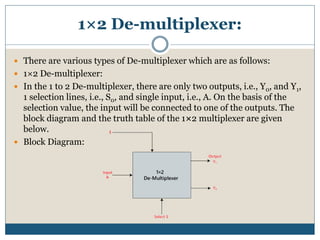
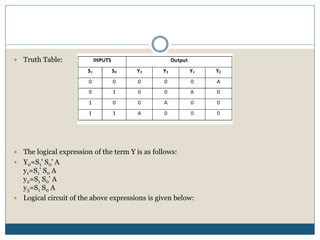
This document discusses demultiplexers, which are combinational circuits with one input and multiple outputs. It describes 1x2 and 1x4 demultiplexers specifically. For a 1x2 demultiplexer, there are two outputs, one selection line, and a single input. The input is directed to one of the two outputs based on the selection line value. A 1x4 demultiplexer has four outputs, two selection lines, and one input. The input is directed to one of the four outputs based on the combination of values on the two selection lines. Block diagrams and truth tables are provided to illustrate the functionality of 1x2 and 1x4 demultiplexers.