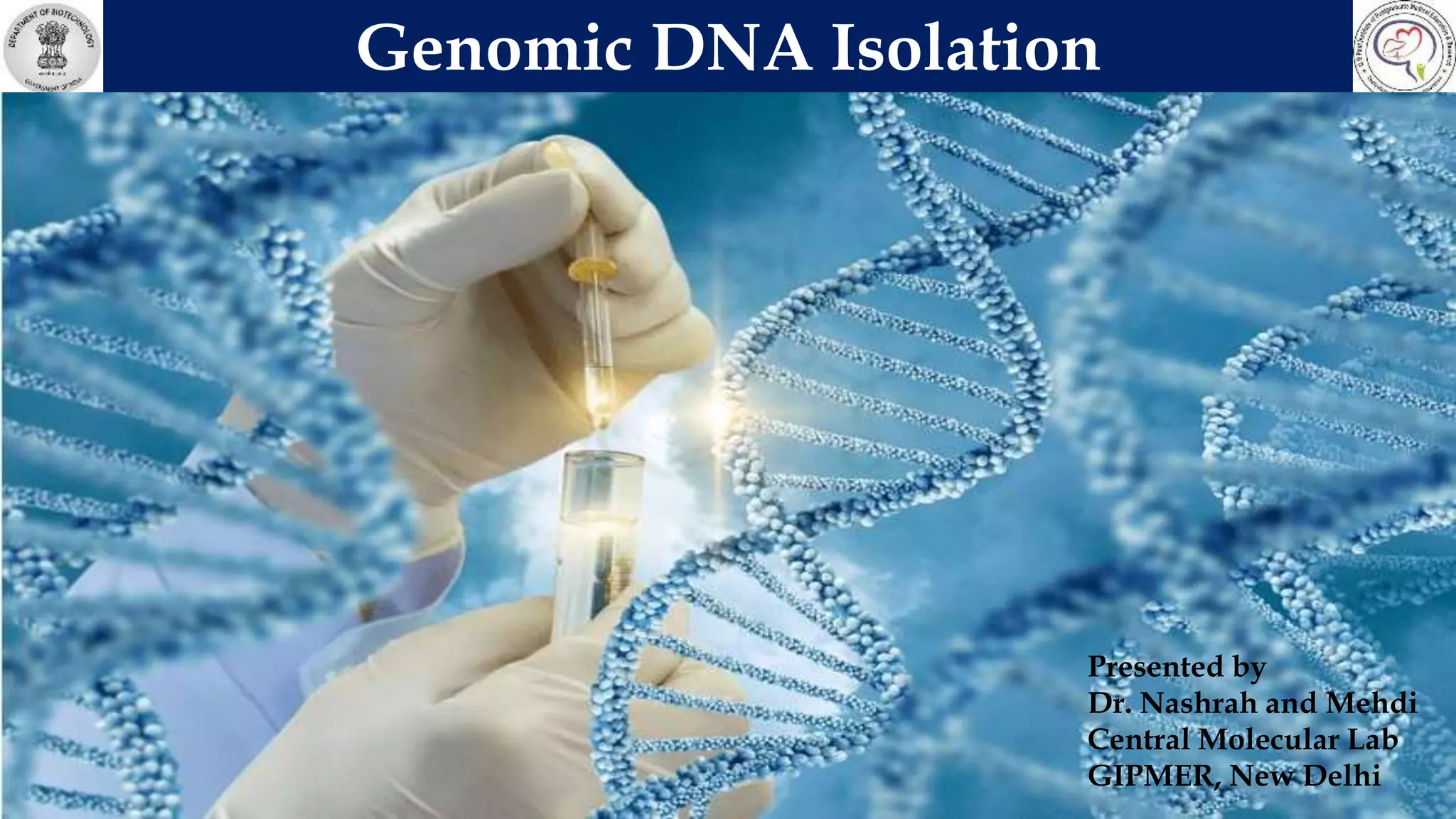
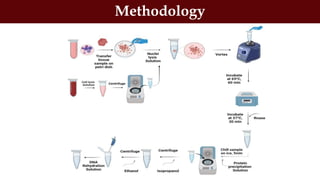
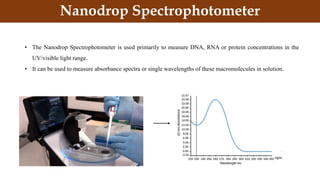
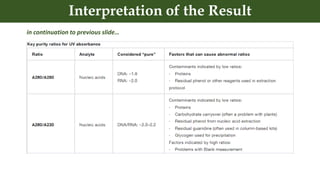
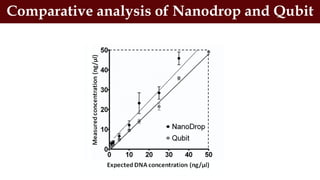
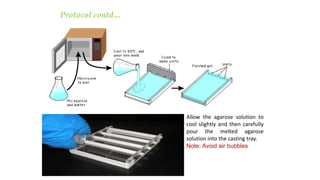
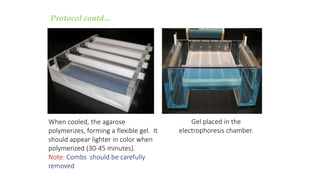
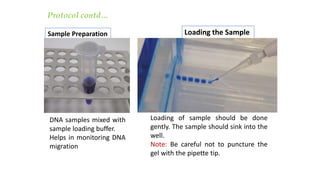
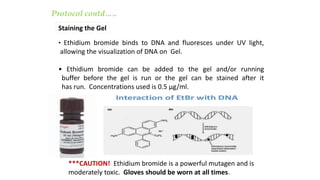
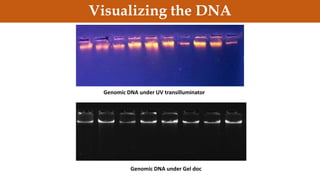
This document discusses genomic DNA isolation. It describes how DNA was first isolated in 1869 and that both manual methods and commercial kits are used. Various tissues can be used for DNA extraction, which involves lysing cells, separating and solubilizing the DNA, washing away proteins and other contaminants, and eluting the purified DNA. Several reagents and equipment are required for the isolation process. Quantification of the isolated DNA can be done using Nanodrop spectrophotometry, Qubit fluorometry, or agarose gel electrophoresis.