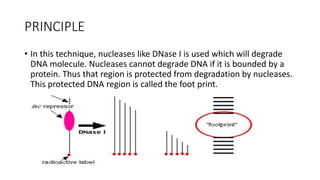
DNA footprinting is a technique to study how proteins interact with DNA. It involves treating DNA with nucleases or chemicals that cut DNA, but are blocked from cutting where a protein is bound. This leaves a "footprint" of protected DNA that reveals the protein's binding site. The technique was developed in 1978 and can detect even transient protein-DNA interactions to help understand transcriptional control within cells.