Embed presentation
Downloaded 16 times








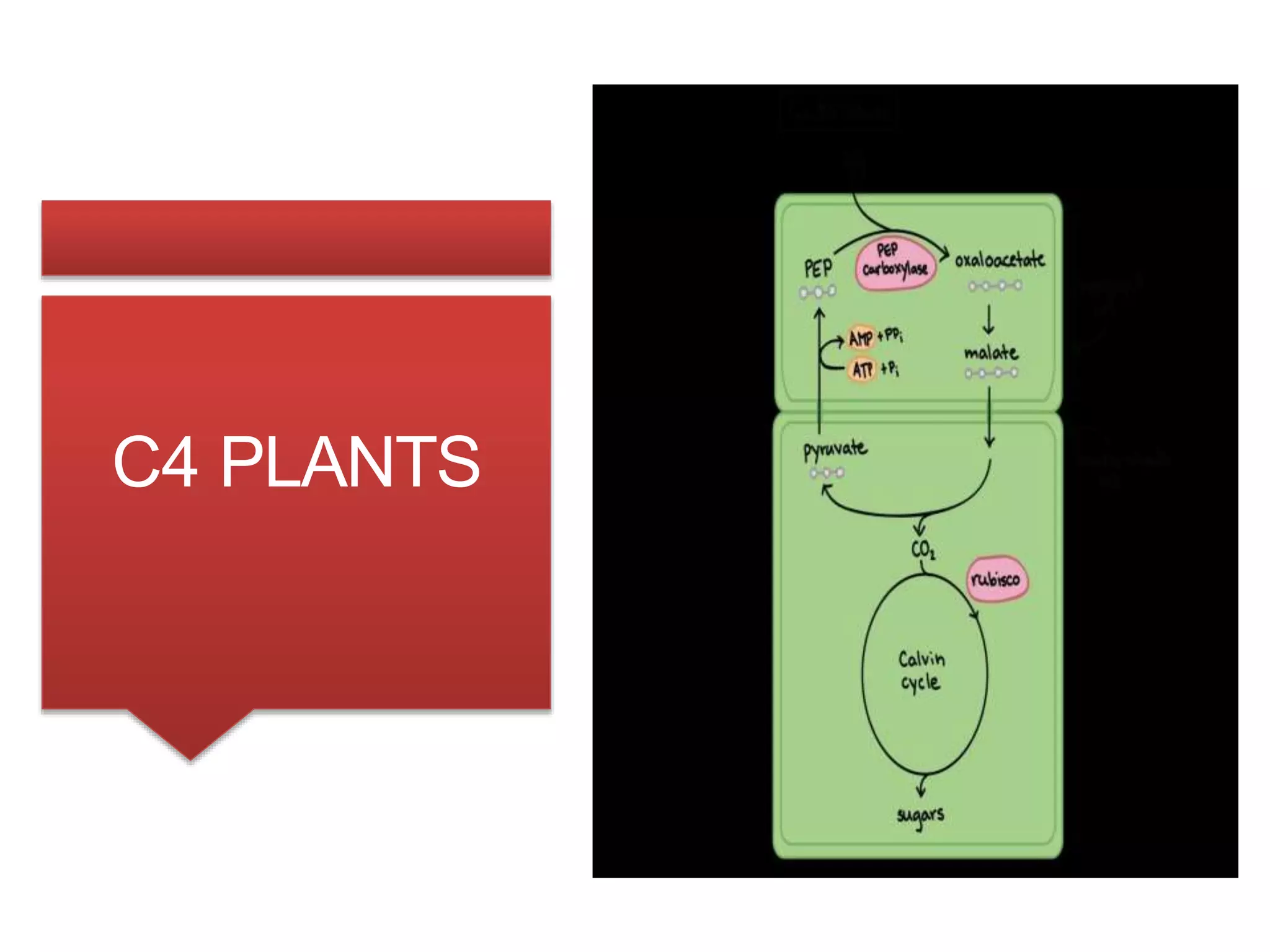

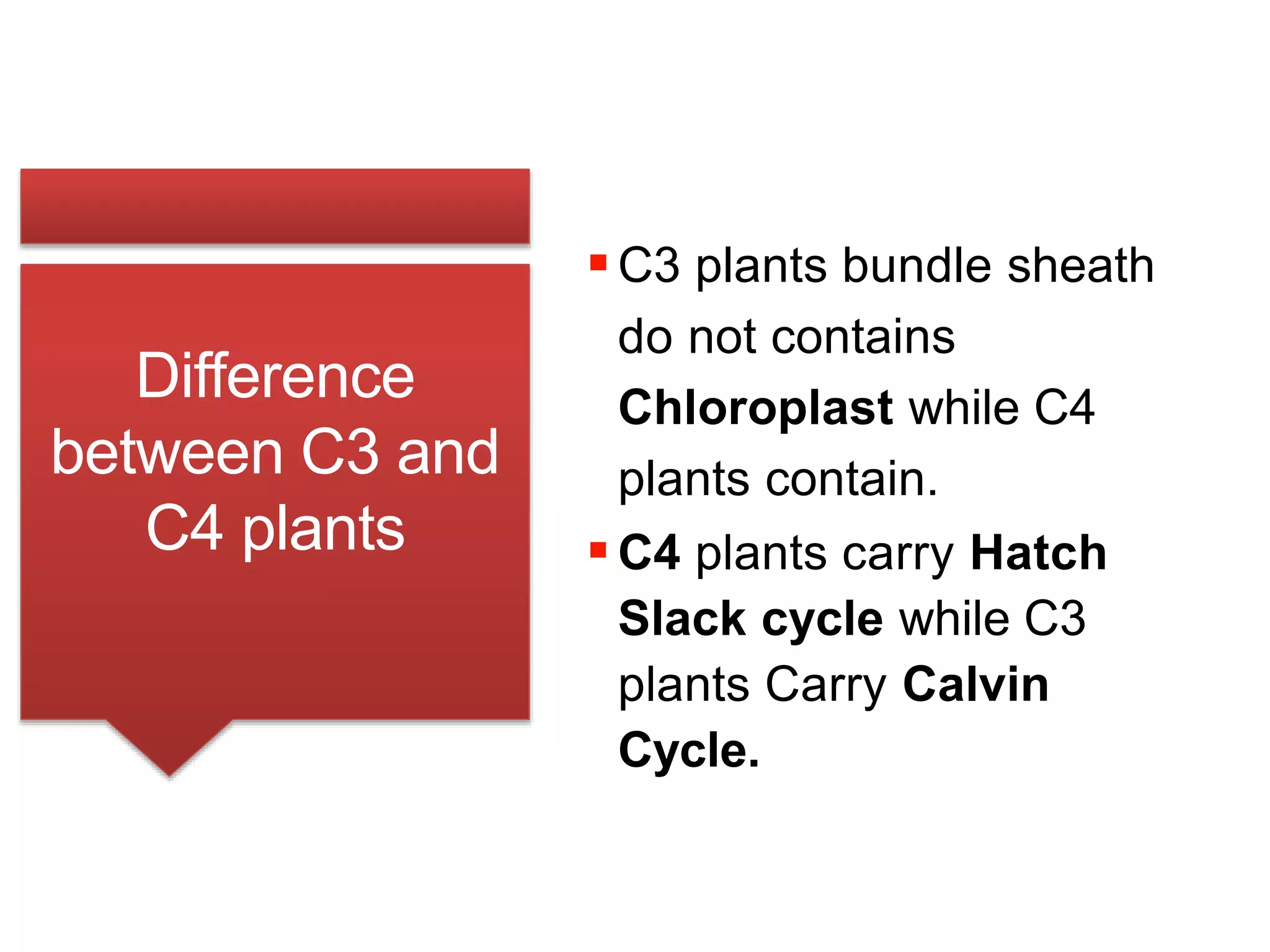

C3 and C4 plants differ primarily in their photosynthesis processes; C3 plants produce 3-phosphoglycerate and are more common, accounting for about 85% of plants, thriving in cool, wet climates. In contrast, C4 plants form a 4-carbon sugar and are more efficient in hot, dry environments, comprising around 5% of plant species. Notably, C3 plants utilize the Calvin cycle, while C4 plants employ the Hatch-Slack cycle and have specialized structures that enhance their efficiency.











