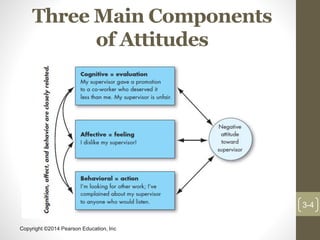
This chapter discusses attitudes and job satisfaction. It defines attitudes as evaluative statements that can be favorable or unfavorable about objects, people or events. Attitudes have three main components - cognitive, affective, and behavioral. The chapter explores how attitudes relate to behavior and the relationship between cognitive dissonance and reducing inconsistencies. It also examines how job satisfaction, involvement, empowerment, and other job attitudes are measured and what causes job satisfaction. Managers are advised to focus on making work interesting in order to improve attitudes.