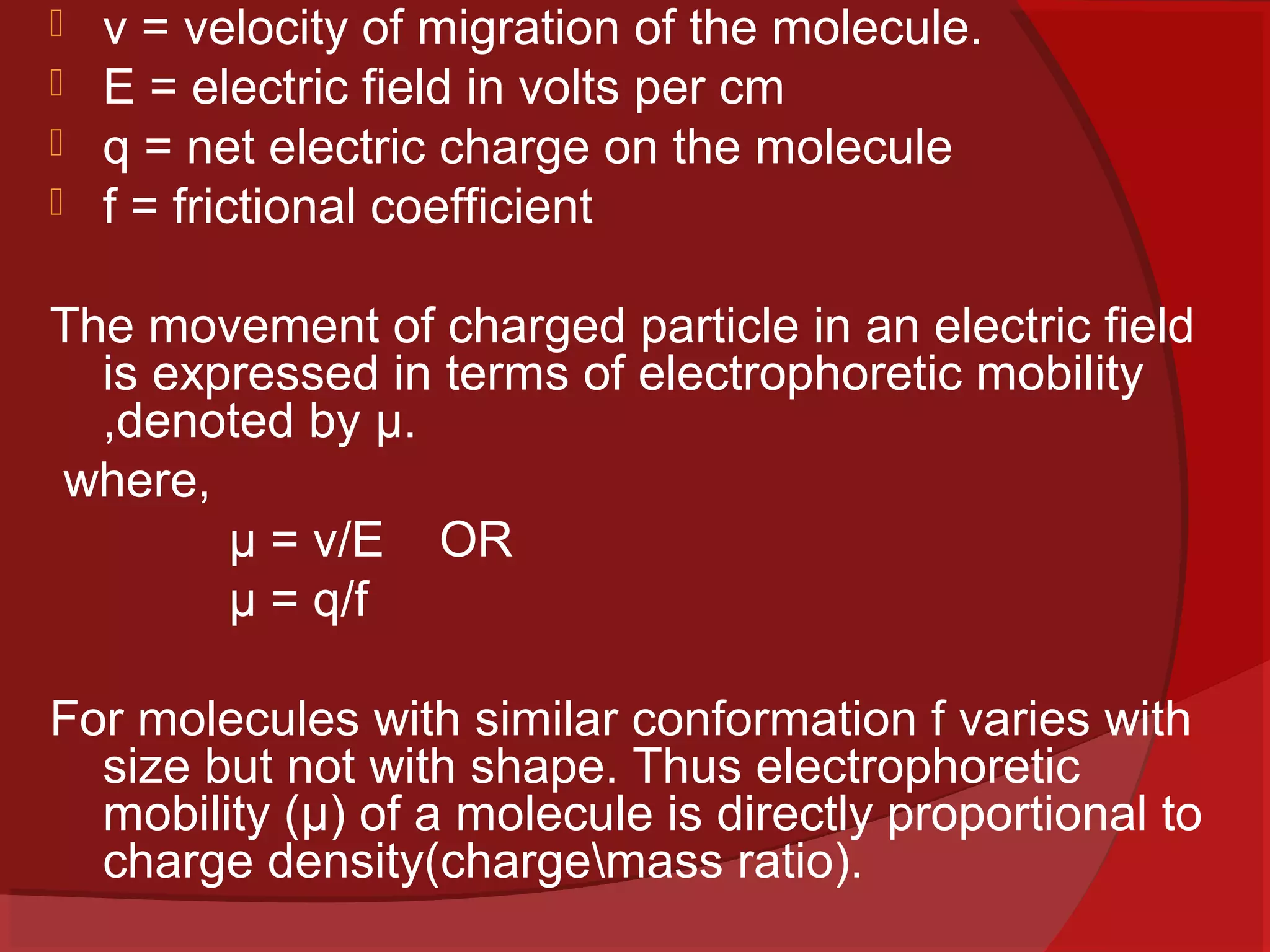
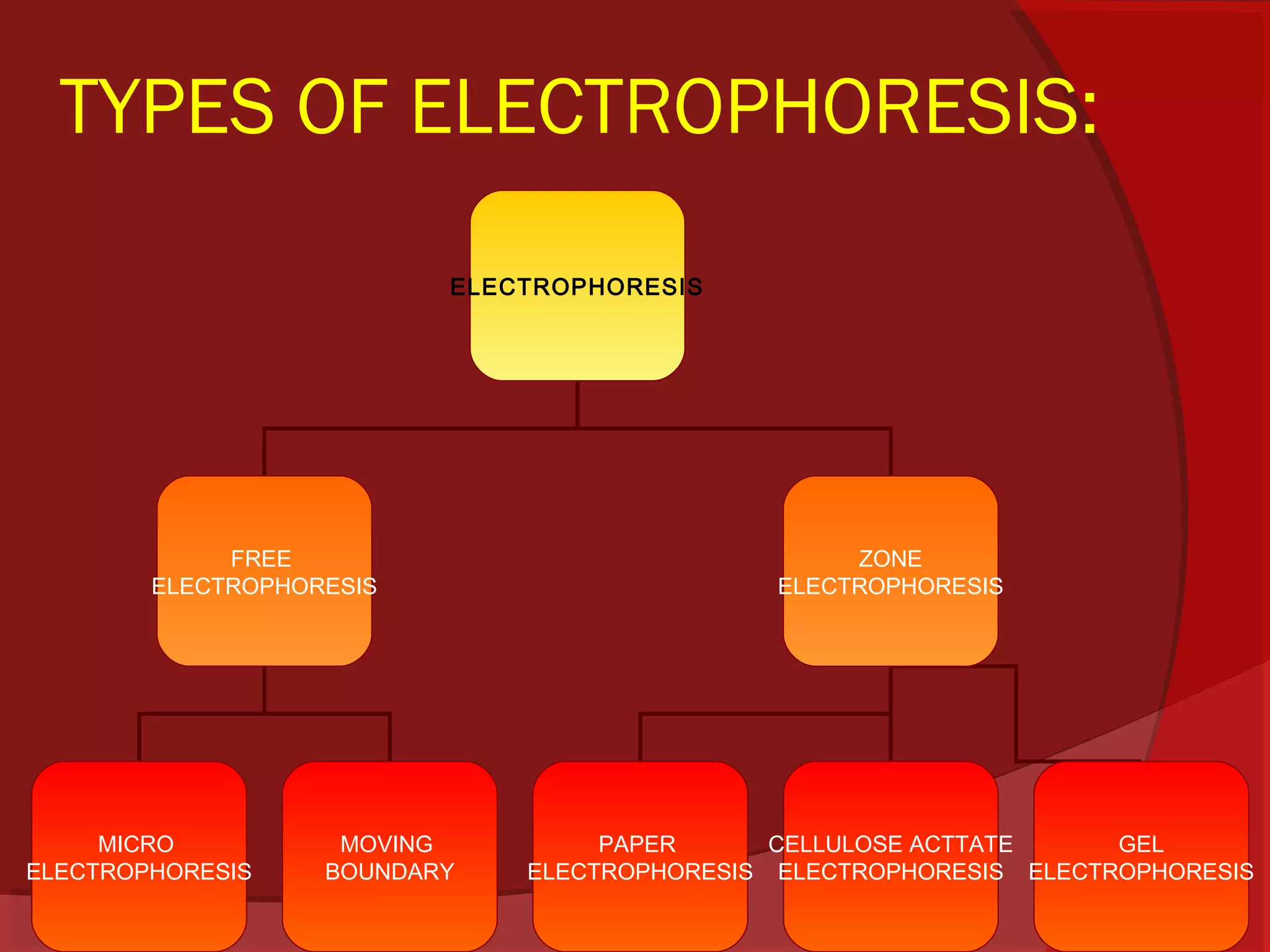
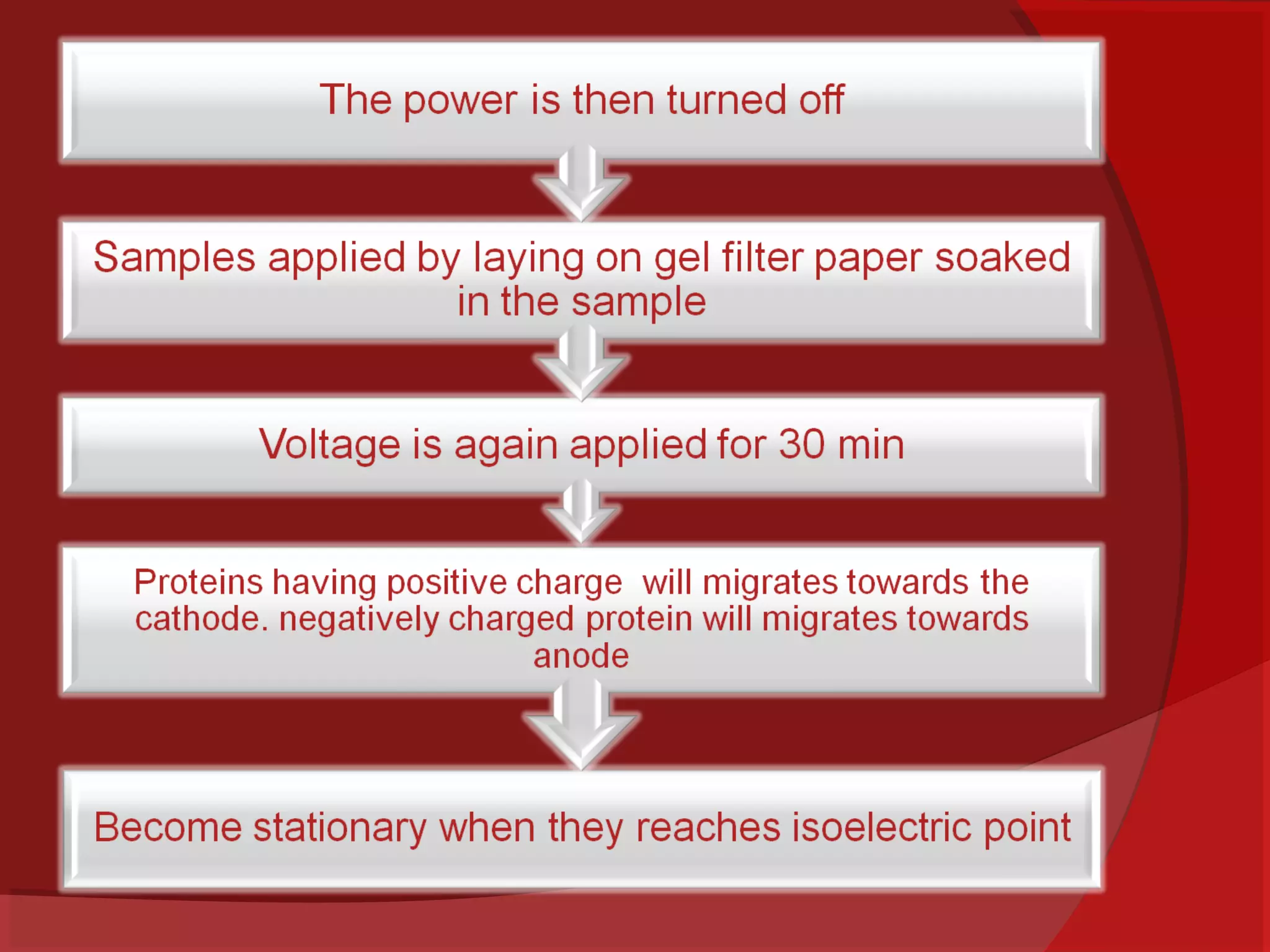
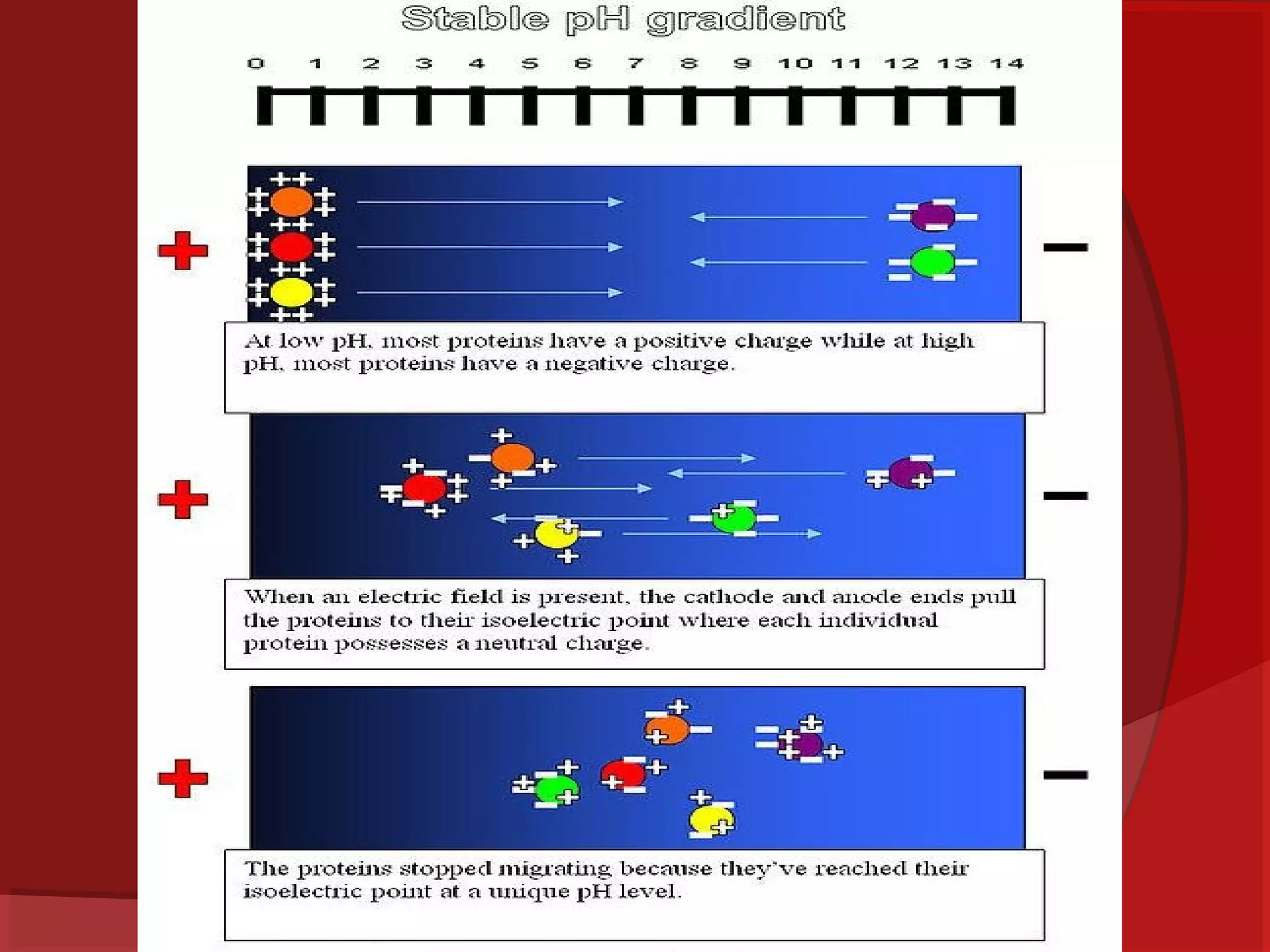
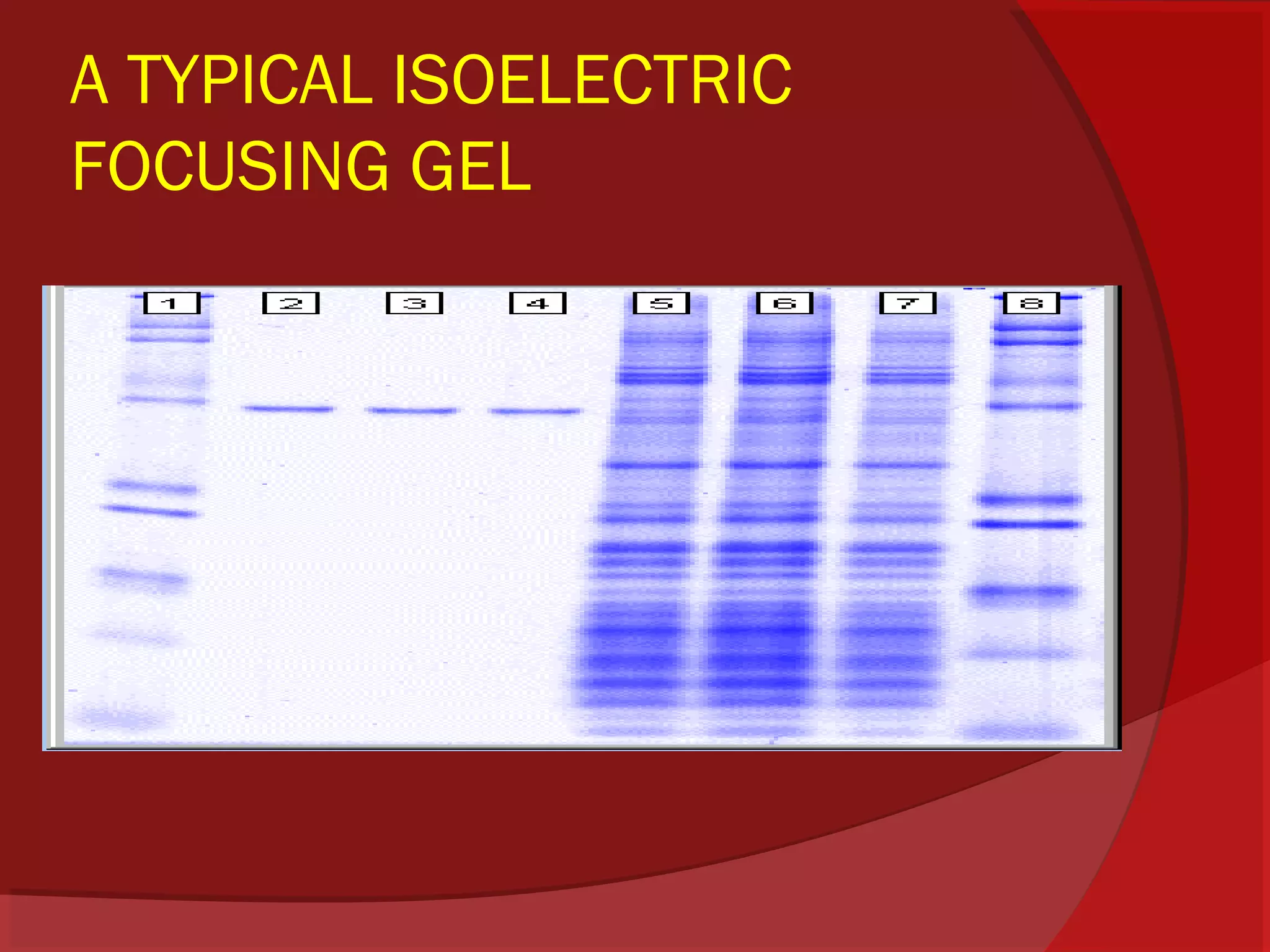
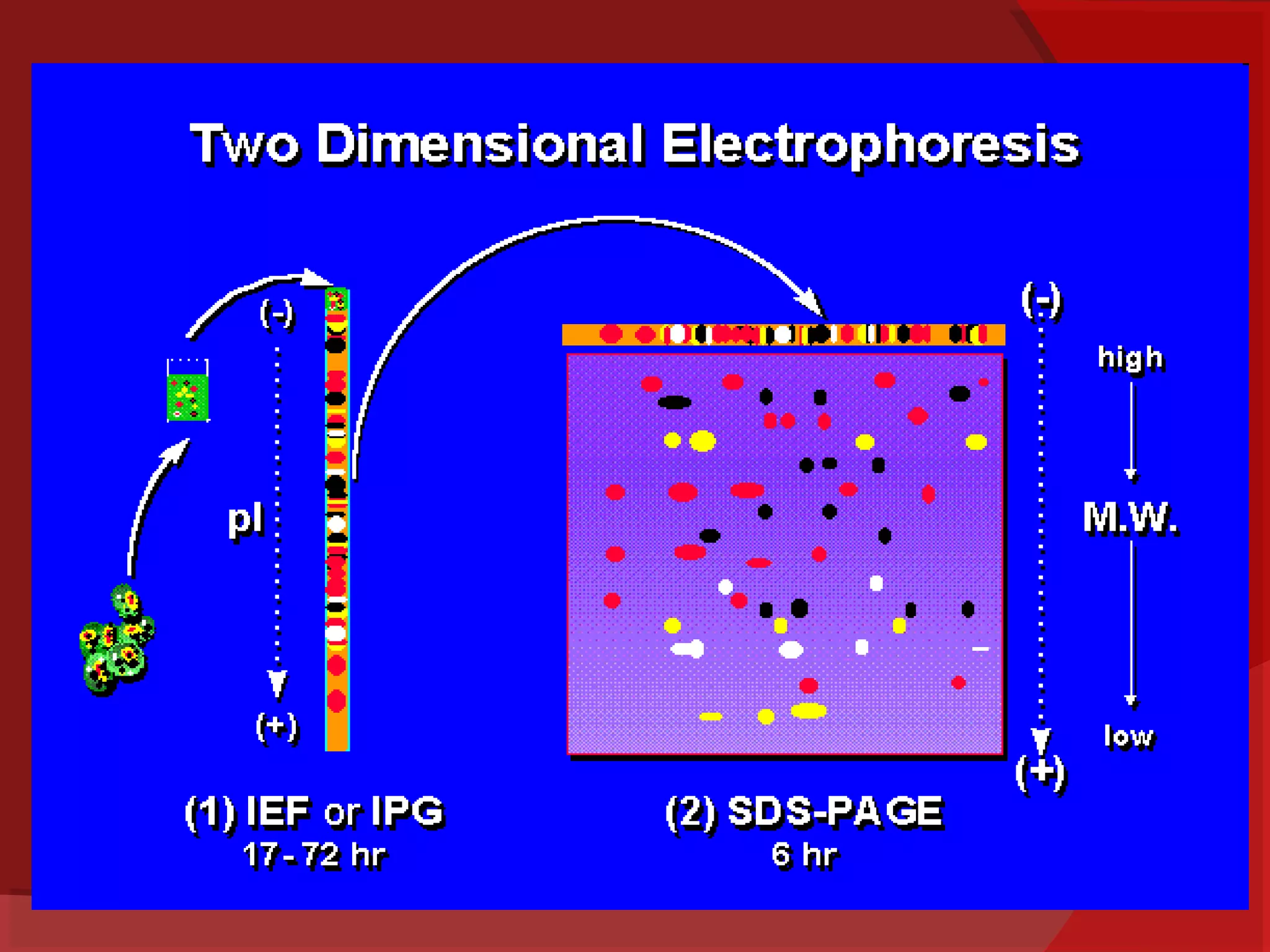
This document provides information about electrophoresis. It begins by defining electrophoresis as the migration of charged particles or molecules under the influence of an electric field. Some purposes of electrophoresis are to determine components in a sample, separate them, and obtain information about electrical double layers or determine molecular weights. The principle described is that charged particles migrate in an electric field at a velocity depending on factors like charge, size, shape and applied current. Different types of electrophoresis are described like paper, gel, and isolectric focusing electrophoresis. Key aspects of each technique including apparatus, sample application, detection, and preparation of gels are explained. Two-dimensional electrophoresis combining isolectric focusing and SDS-PAGE is also summarized.