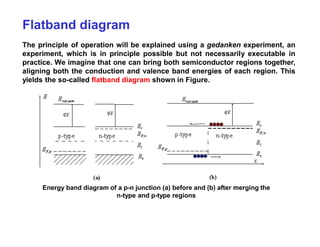
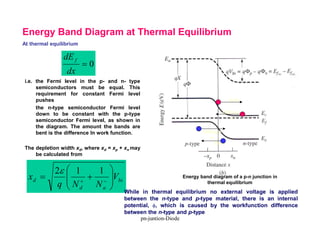
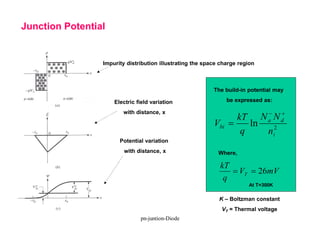
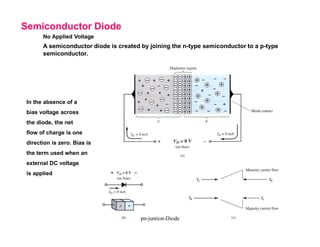
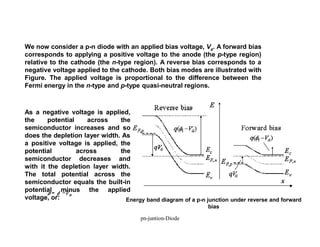
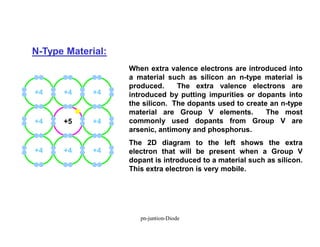
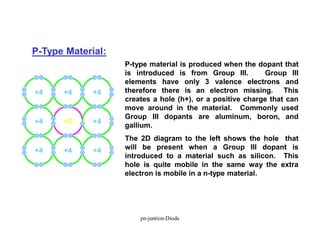
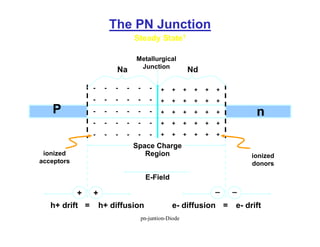
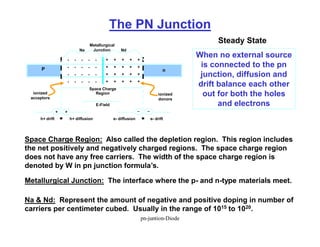
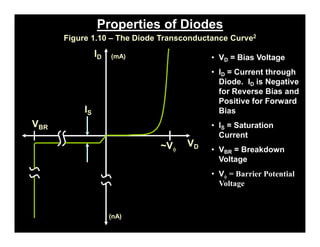
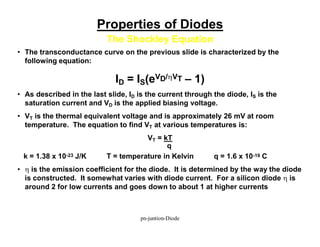
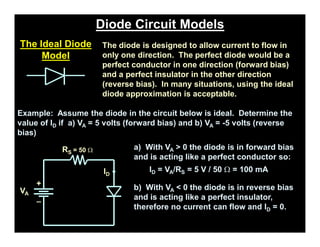
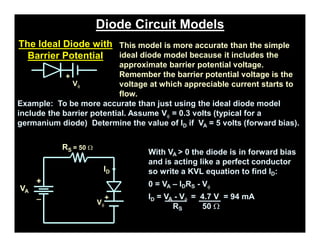
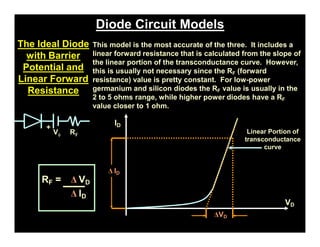
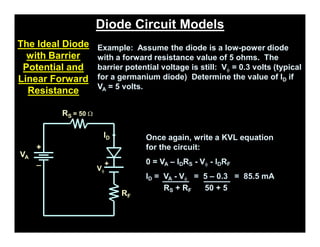
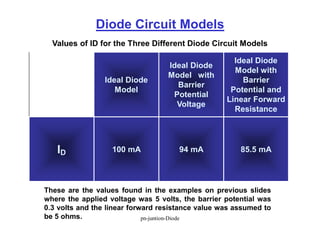
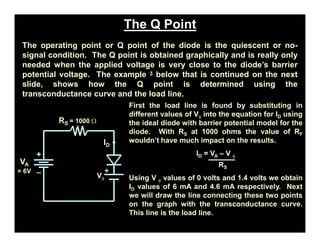
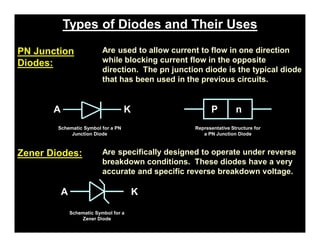
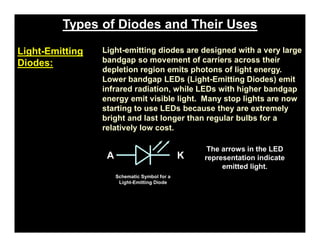
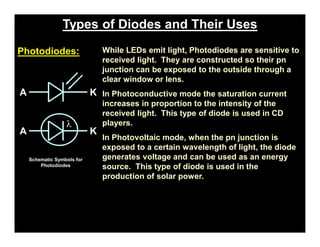
A p-n junction diode consists of a p-type semiconductor joined to an n-type semiconductor. When the two materials are joined, charge carriers diffuse across the junction leaving a depletion region devoid of free carriers. This creates a built-in electric field.
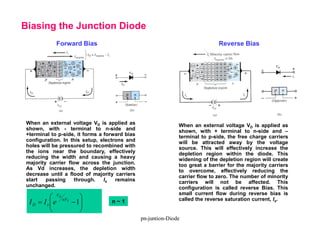
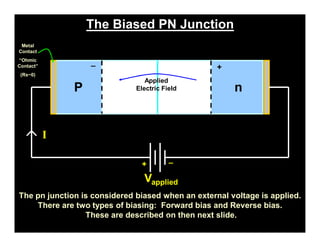
When a p-n junction diode is forward biased, the depletion region narrows allowing majority carriers to flow more easily across the junction. When reverse biased, the depletion region widens blocking the flow of majority carriers and only allowing a small leakage current of minority carriers.
P-n junction diodes have applications as rectifiers, solar cells, LEDs, and are components of other semiconductor devices like transistors. The behavior of diodes is modeled by the