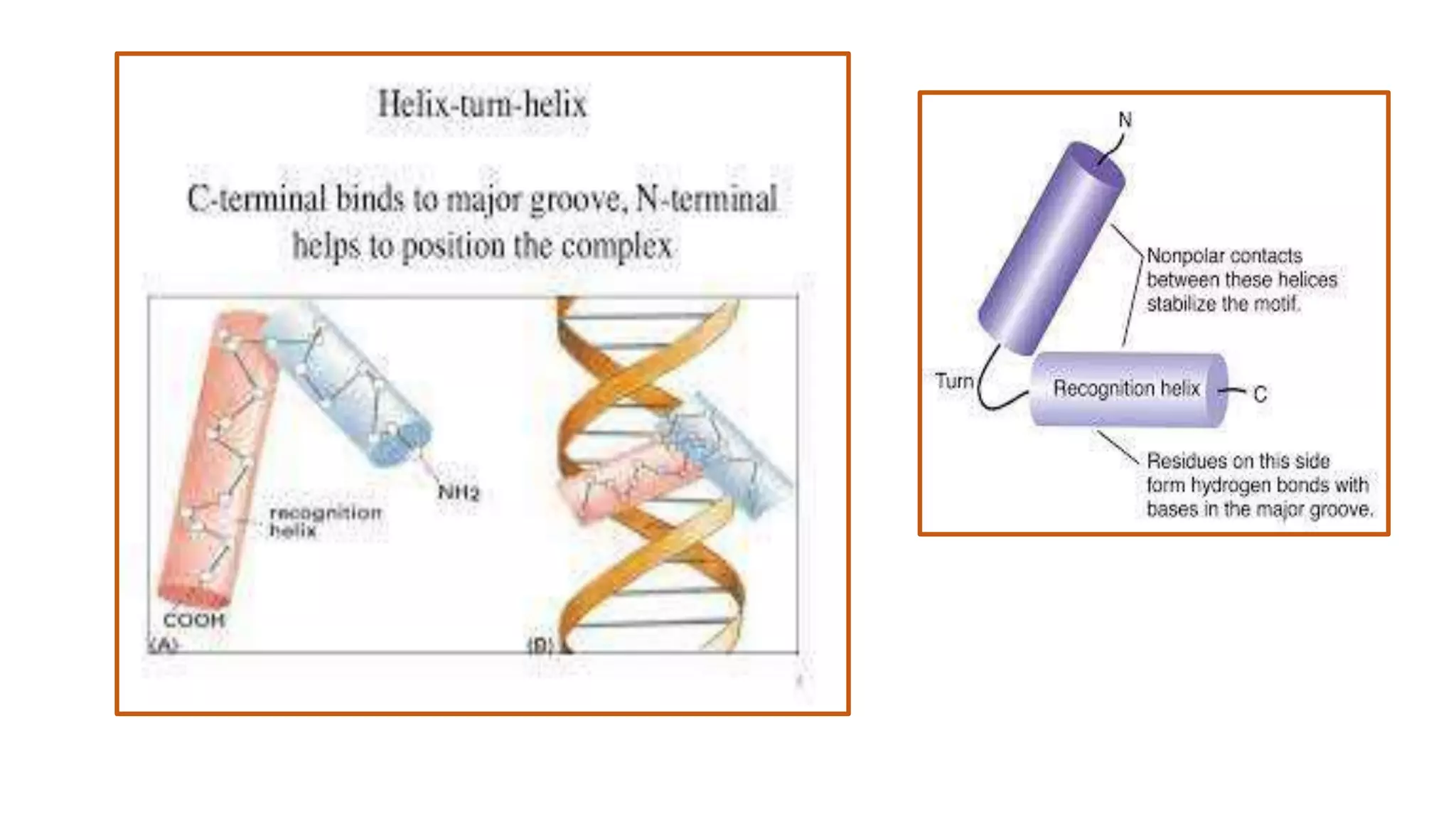
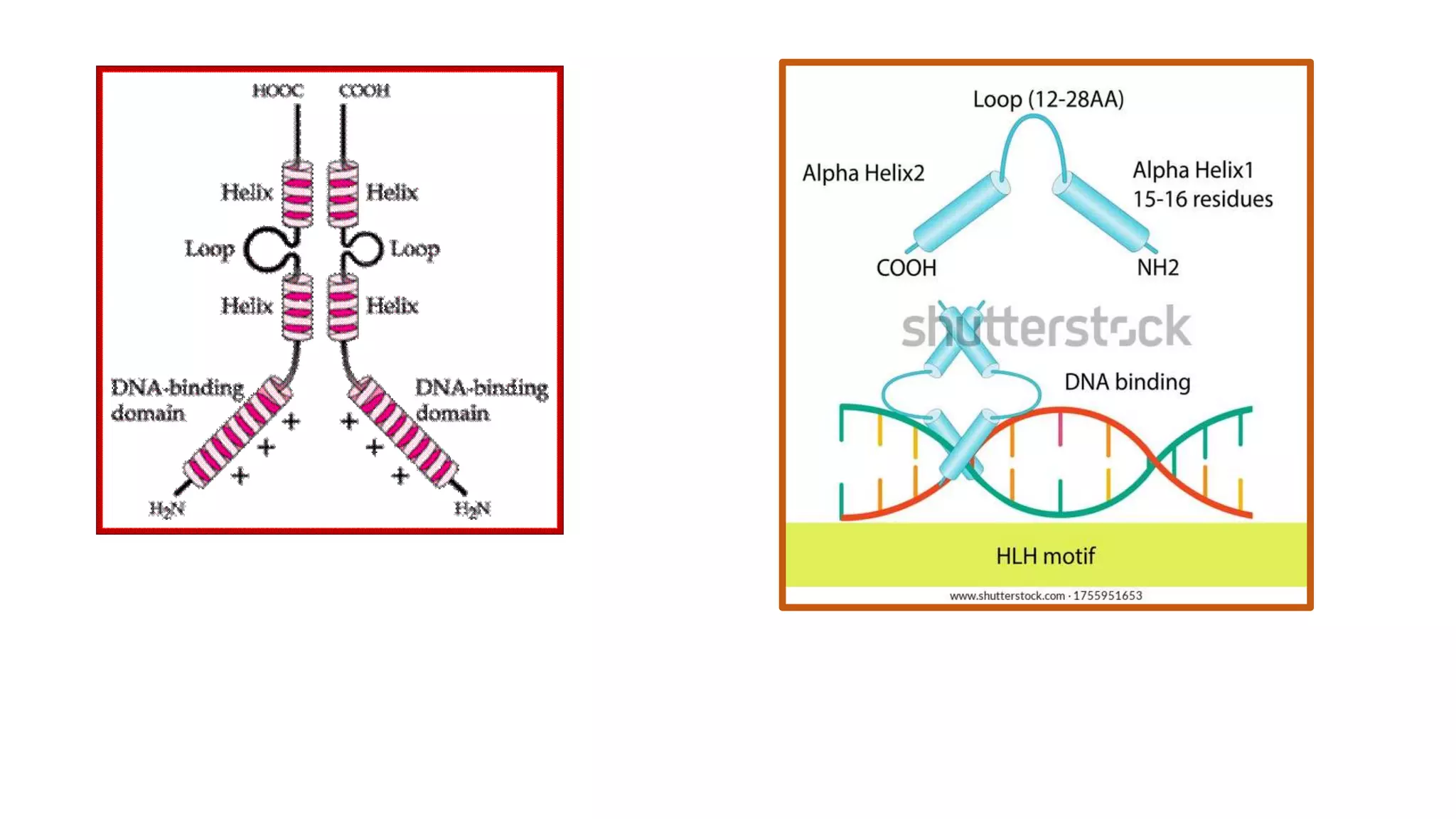
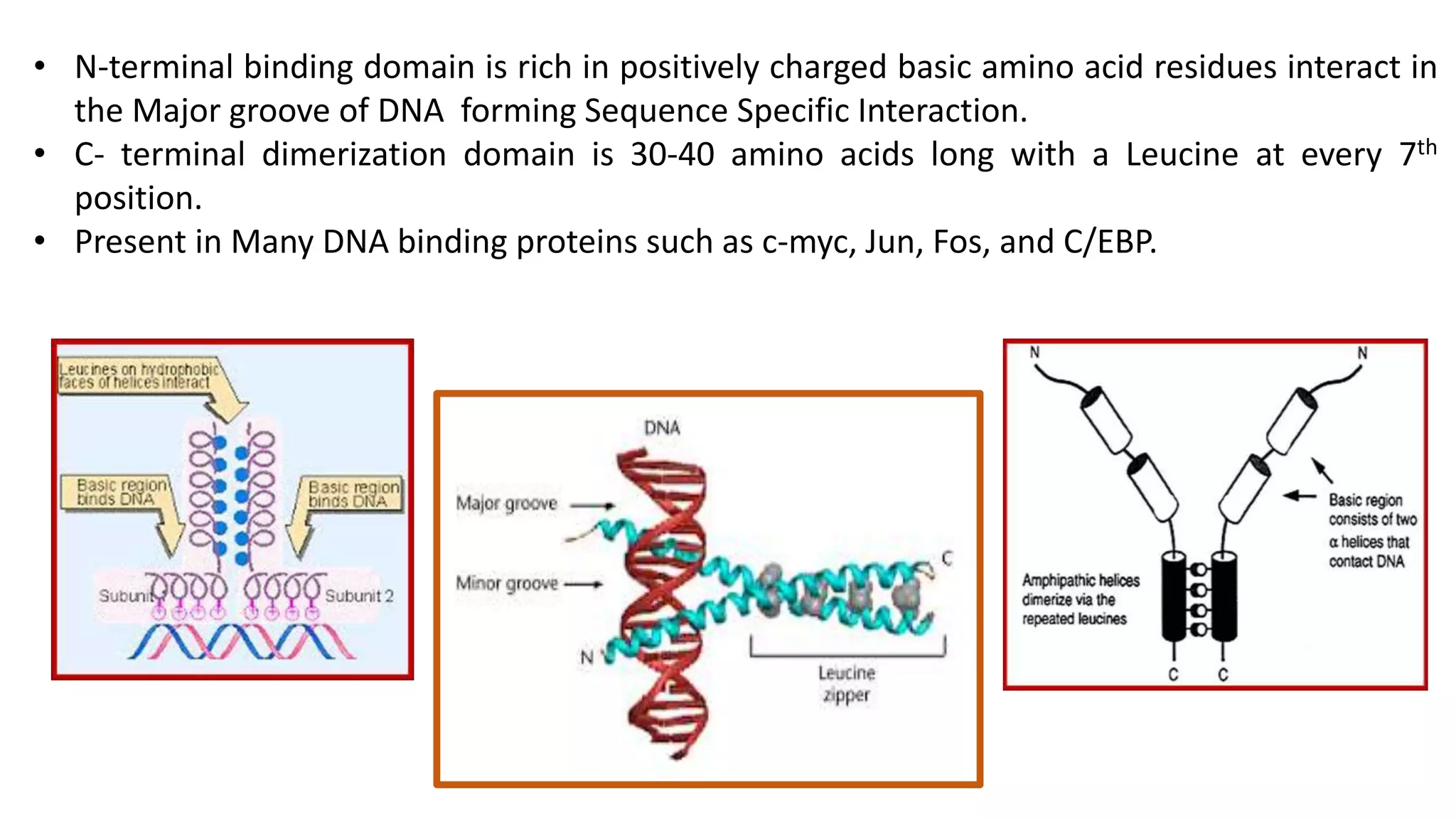
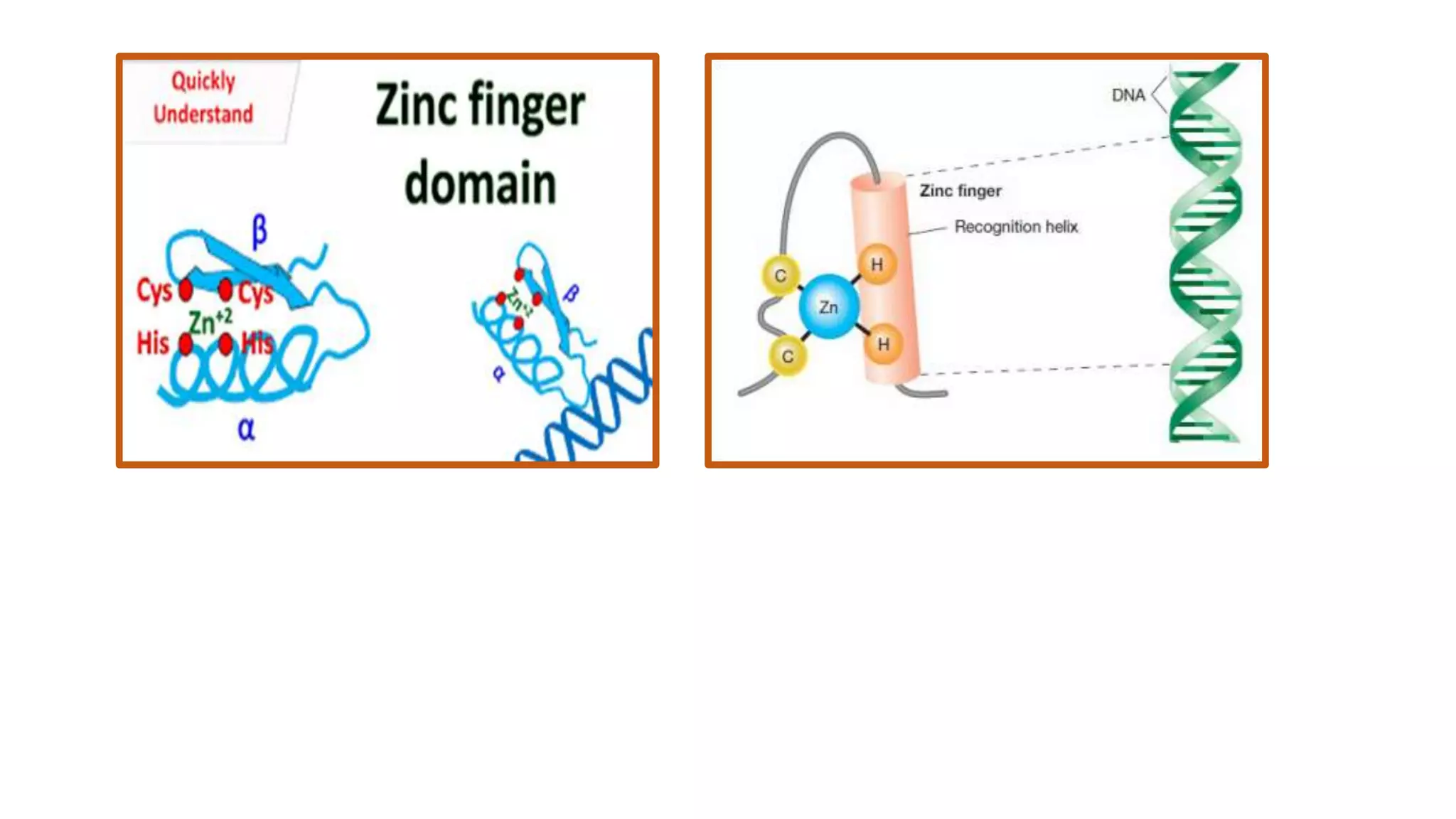
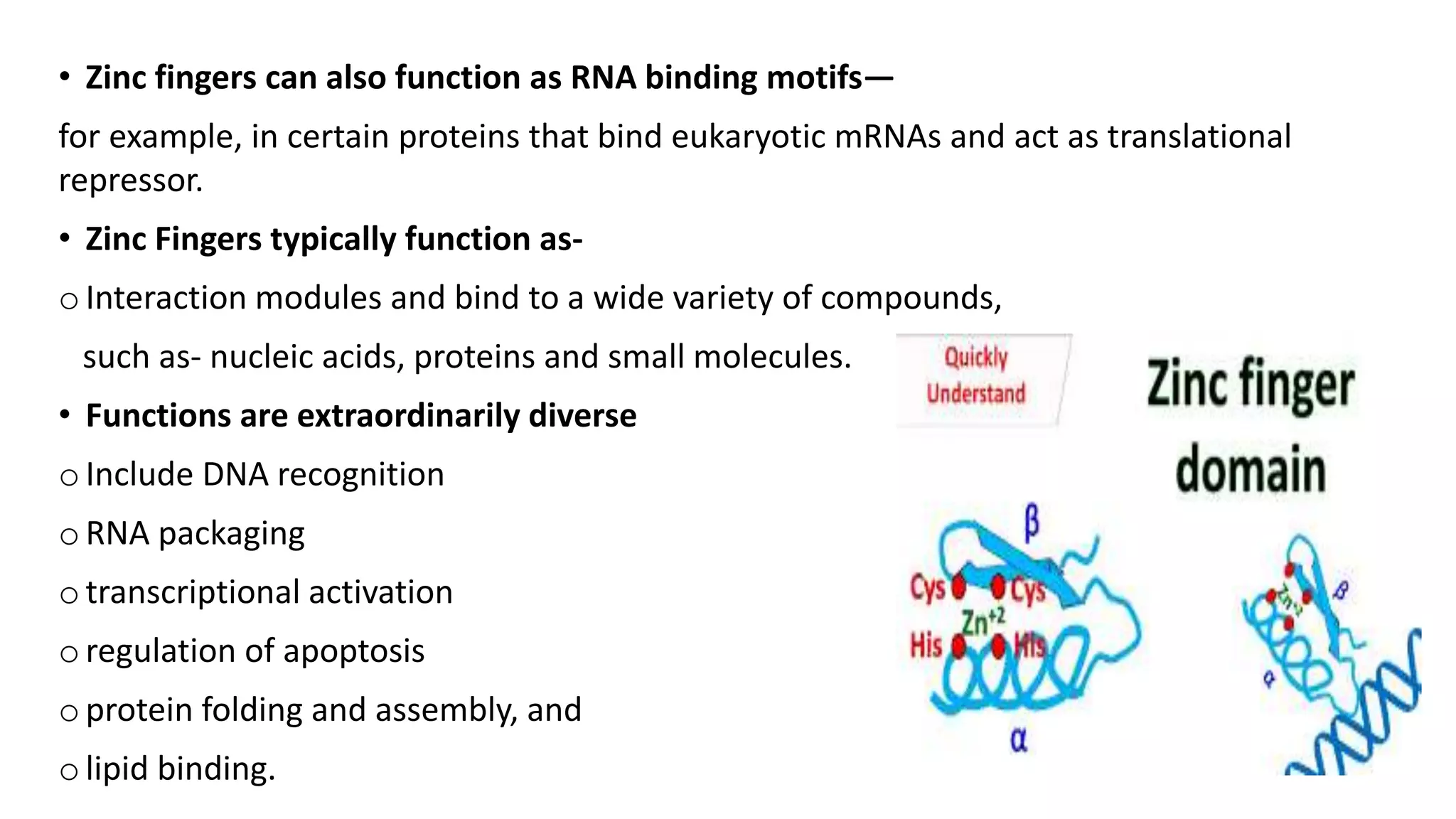
La interacción entre ADN y proteínas es fundamental en las células vivas, controlando procesos como replicación, transcripción y reparación del ADN. Las proteínas que interactúan con el ADN pueden ser específicas o no específicas, y poseen diferentes dominios de unión al ADN, como el motivo de hélice-giro-hélice y el motivo de dedo de zinc. Existen diversas técnicas para detectar estas interacciones, como el ensayo de huella de DNase y la inmunoprecipitacion de cromatina.