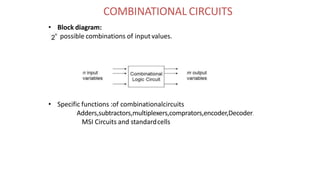
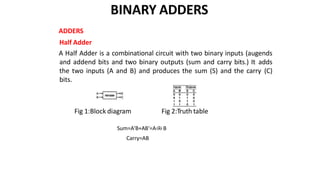
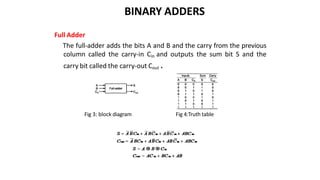
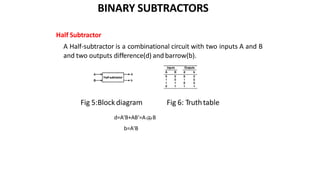
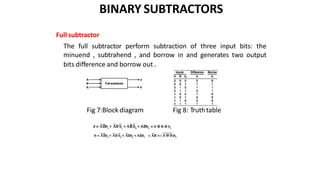
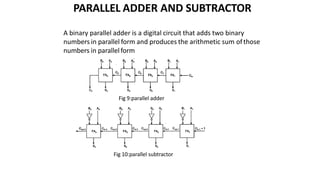
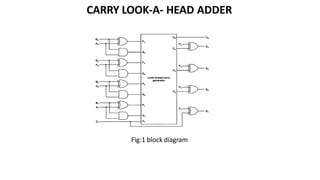
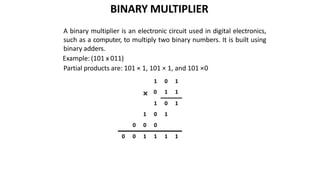
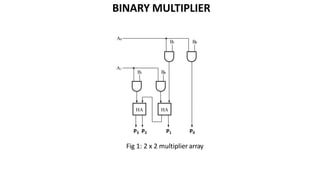
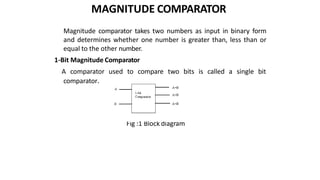
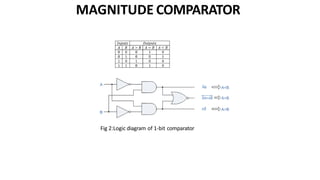
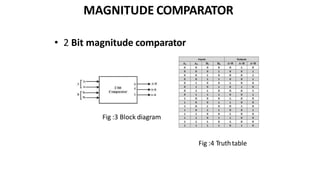
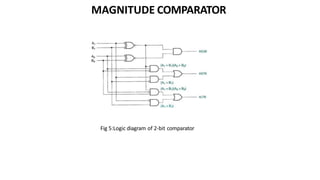
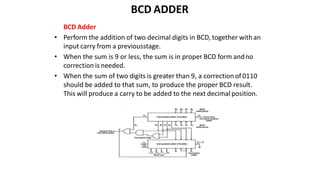
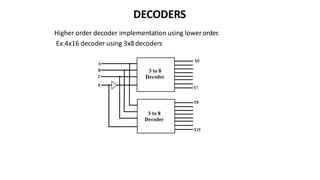
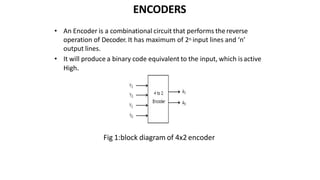
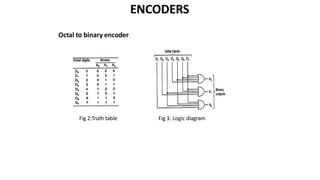
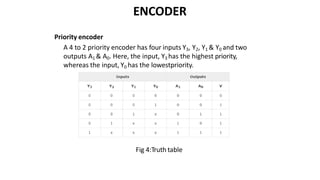
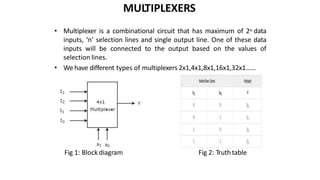
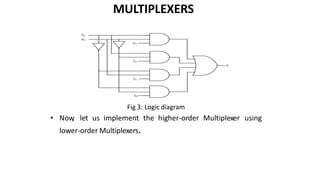
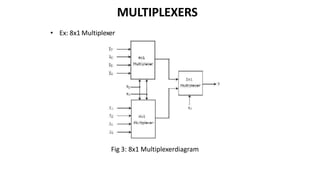
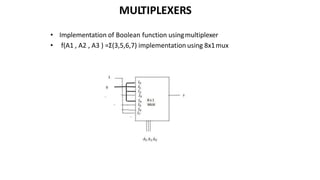
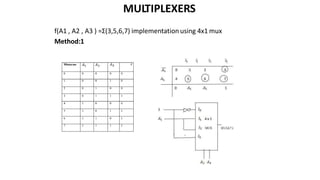
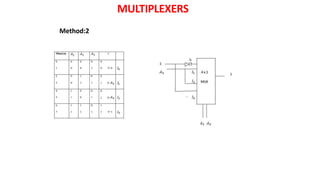
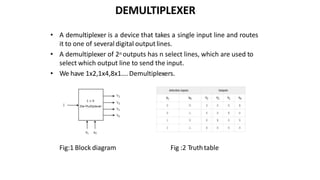
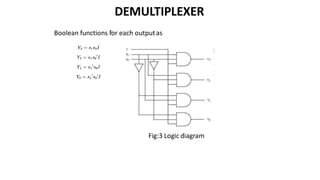
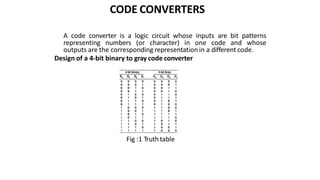
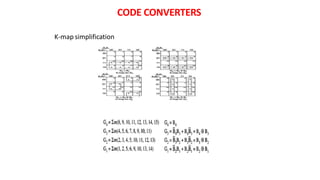
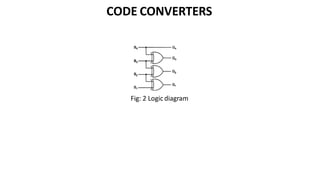
This document discusses combinational circuits. It defines combinational circuits as circuits whose outputs only depend on the current inputs and not previous states. The document covers various types of combinational circuits like adders, subtractors, encoders, decoders, multiplexers, demultiplexers and code converters. It provides block diagrams, truth tables and logic diagrams to explain the working of these combinational circuits.