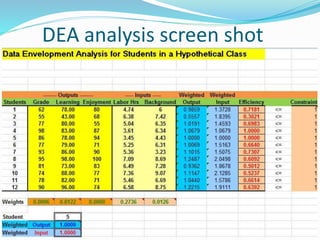
This document discusses Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA), a linear programming methodology used to measure the efficiency of decision-making units with multiple inputs and outputs. It provides a brief history of DEA, explaining that it was created to evaluate efficiency using an empirical production frontier. The document also outlines how DEA works by establishing an efficiency frontier using selected variables, defining the frontier, and giving each unit an efficiency coefficient. Finally, it discusses the advantages of DEA in handling multiple inputs/outputs without specifying a production function, as well as the disadvantages of being sensitive to input/output selection.