1) Carrefour is a large French international hypermarket chain with over 11,000 stores in more than 32 countries and 495,000 employees.
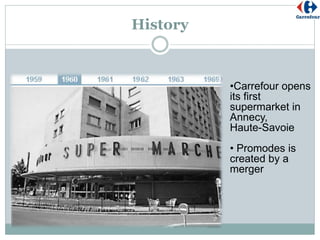
2) It was founded in the 1960s in France and has since expanded globally, opening its first overseas store in 1969 and continuously entering new markets.
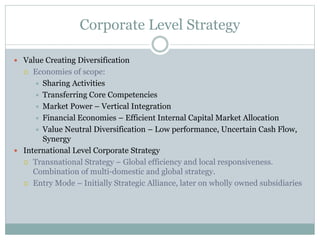
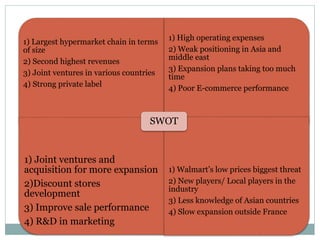
3) As the largest retailer in Europe and one of the largest in the world, Carrefour faces competition from other large retailers but maintains strategies around low prices, private labels, and international expansion.