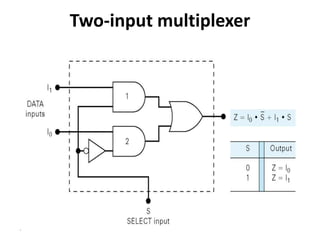
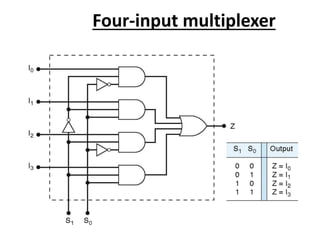
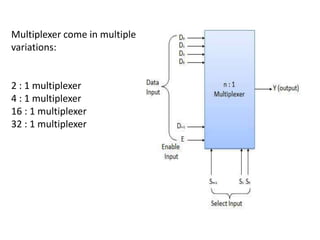
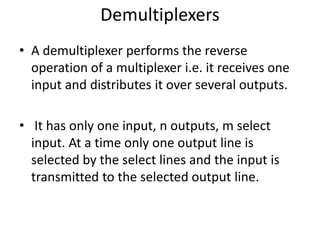
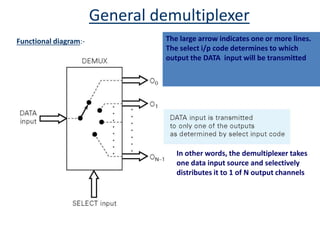
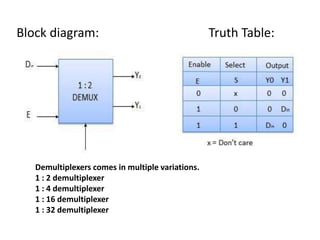
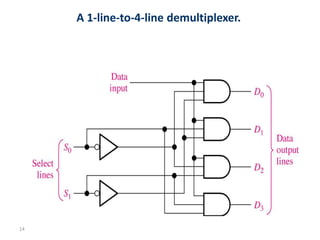
A multiplexer is a device that selects one of several analog or digital input signals and forwards the selected input into a single line. It has multiple data inputs, a single output, and select lines that determine which input is directed to the output. A demultiplexer performs the opposite function, taking a single input and distributing it to one of multiple outputs based on the select lines. Multiplexers and demultiplexers come in various configurations depending on the number of inputs and outputs, such as 2:1, 4:1, 16:1 or 32:1. They are basic building blocks used in digital systems and communication networks to efficiently route signals.