Embed presentation
Downloaded 30 times

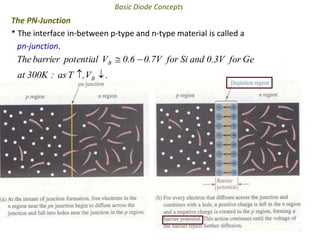
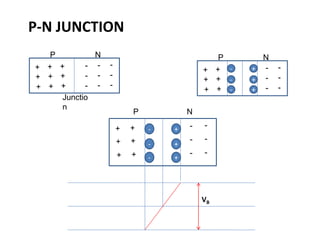
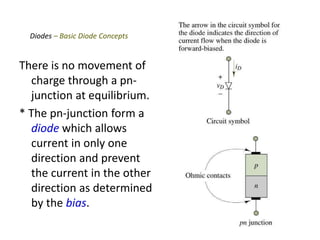
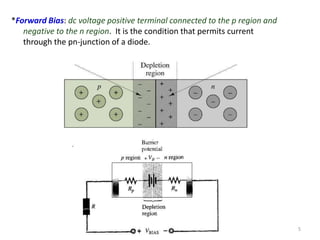
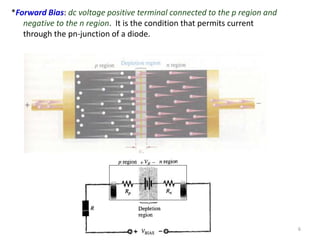
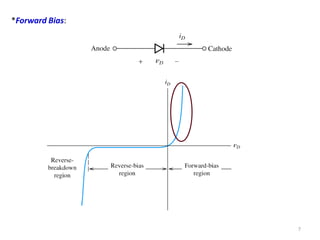
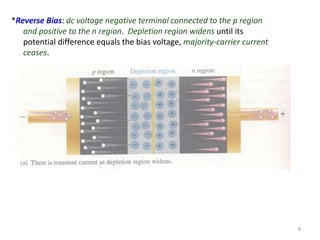
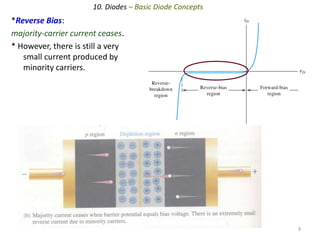
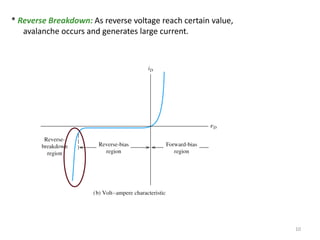
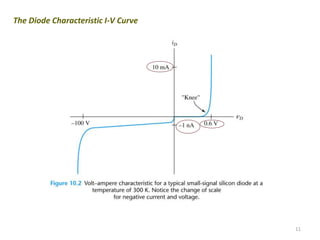
The document discusses the basics of a PN junction and diode. A PN junction forms at the interface between P-type and N-type semiconductor materials. This junction acts as a diode that allows current to flow easily in one direction, but restricts it in the reverse direction. Forward bias occurs when the positive terminal is connected to the P region and negative to the N region, allowing current flow. Reverse bias widens the depletion region until the potential stops majority carrier current, while a very small minority carrier current still flows.










