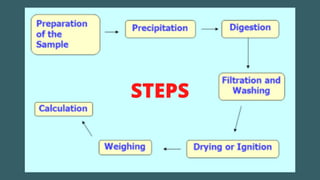
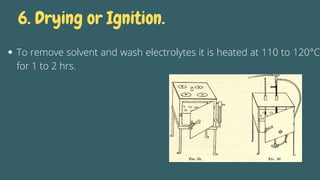
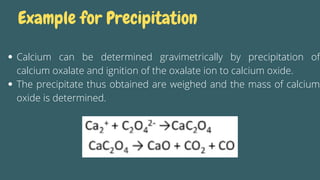
Gravimetric analysis is an analytical method that determines the quantity of analyte by measuring the mass of a substance containing it, involving steps such as preparation, precipitation, digestion, filtration, washing, drying, and weighing. The method can be divided into two types: precipitation and volatilization, with advantages including higher accuracy and precision compared to volumetric methods, but also disadvantages such as being time-consuming and susceptible to coprecipitation errors. Key examples include the determination of calcium through precipitation of calcium oxalate and the separation of water through volatilization.