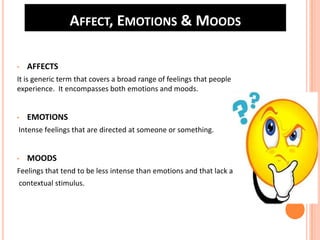
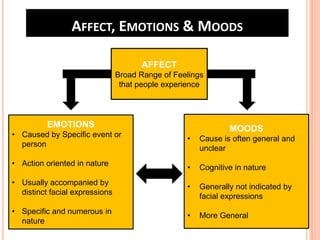
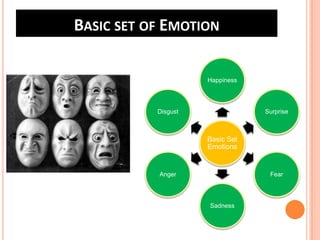
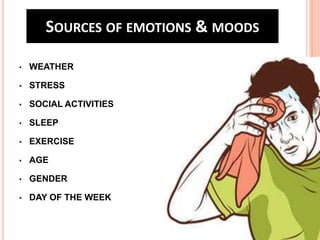
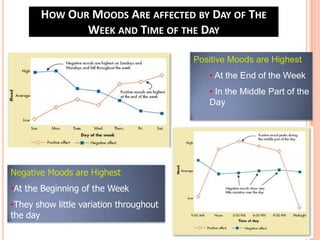
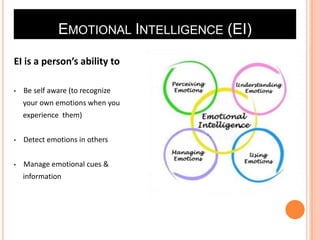
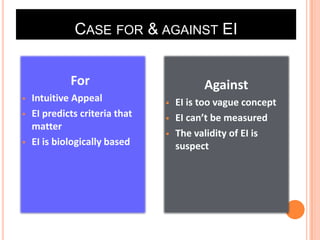
Team 2's document discusses affect, emotions, and moods. It defines affect as a broad range of feelings, emotions as intense feelings directed at someone or something, and moods as less intense feelings without a clear cause. Emotions are specific, cognitive, and action-oriented, while moods are more general. Basic emotions include happiness, disgust, surprise, anger, fear, and sadness. Moods can be positive or negative. Emotions serve functions and are influenced by factors like weather, stress, sleep, and gender. The document also covers emotional labor, intelligence, and implications for management.