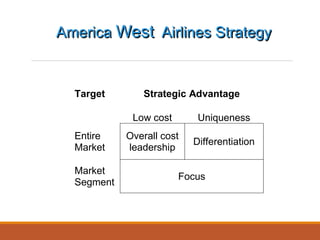
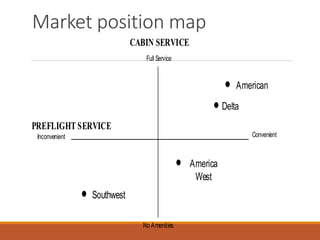
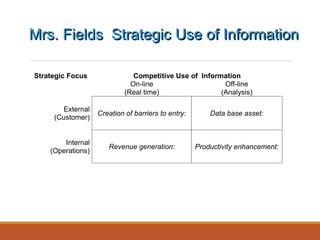
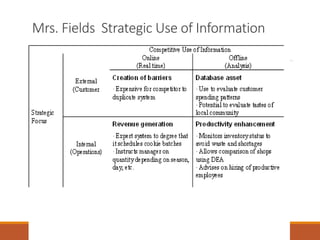
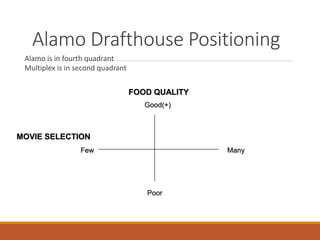
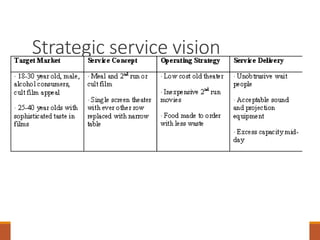
The document discusses strategic service concepts for Alamo Drafthouse, including its target market segments, service concept, operating strategy, and service delivery system. It analyzes Alamo's market position compared to competitors based on food quality and movie selection. Alamo is positioned in the fourth quadrant with good food quality and few movie selections. The summary also identifies qualifiers, service winners, and service losers for both Alamo and multiplex movie theaters that differentiate their customer criteria.