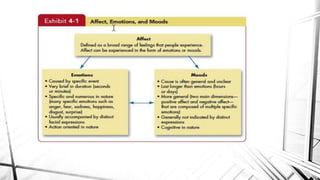
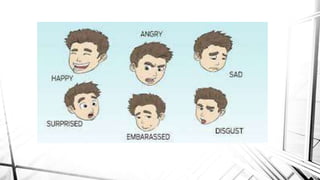
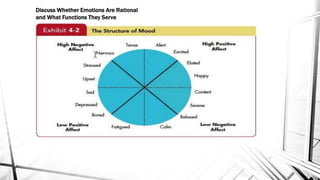
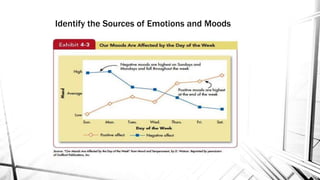
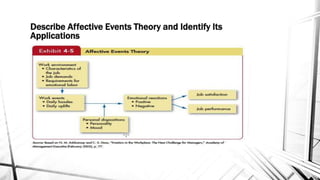
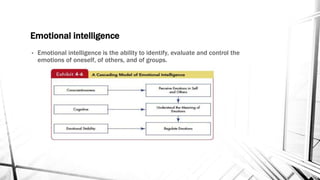
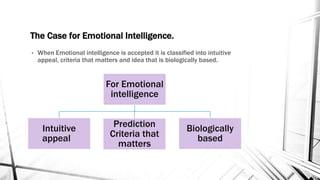
This document discusses emotions and moods in the workplace. It defines affect and effect, noting that affect is a verb meaning to cause something to happen, while effect is a noun referring to a result. It also discusses why emotions were previously ignored in organizational behavior research due to views of emotionality as irrational and disruptive. However, it is now understood that emotions cannot be separated from the workplace. The document identifies sources of emotions and moods like personality, time of day, social activities, sleep, exercise, and age. It describes affective events theory and emotional labor, noting how emotions accumulate and surface acting can be damaging. Finally, it discusses implications for managers, emphasizing that emotions are natural and cannot be divorced from people