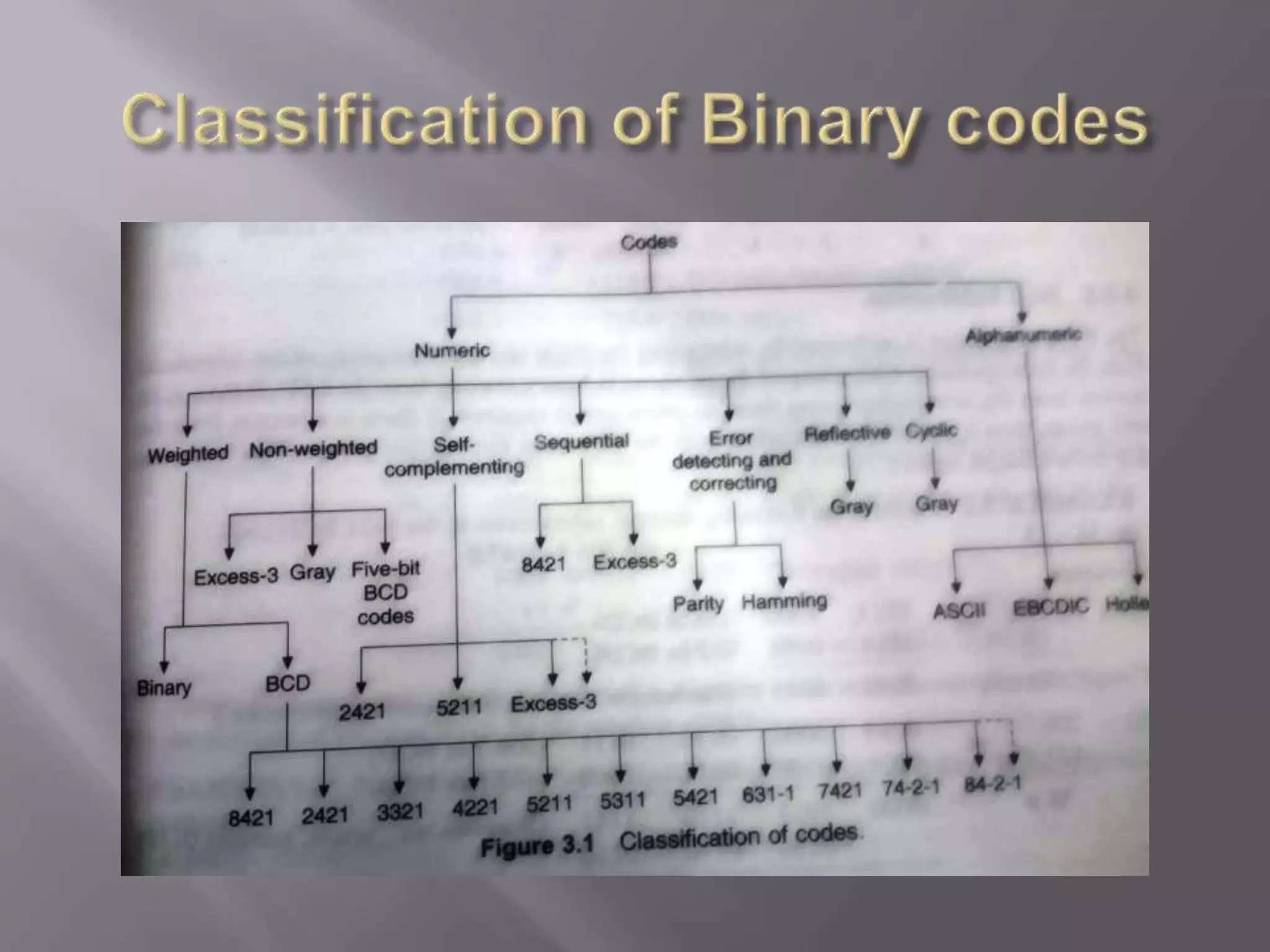
1) Binary codes represent numbers, letters, and other data using groups of bits or symbols. Weighted binary codes follow a positional weighting principle where each bit position represents a specific weight.
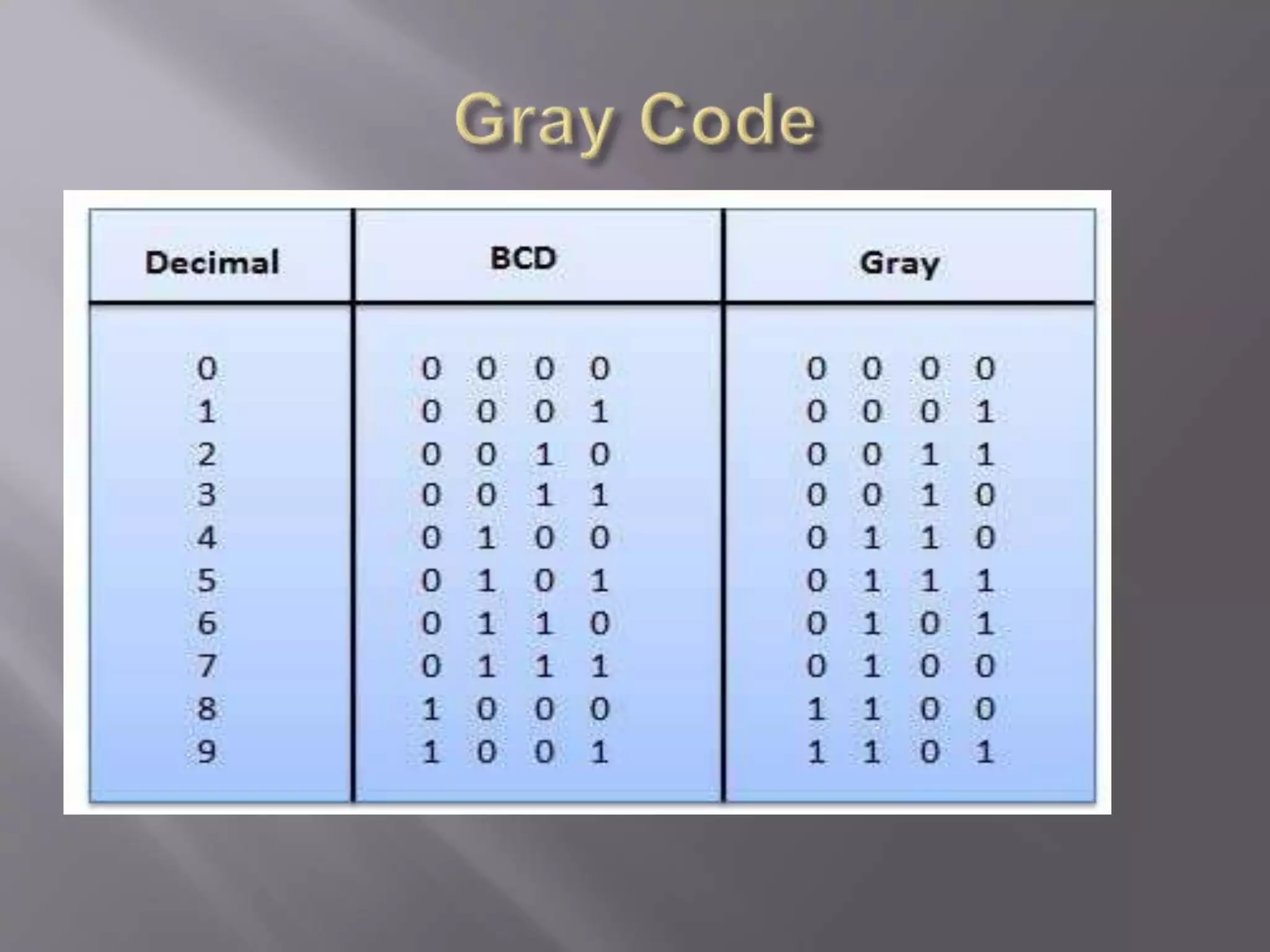
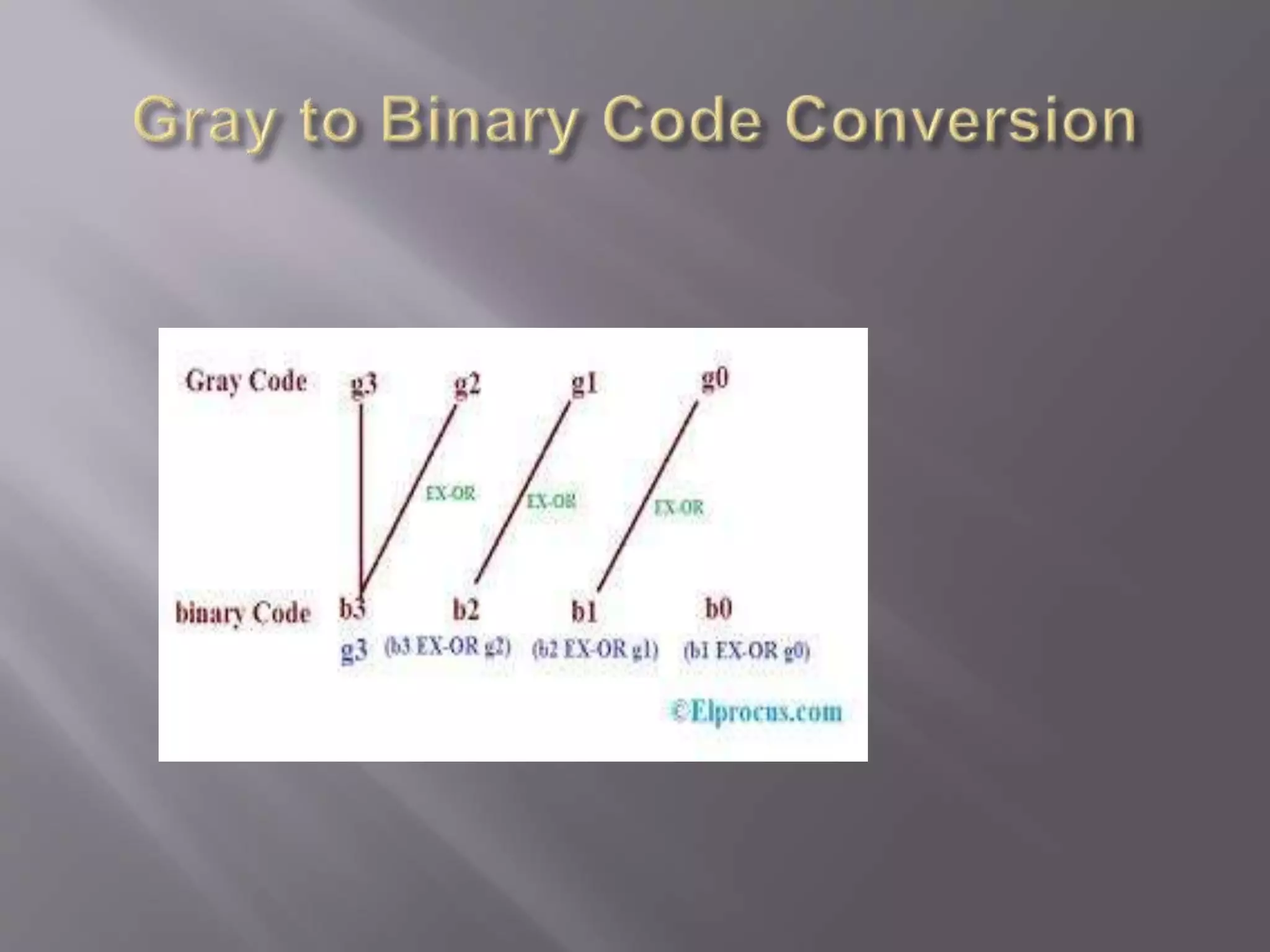
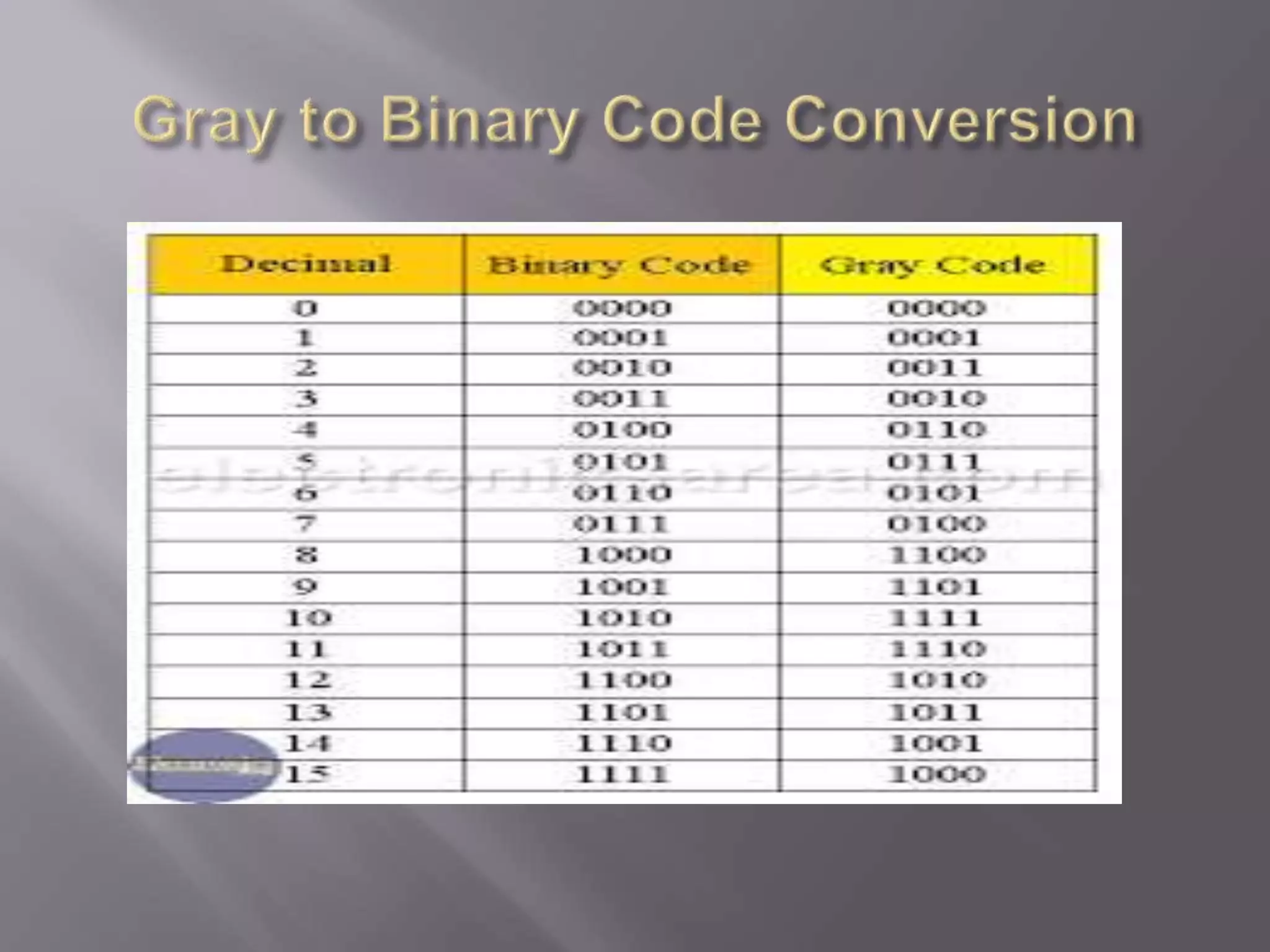
2) Non-weighted codes like excess-3 code and Gray code do not assign positional weights. Gray code is used in shaft position encoders to prevent multiple bit changes that can cause problems.
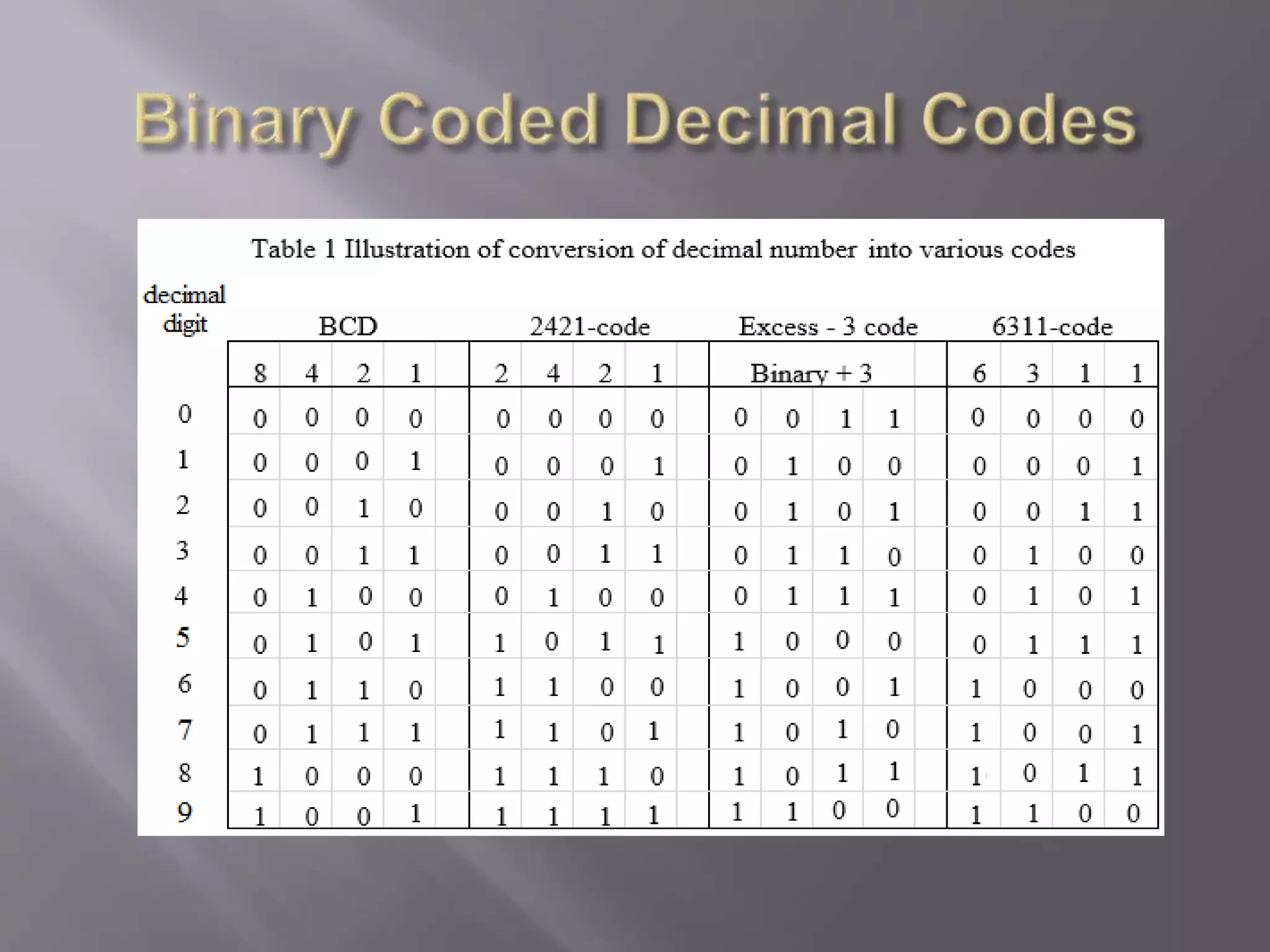
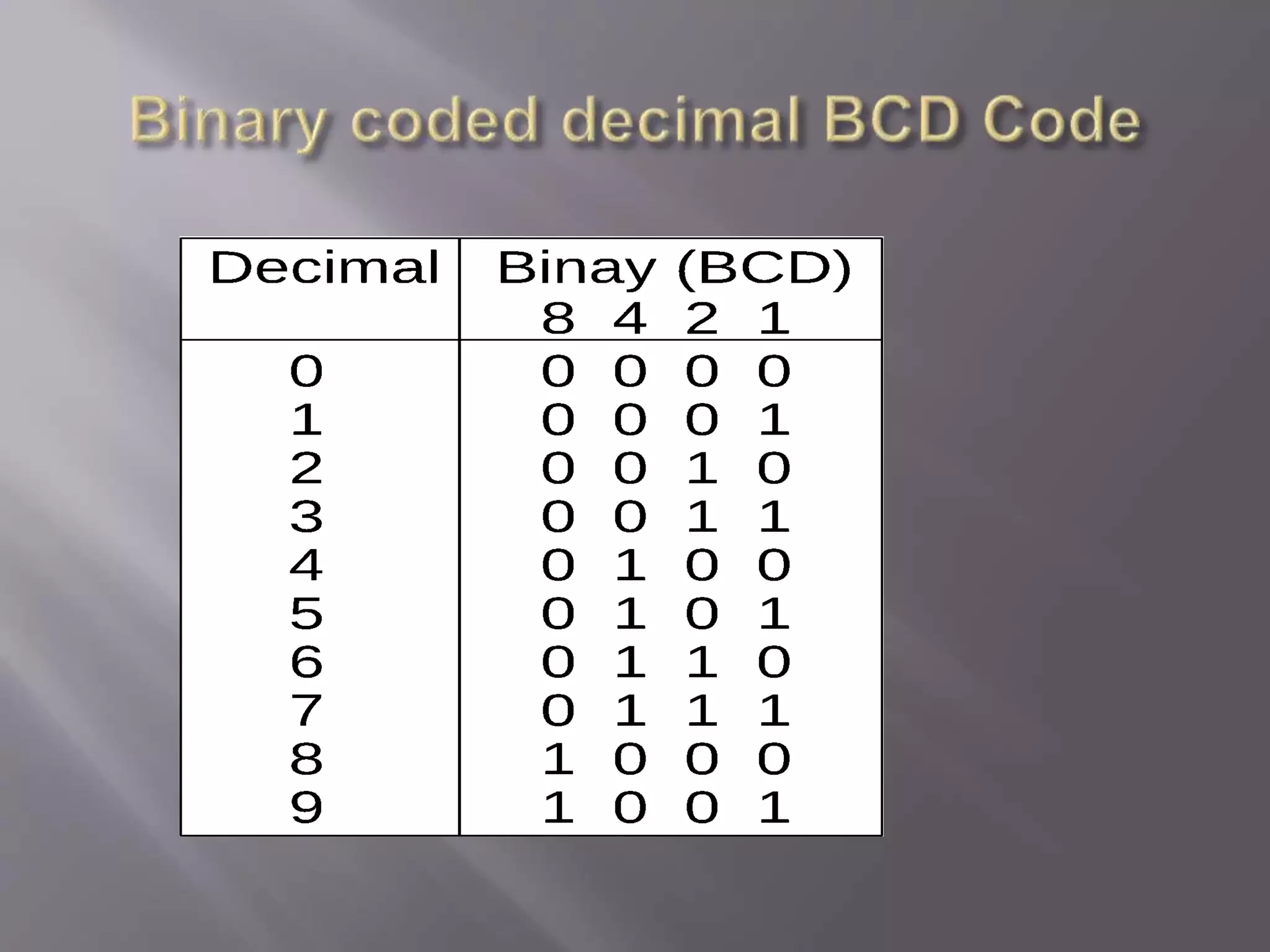
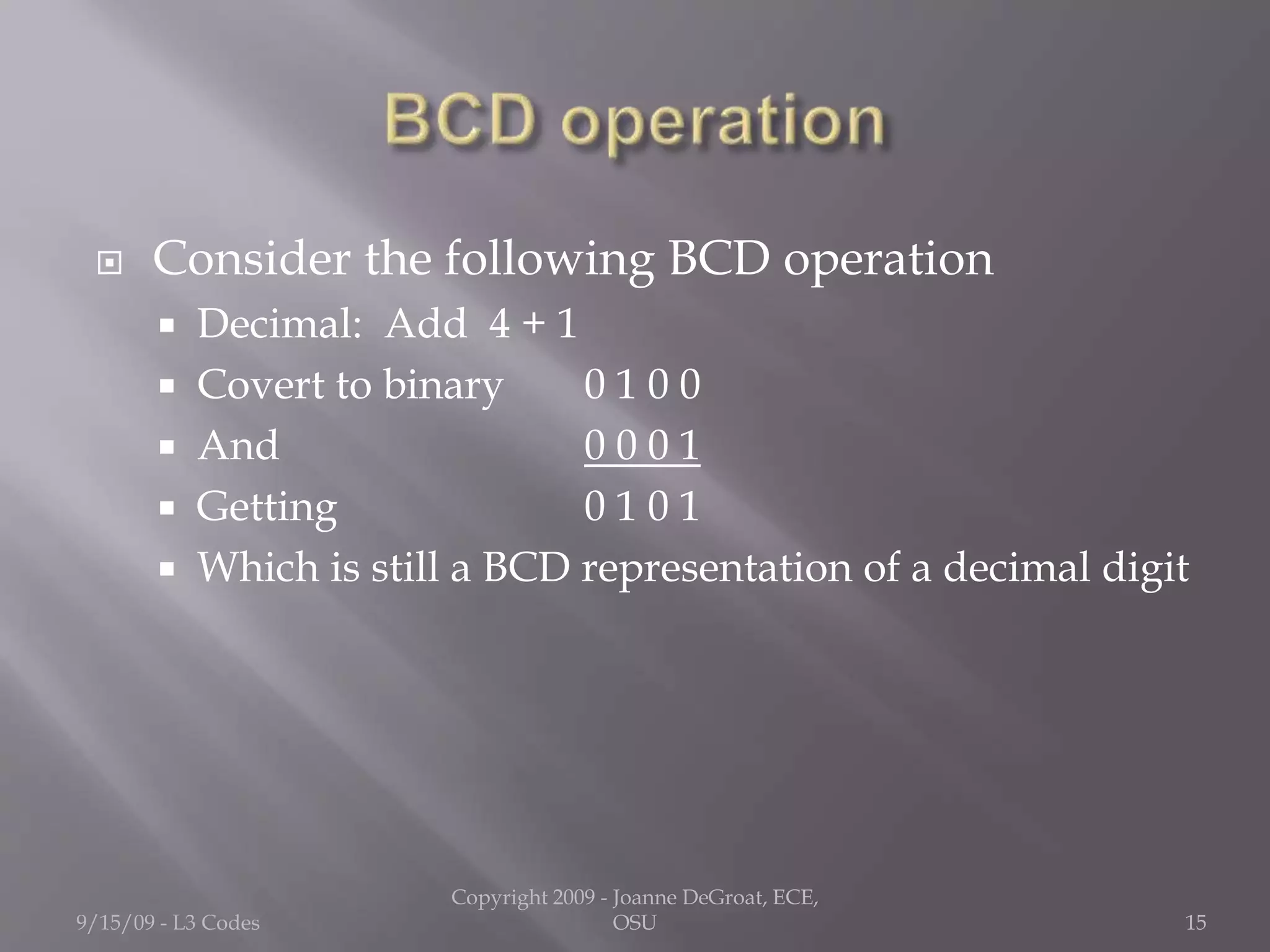
3) BCD (binary coded decimal) represents each decimal digit with a 4-bit binary number, allowing representation of numbers from 0-9. BCD addition can result in numbers outside the valid 0-9 range, requiring carries between digits.