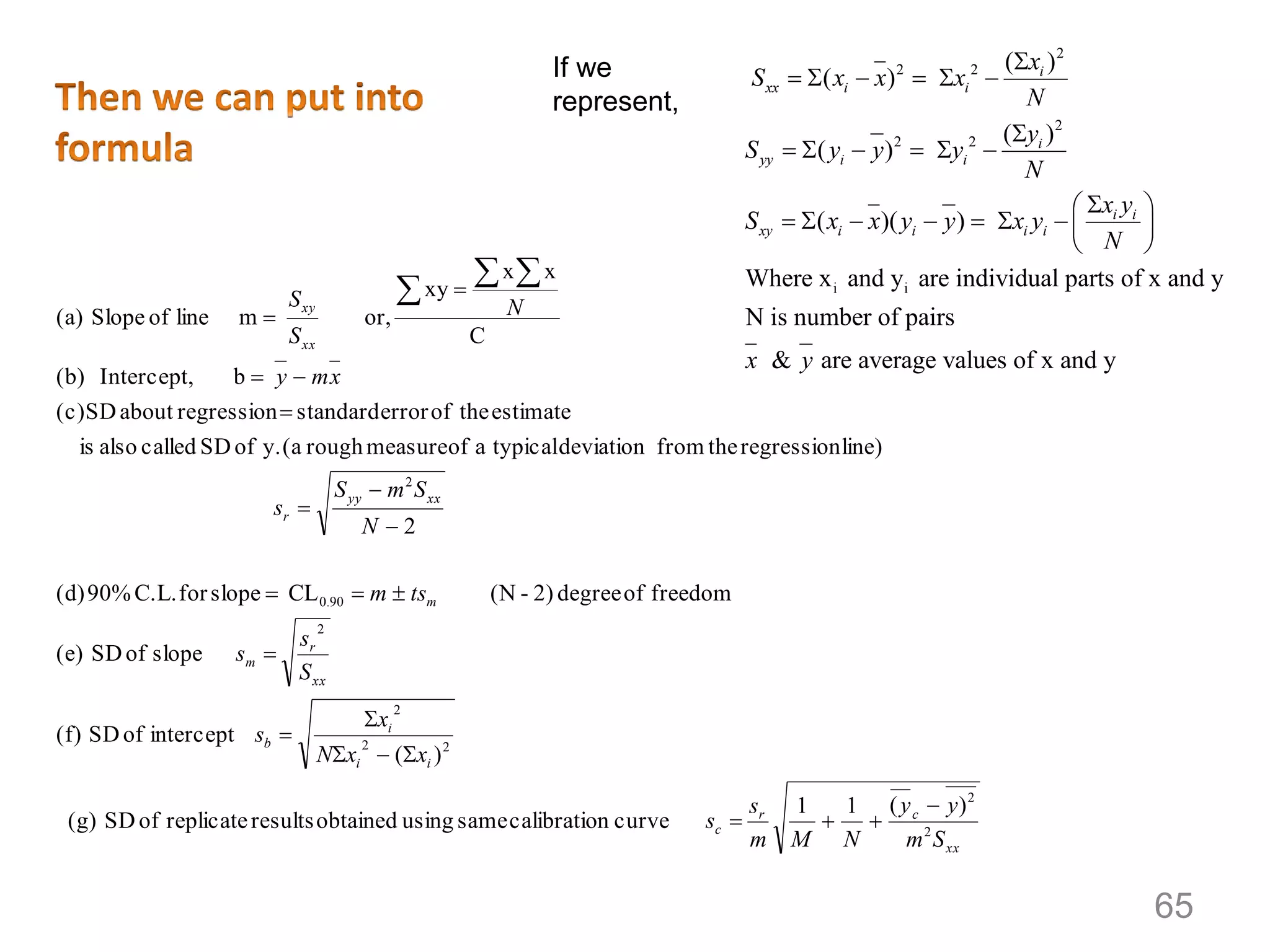
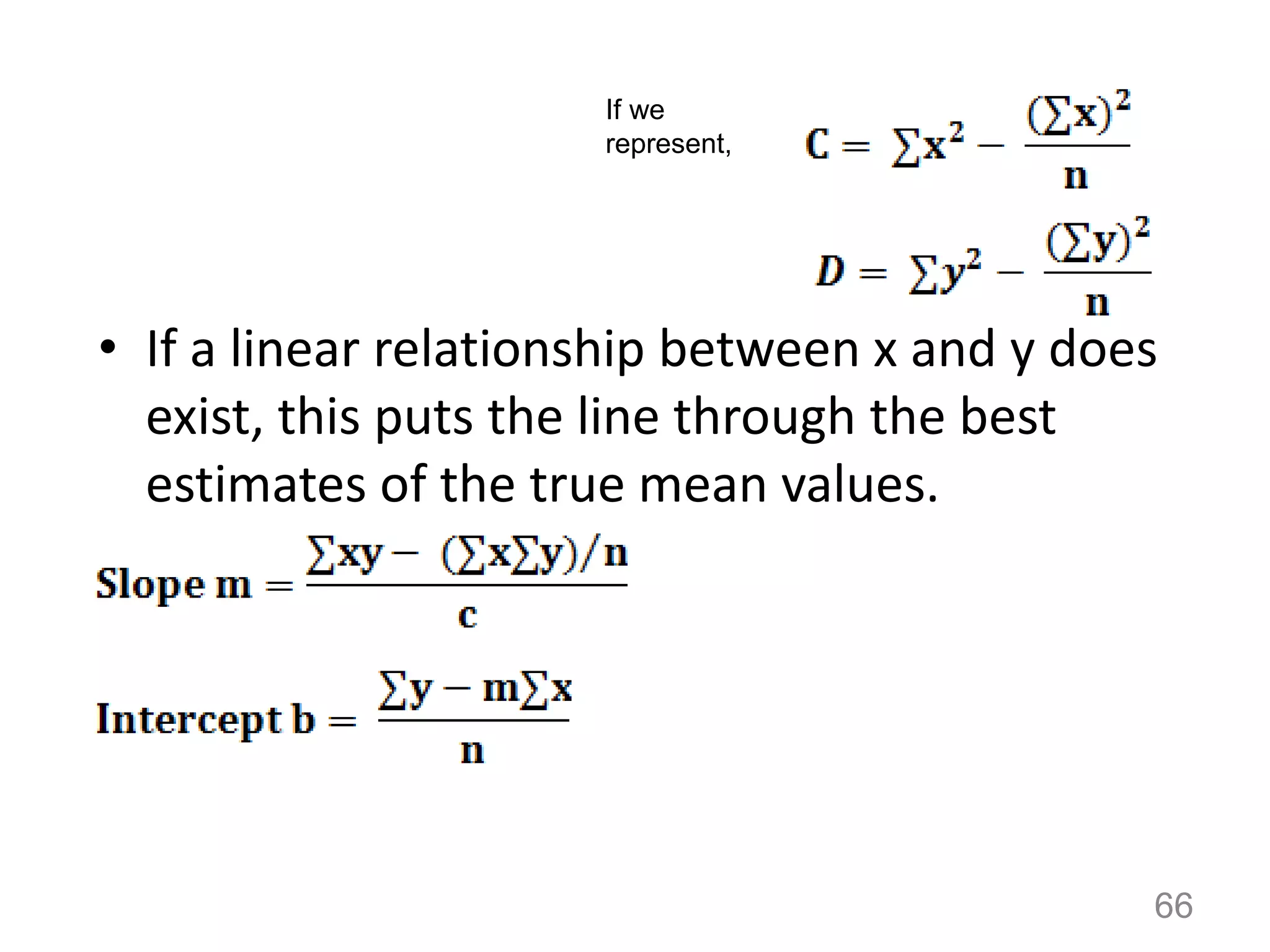
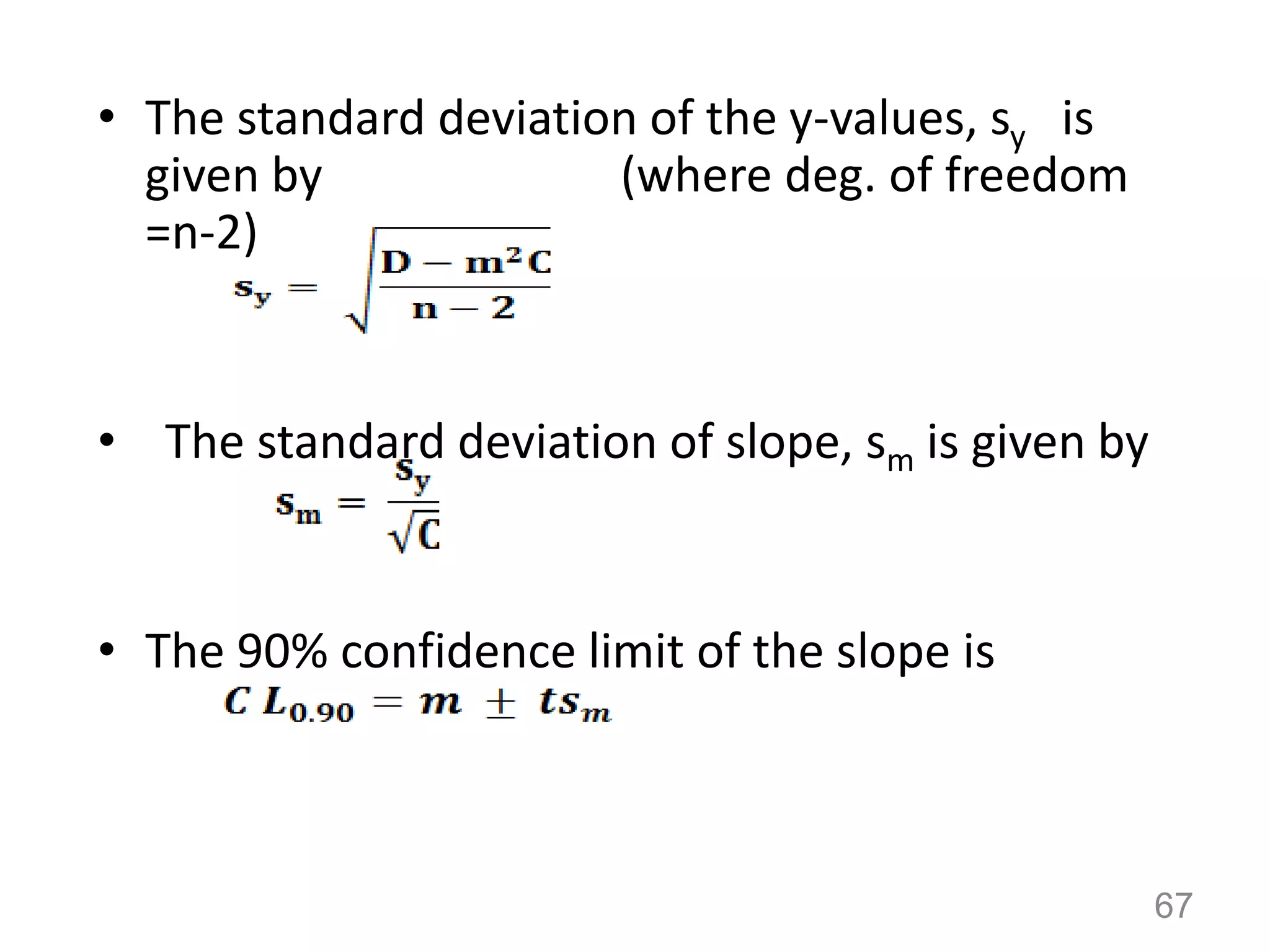
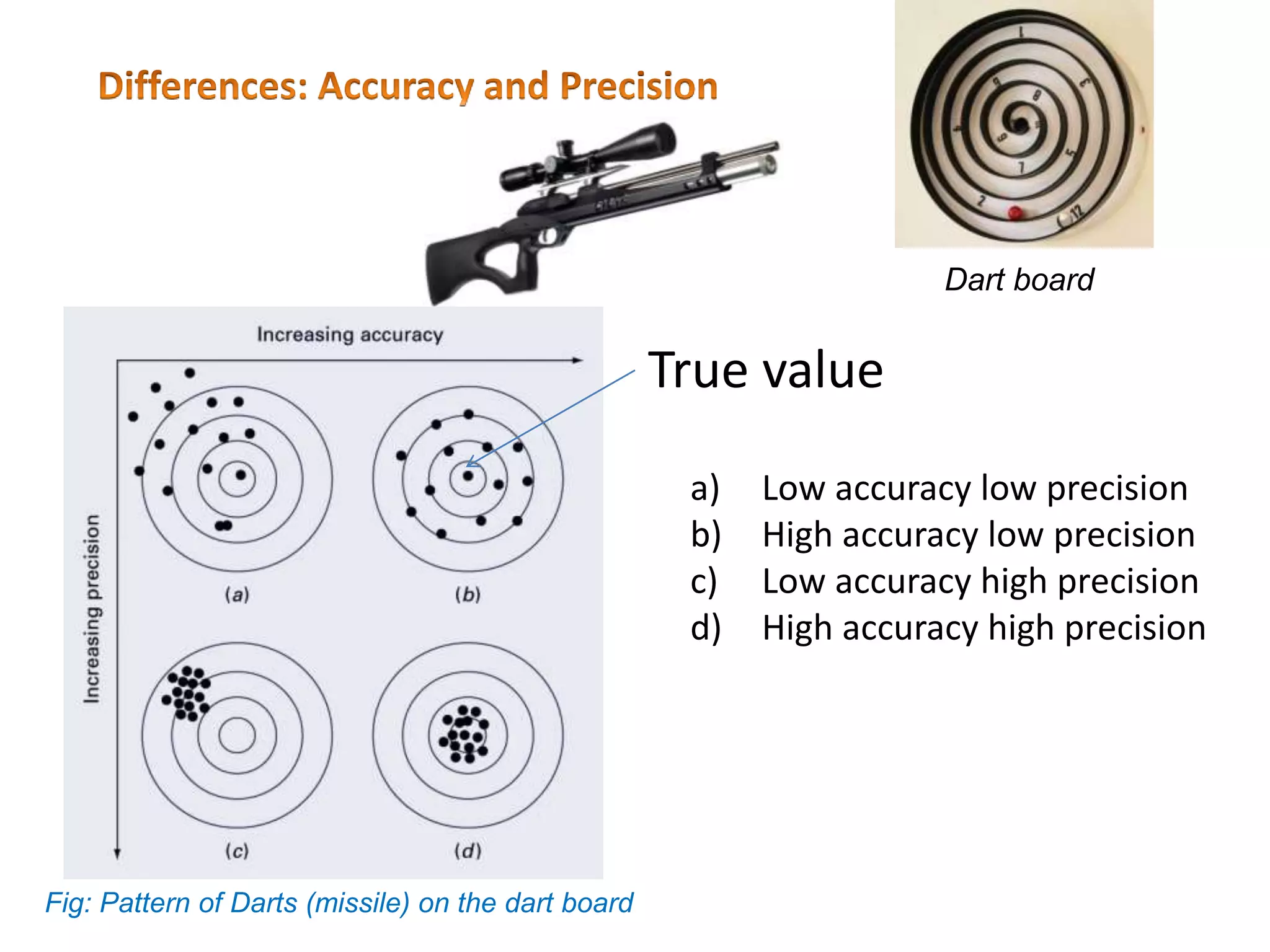
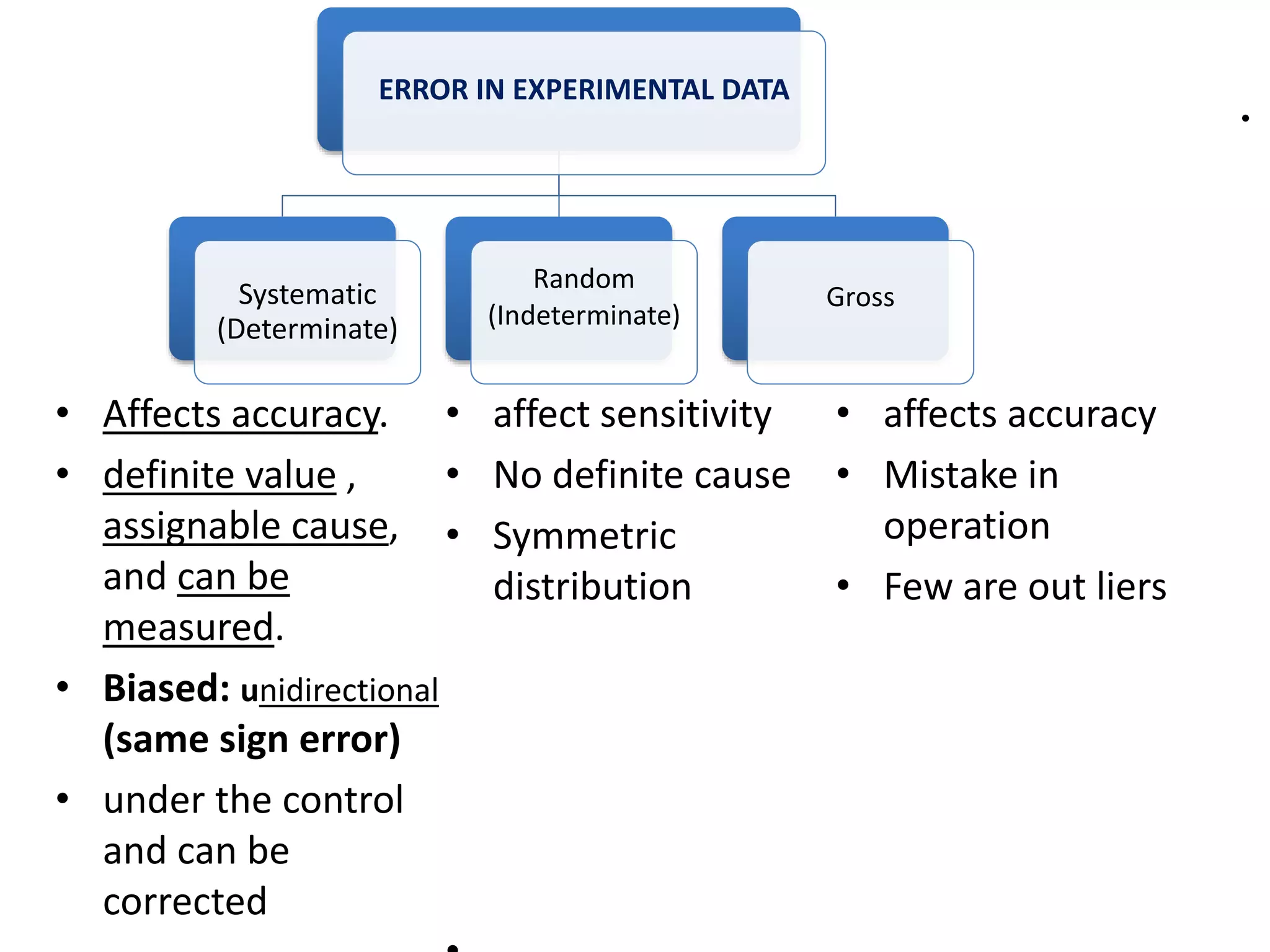
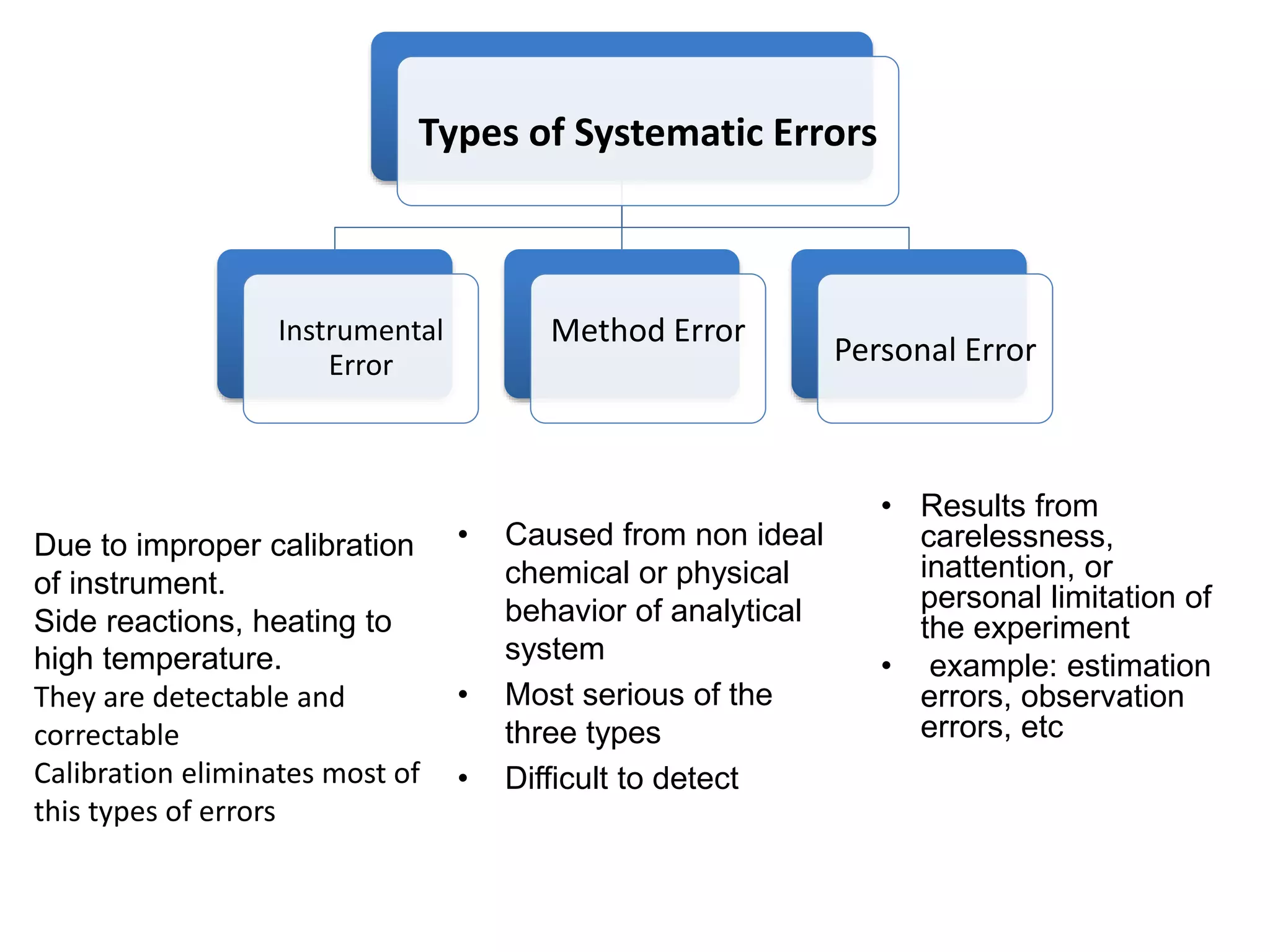
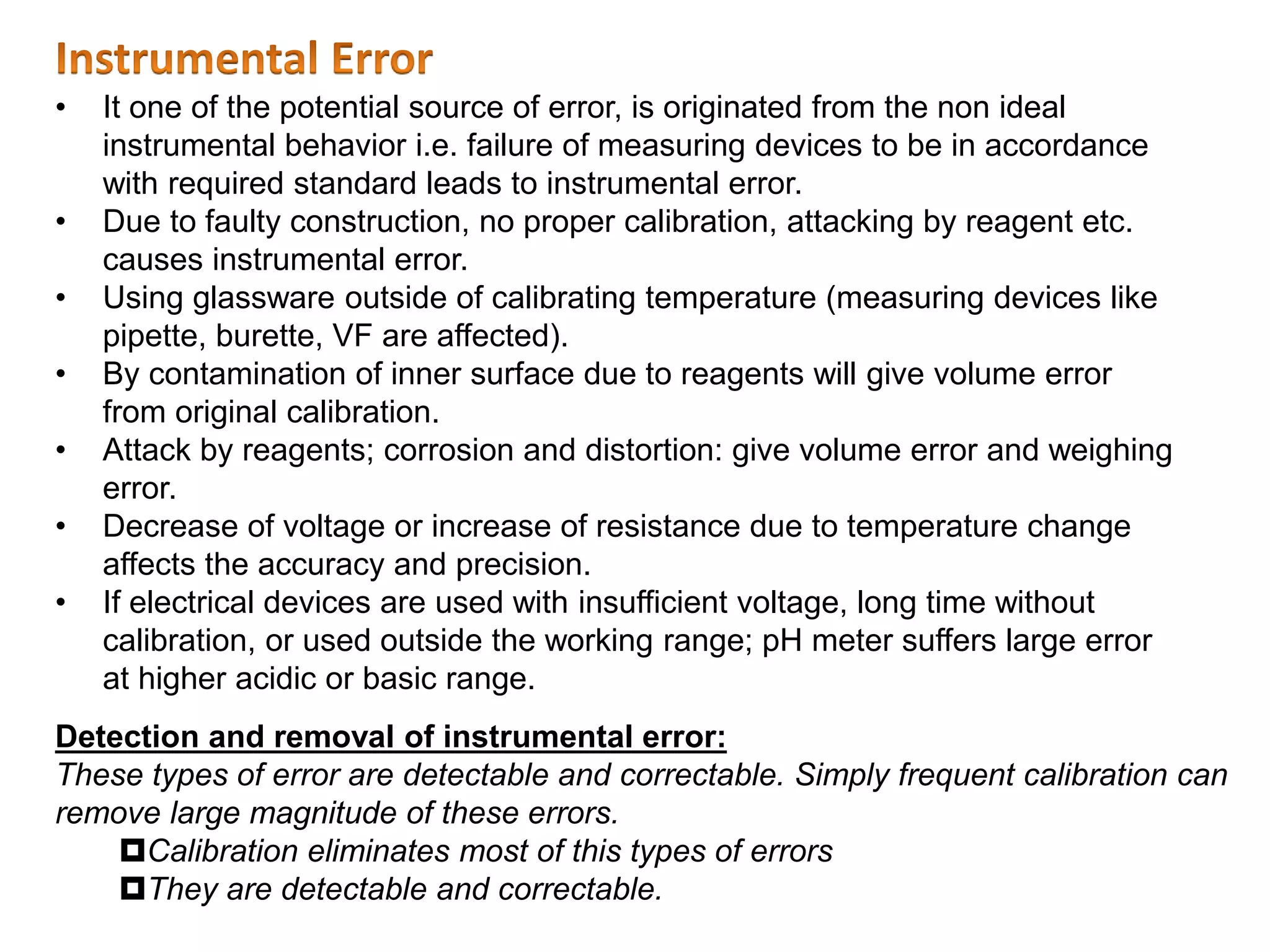
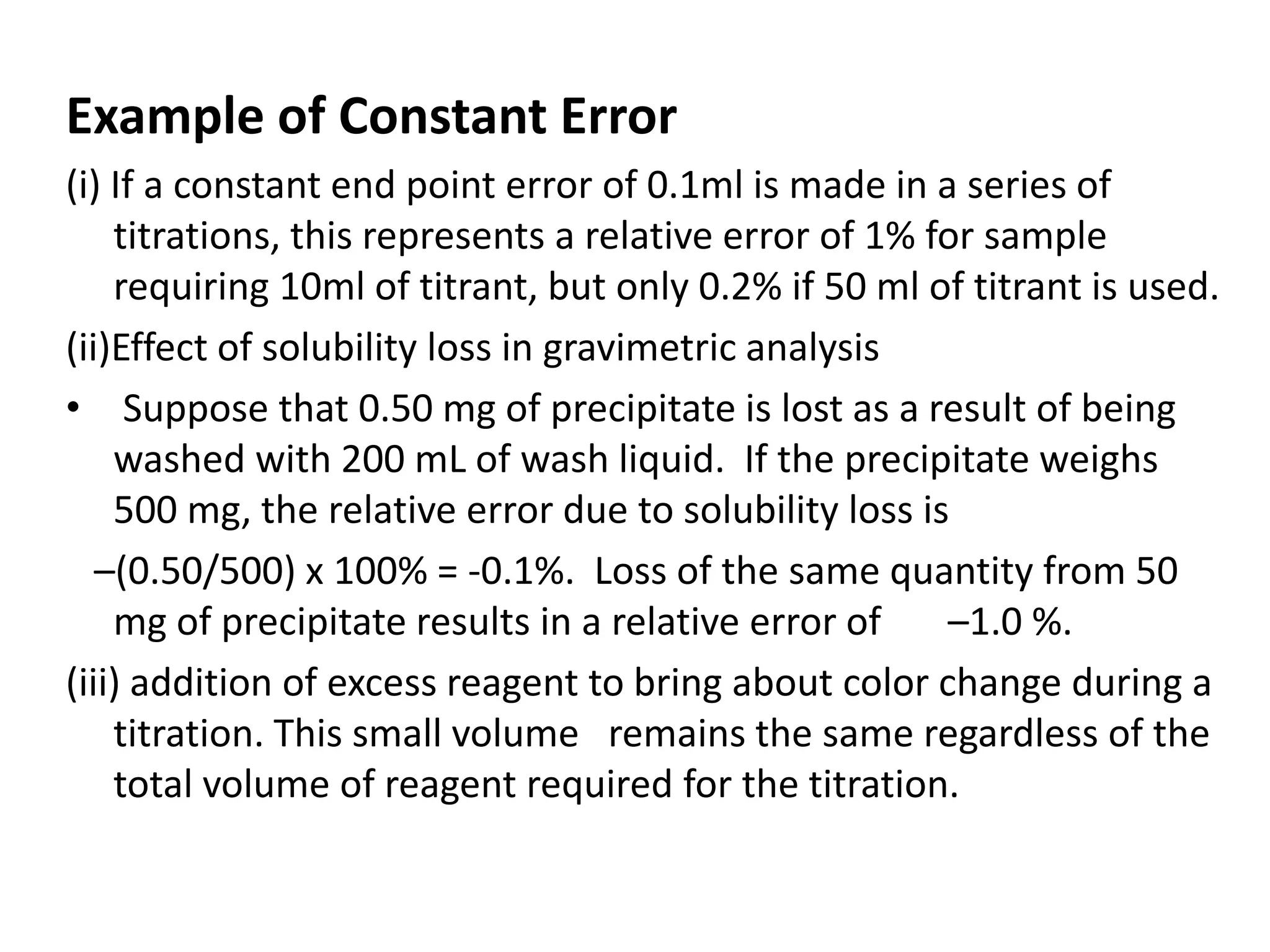
1. Systematic errors affect the accuracy of results and are caused by factors like improper instrument calibration, faulty methodology, or personal biases.
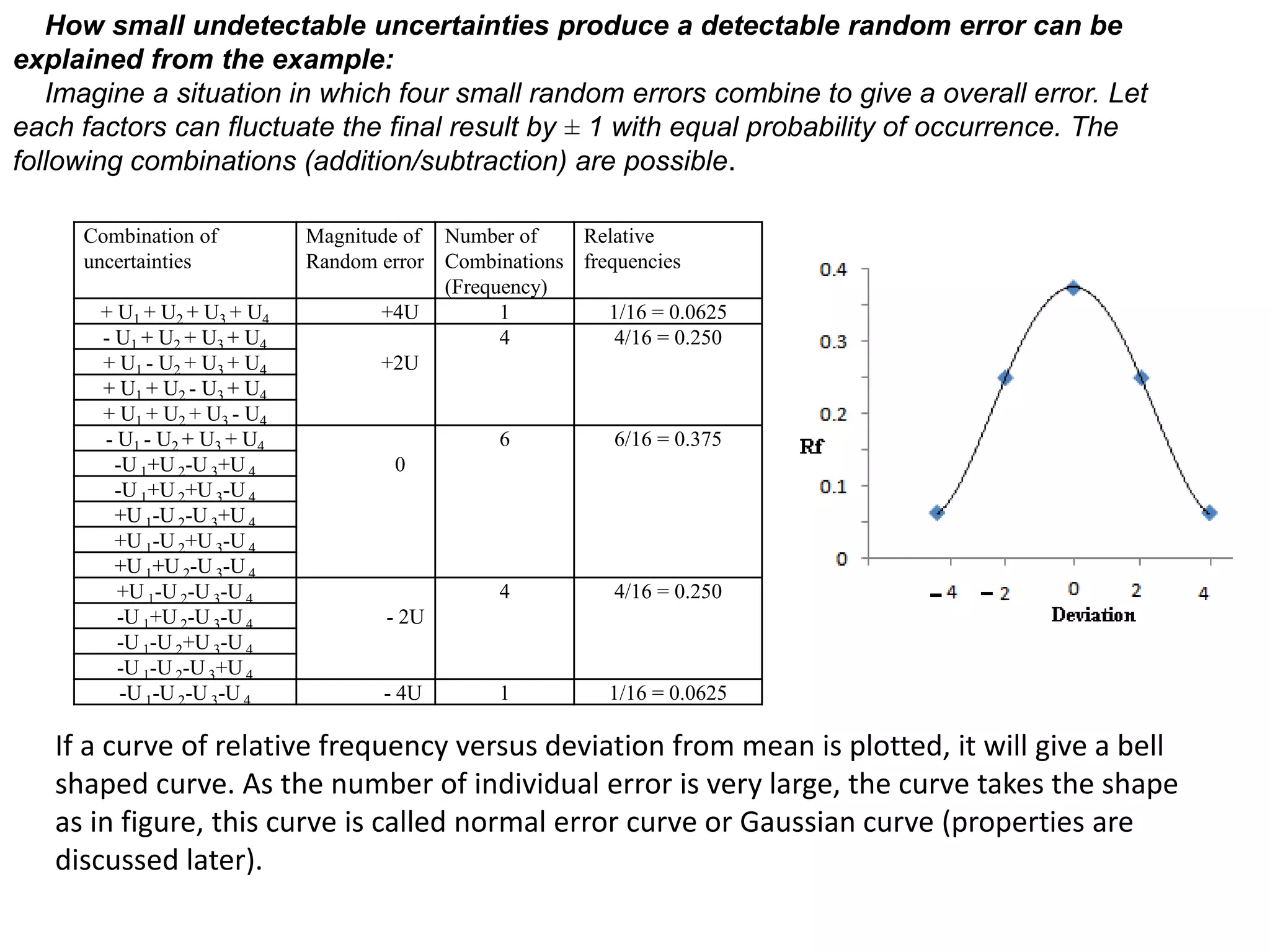
2. Random errors affect precision and result from unpredictable factors that cause random scatter in measurements.
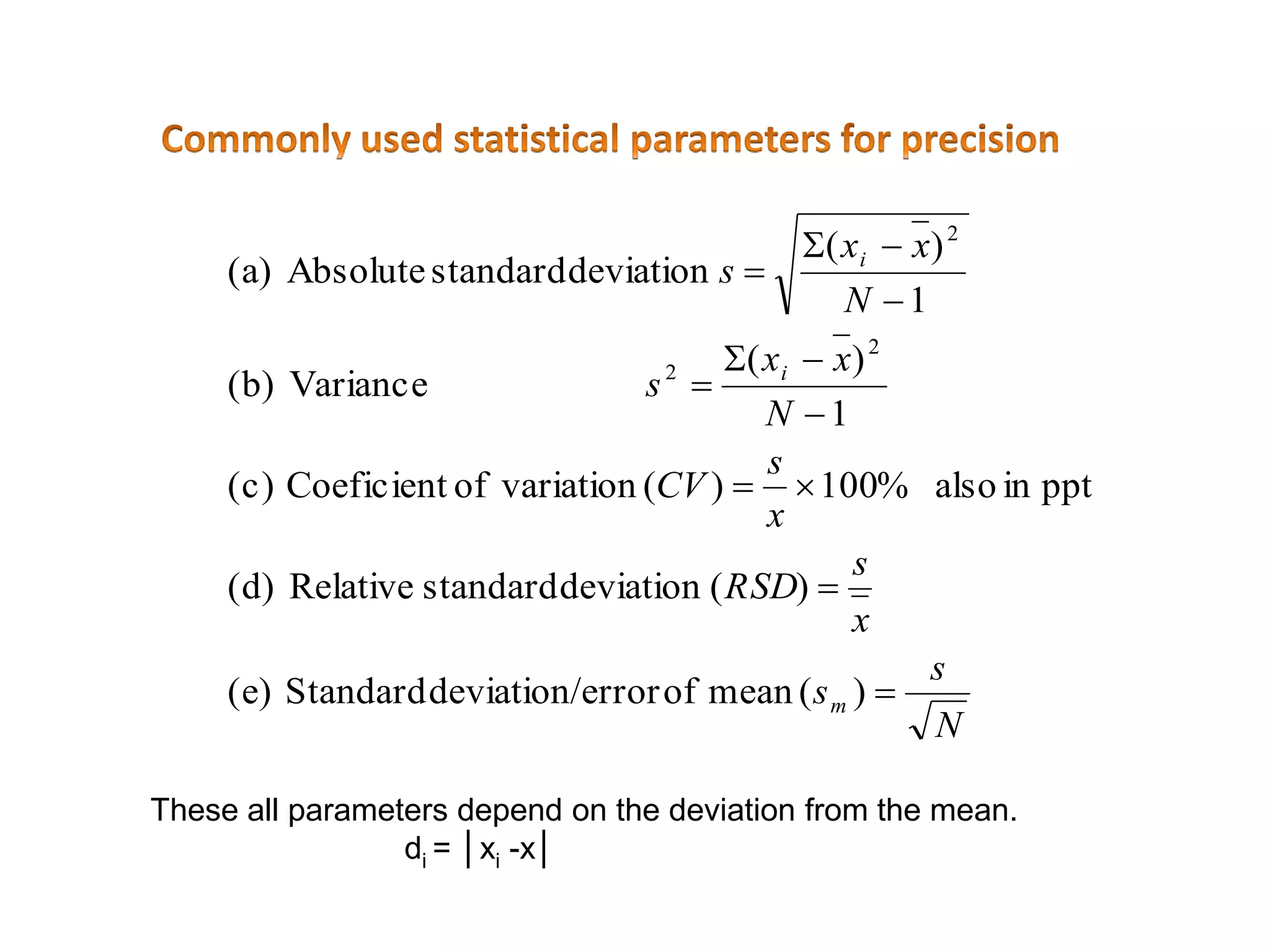
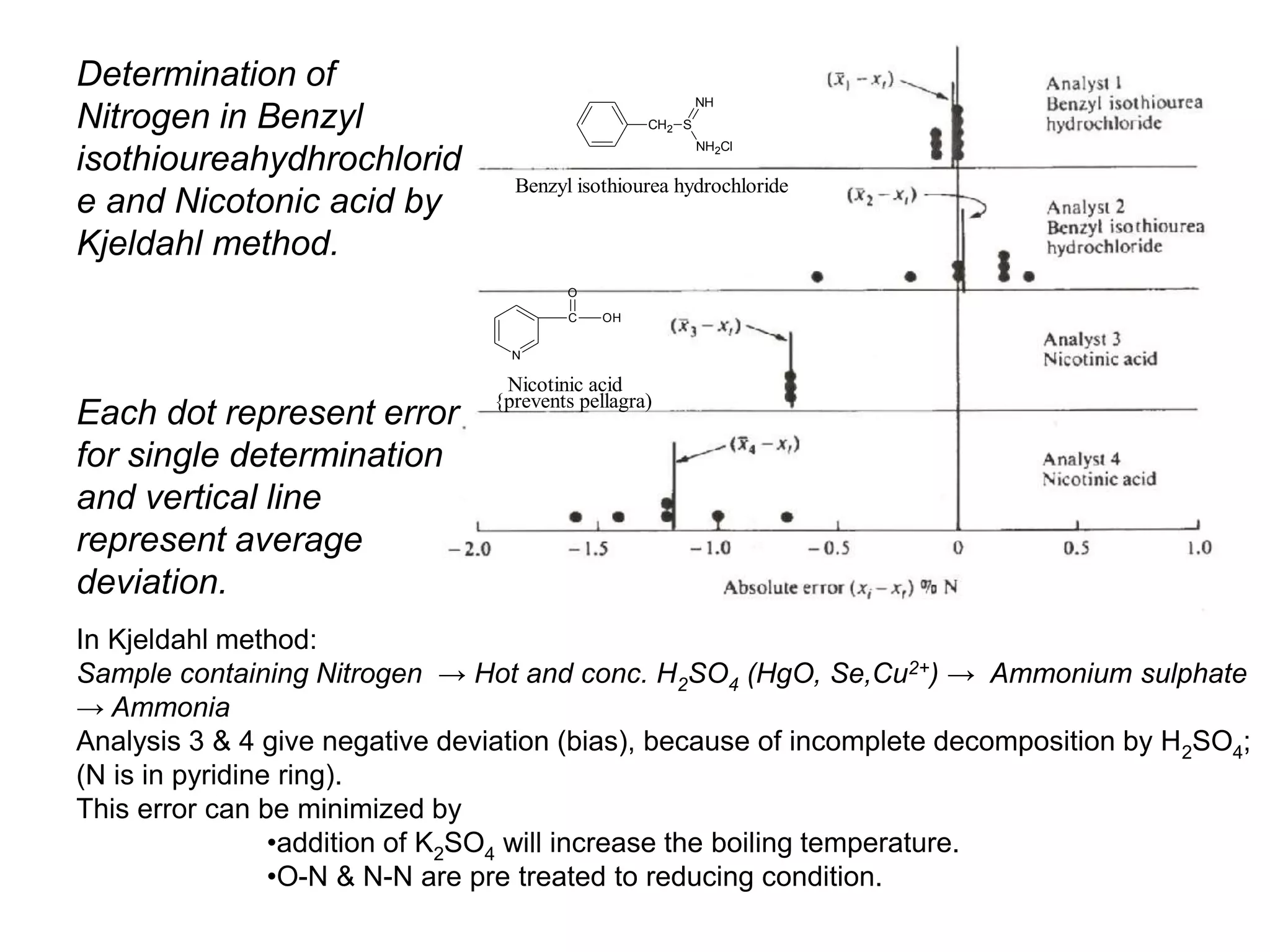
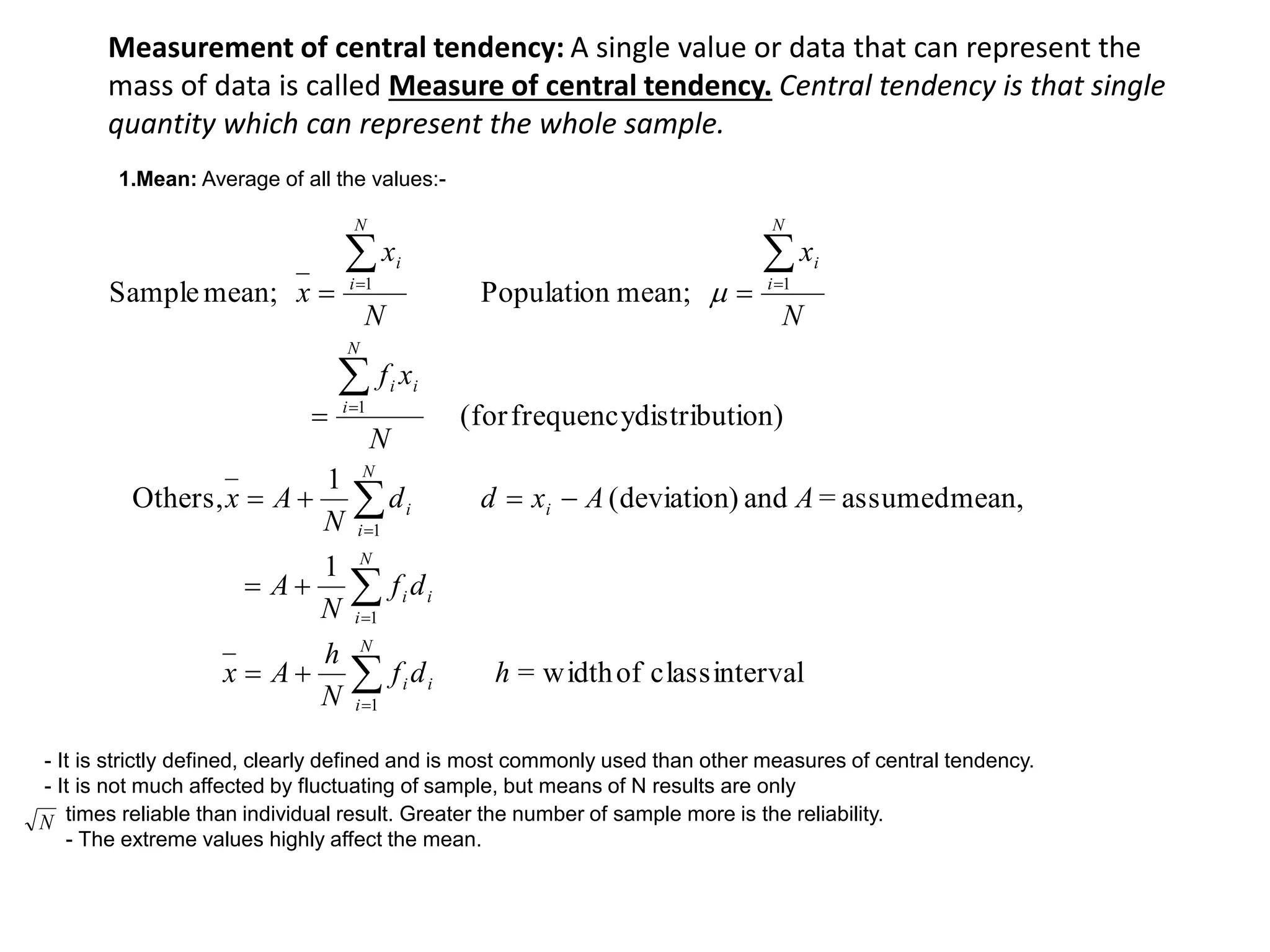
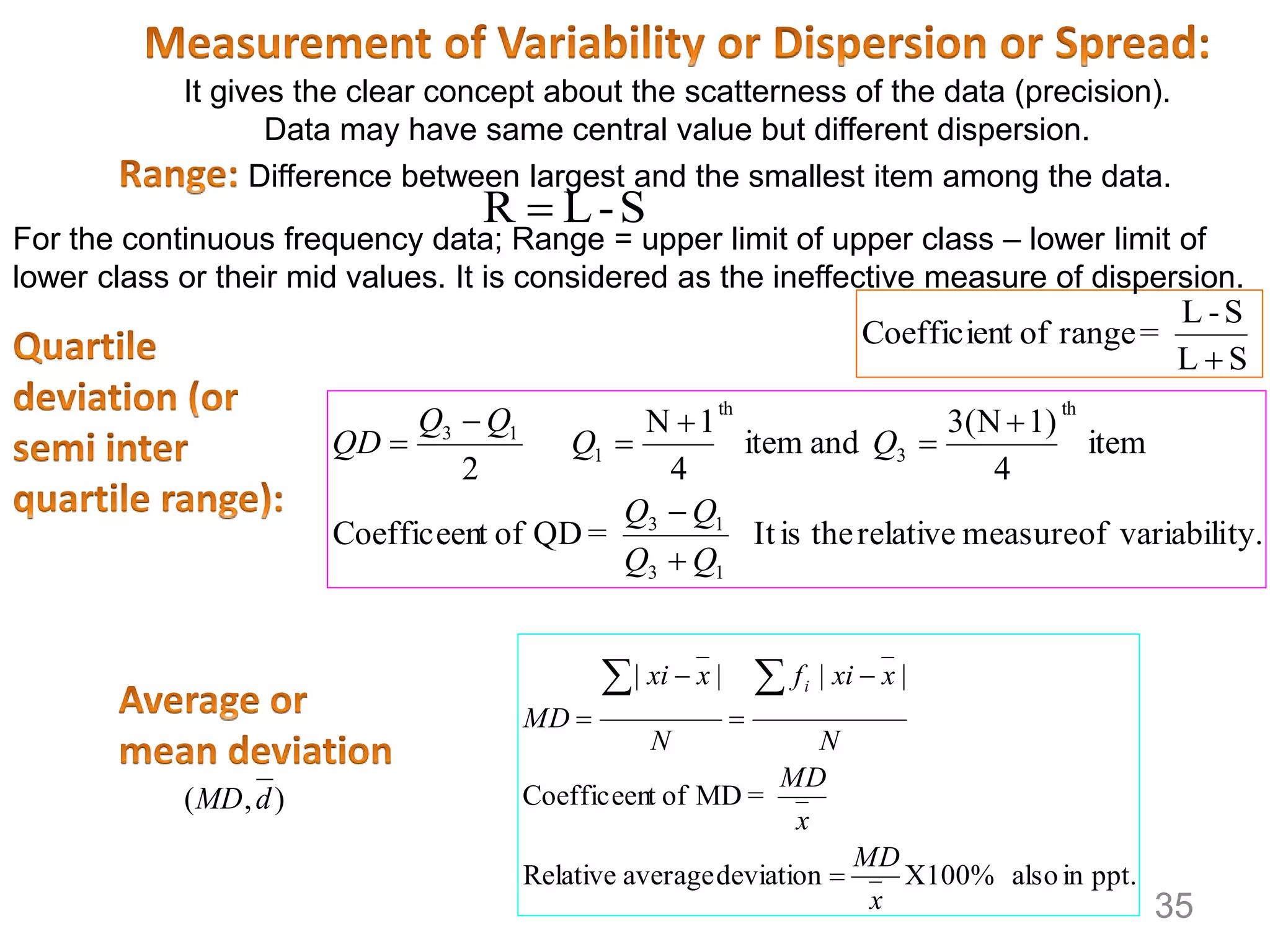
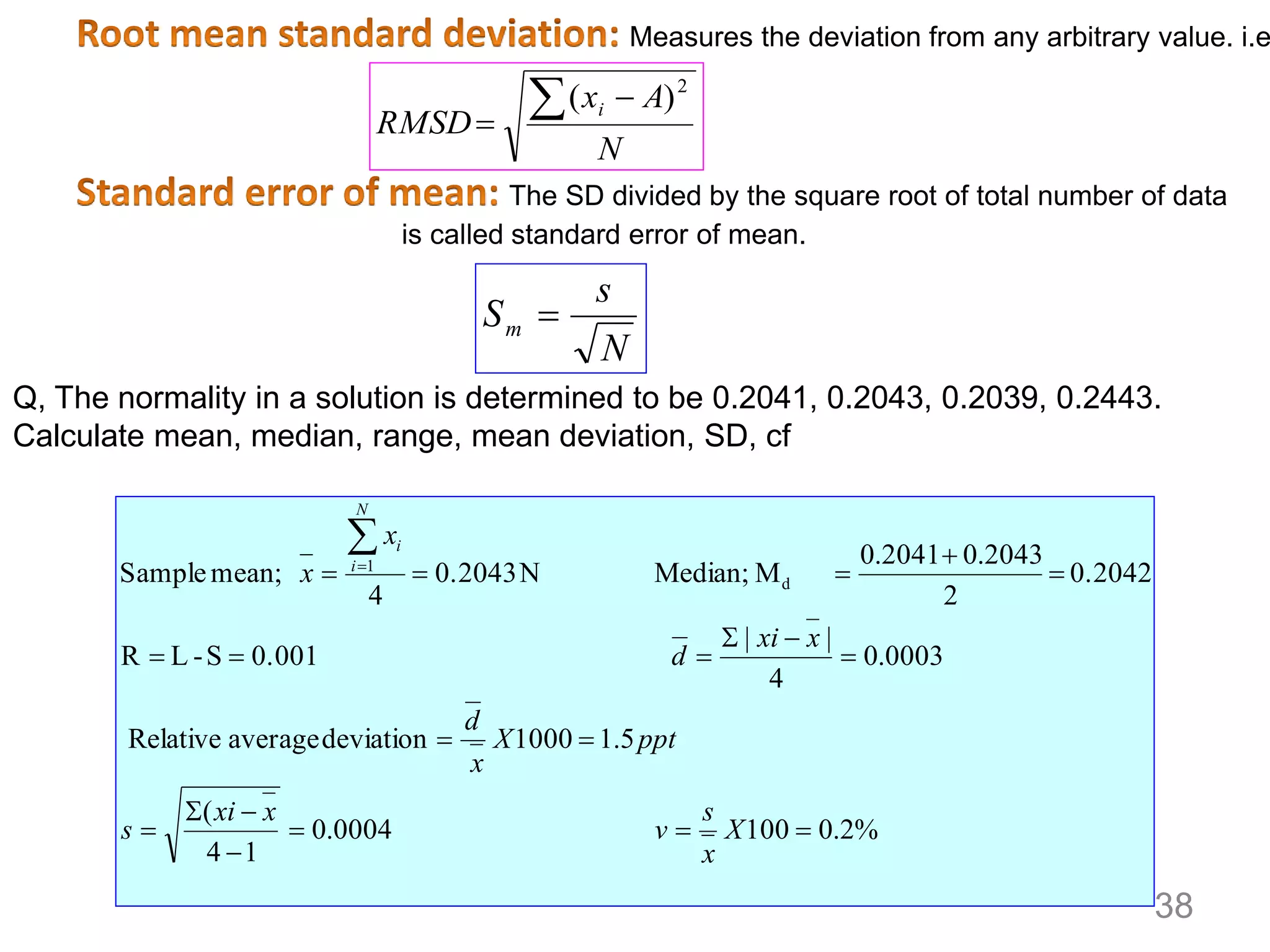
3. Various statistical analyses can be used to determine systematic and random errors in experimental data, including calculating measures of central tendency, variability, and confidence limits. Propagation of errors must also be considered.



























![•In the case of
multiplication and
division,
CBAR
CCC
AB
C
CC
ABACBC
R
iv
vi
CC
ABACBC
CC
ABABCACBCABC
C
AB
C
ABAB
viv
v
C
ABAB
R
C
ABAB
C
BA
R
ivCABR
so,tocomparedassmallveryisSince
)(
)(it withCombining
).......(..........
)(
)(
gives)(&)(Solving
).......(..........
)(
)(
so;negligibleare&
.
)(
)(
)(
)()(
errorsrespectivethegIntroducin
).........(..........
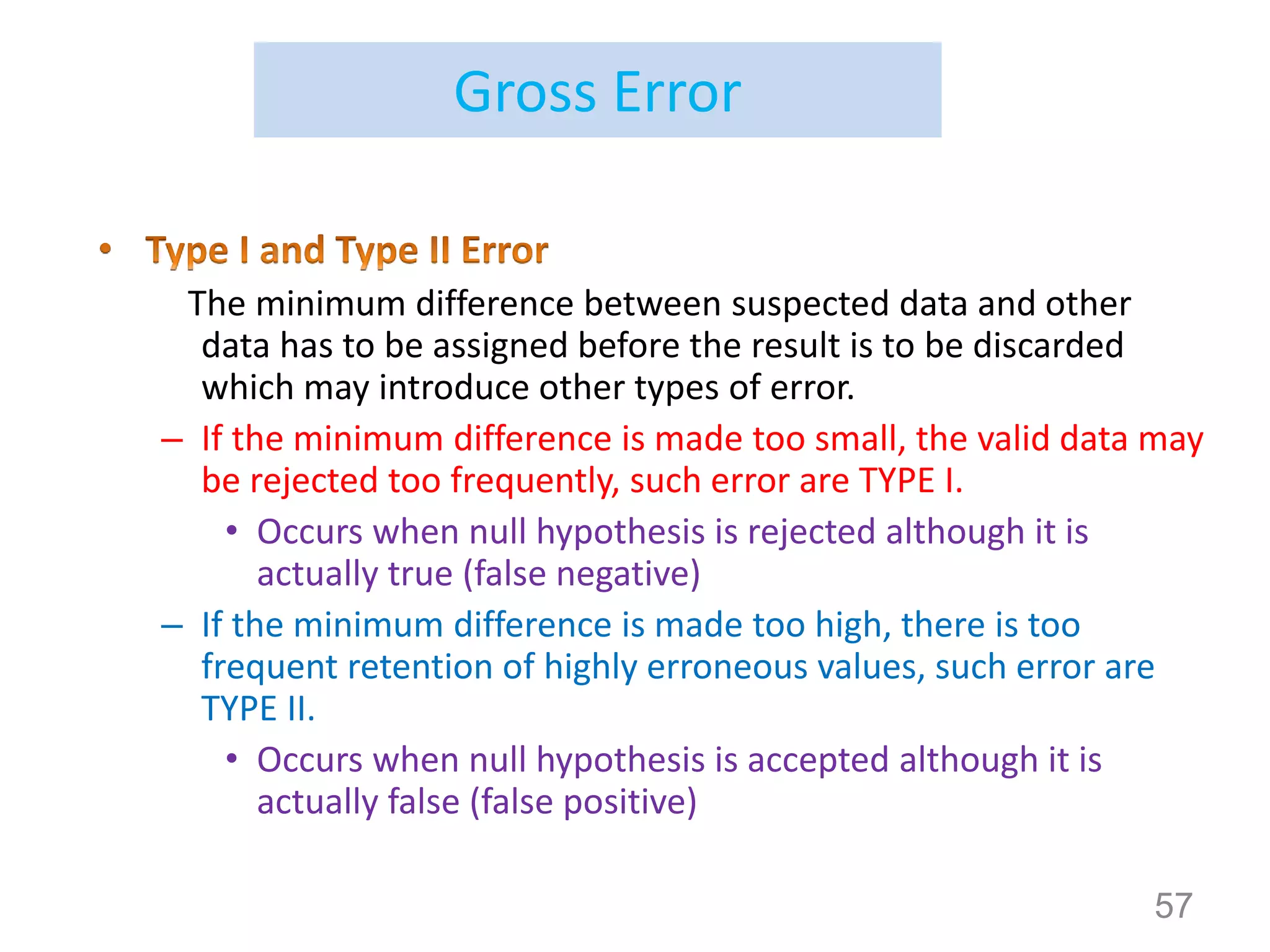
i.e. if multiplication and division are involved , relative determinate error are
transmitted directly into the result.
[For the case to obtain maximum relative error, the expression C- γ should be
used in place of C + γ]
60](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/error2015lamichhaneji-150718223151-lva1-app6891/75/Error-2015-lamichhaneji-60-2048.jpg)
![Y
X
Concentration
InstrumentalResponse
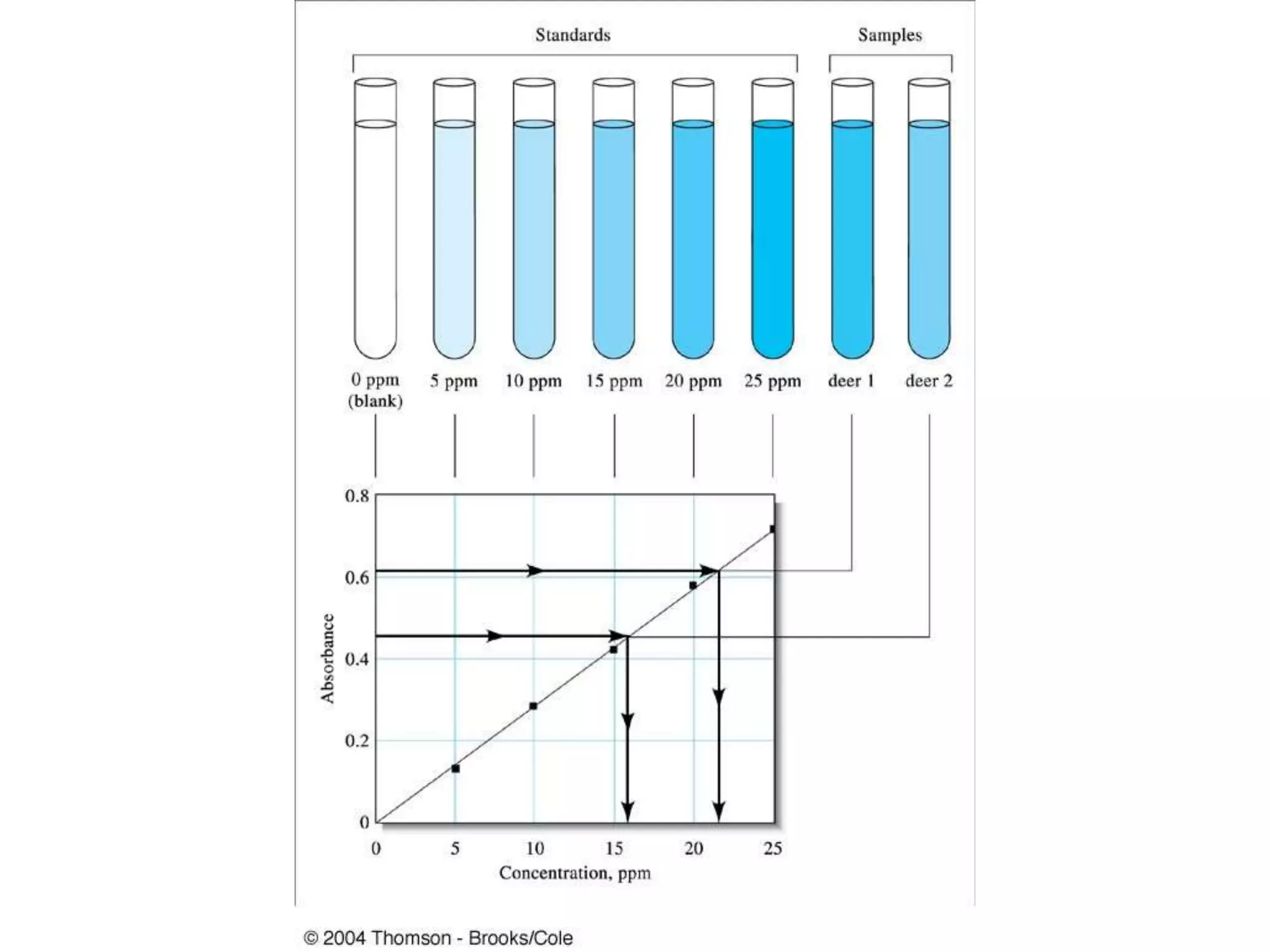
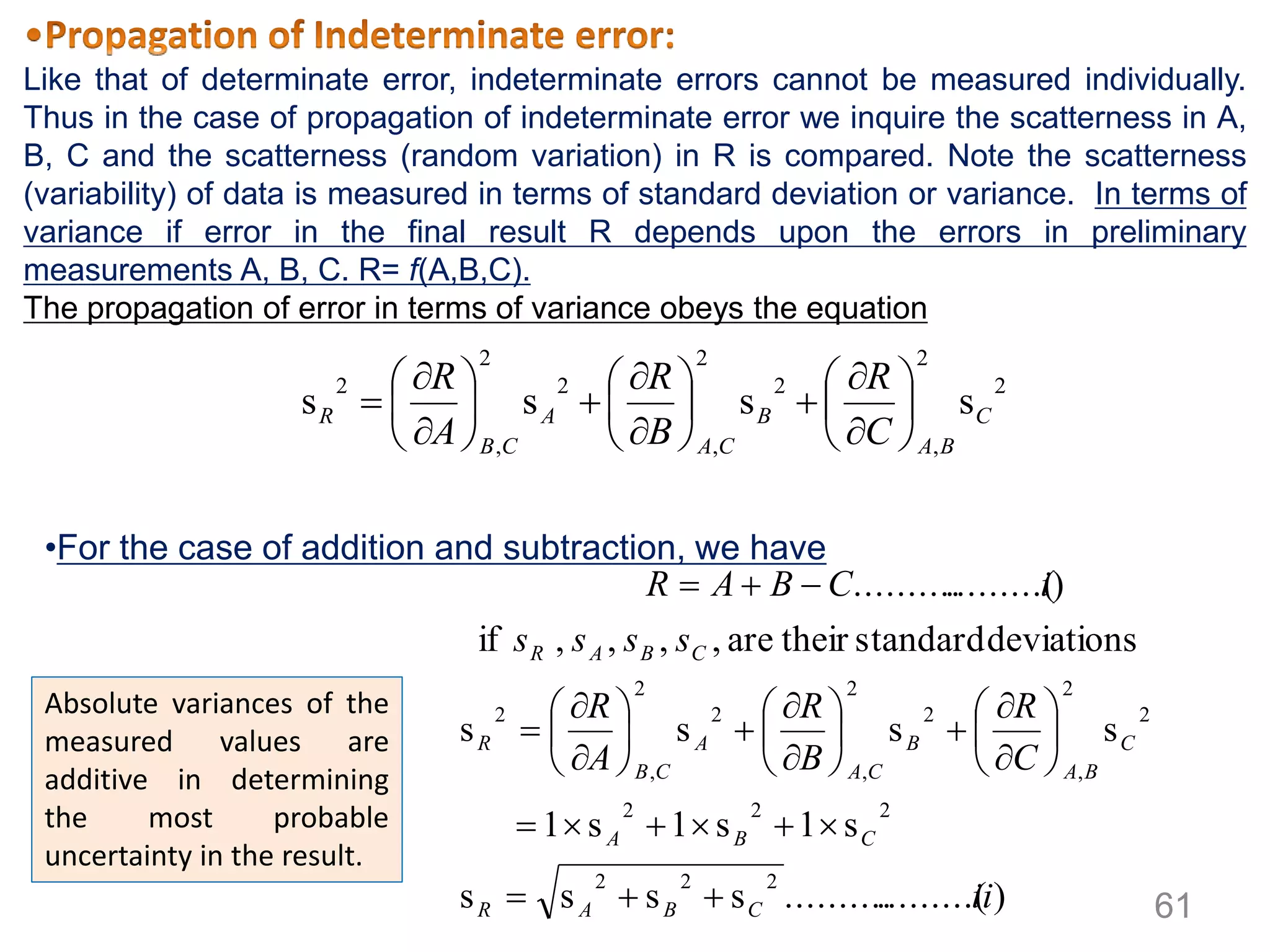
• Most of chemical analysis requires a plot of
linear curve (i.e. the detector response or the
final result is linearly related with the
concentration of the analyte)
• By using different standard solutions we can
plot the curve, called calibration curve. But due
to accumulation of errors all readings may not
be located in the line. In such a situation we
have to draw the line of best fit, which is
determined by the method of least square.
Only then the concentration of unknown can
be determined accurately.
• The uncertainties of the analysis can also be
determined from this regression line.
• In the least square method the slope and
intercept of the line is determined
mathematically. If the equation for the best fit
be, y = mx + b……….. (i); where m= slope
and b = intercept
• The least square method assumes that;
– The sum of squares of residuals from all the
points is minimum. [The vertical deviation from
each point to the line is called residual]..
Not only can the best line be
determined but also the
uncertainties in the use of the
calibration graph for the
analysis of an unknown can be
specified. 63
y mx b ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/error2015lamichhaneji-150718223151-lva1-app6891/75/Error-2015-lamichhaneji-63-2048.jpg)
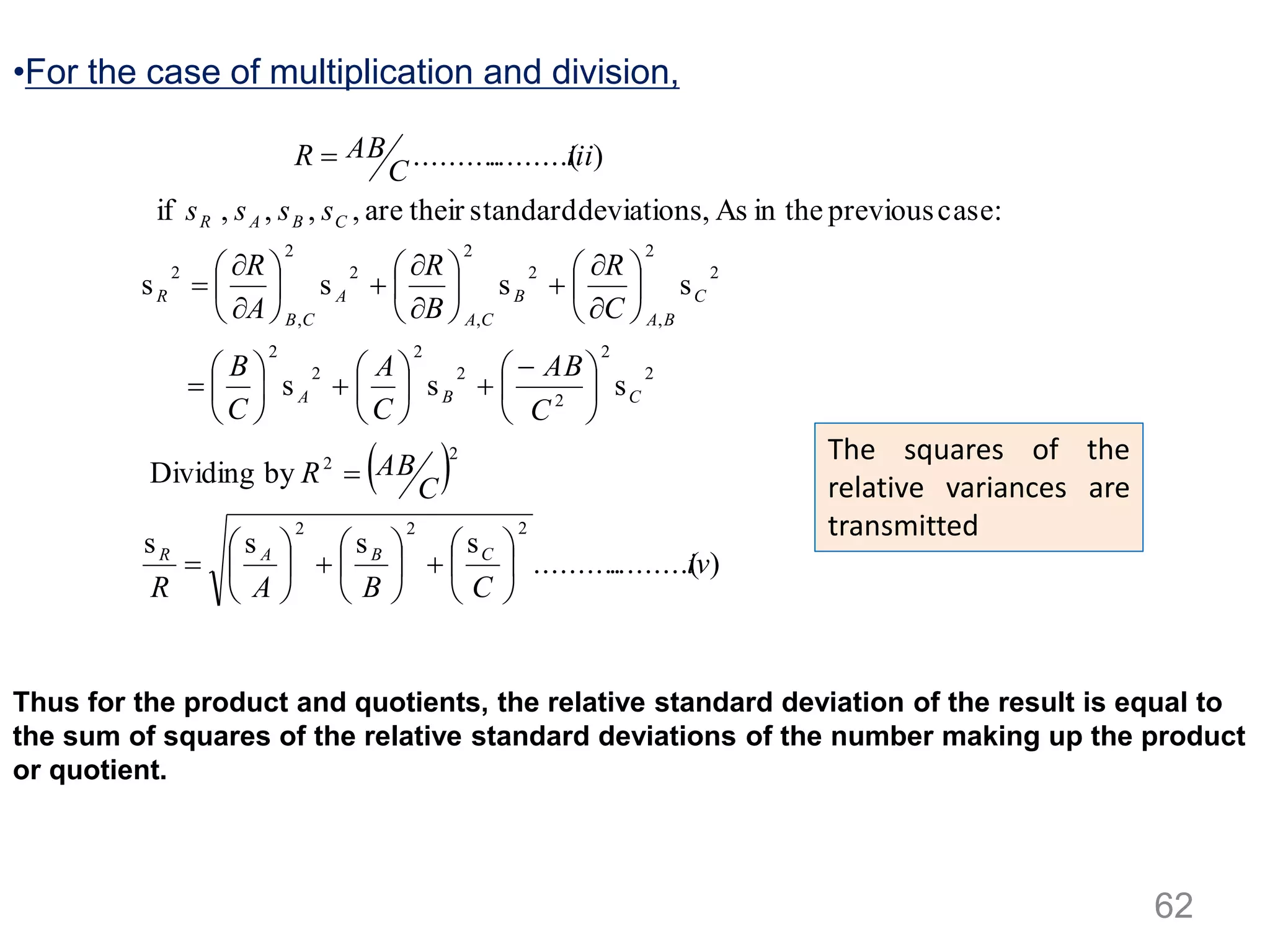
![P(xi,yi)
y = mx + b
Residual = PQ= yi-(mxi+b)Y
Fig: Calibration curve for isooctane (peak area vs % mole)
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
X
• The least square method assumes
that;
– The sum of squares of residuals from
all the points is minimum. [The vertical
deviation from each point to the line is
called residual].
2
[ ( )]resid i i
i
SS y mx b
0&0&0minima,ofprincipletheFrom
b.andmestimatetohaveWe(ii).............0&0
2
2
2
2
b
SS
m
SS
b
SS
m
SS
b
SS
m
SS
residresidresidresid
residresid
(iv).............0][..
0-1)]([2..
0
)]([
,
(iii).............0][..
0-)]([2..
0
)]([
..
2
2
2
bmxyei
bmxyei
b
bmxy
Also
bxmxyxei
xbmxyei
m
bmxy
ei
ii
ii
ii
iiii
iii
ii
•The sum of square of residual is given by, SSresid
•To minimize SSresid ; the first derivative is set to zero w.r.t. the
variables m and b.
•Solving the equations gives,
Equations (iii) and (iv) are normal equations to fix the line. i.e. solving the values of m
and b from the above equations we can get the line of best fit.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/error2015lamichhaneji-150718223151-lva1-app6891/75/Error-2015-lamichhaneji-64-2048.jpg)