This document discusses the characteristics and operation of a PN diode. It describes:
1) How a PN diode is formed by joining P-type and N-type materials, and the three biasing possibilities: no bias, forward bias, and reverse bias.
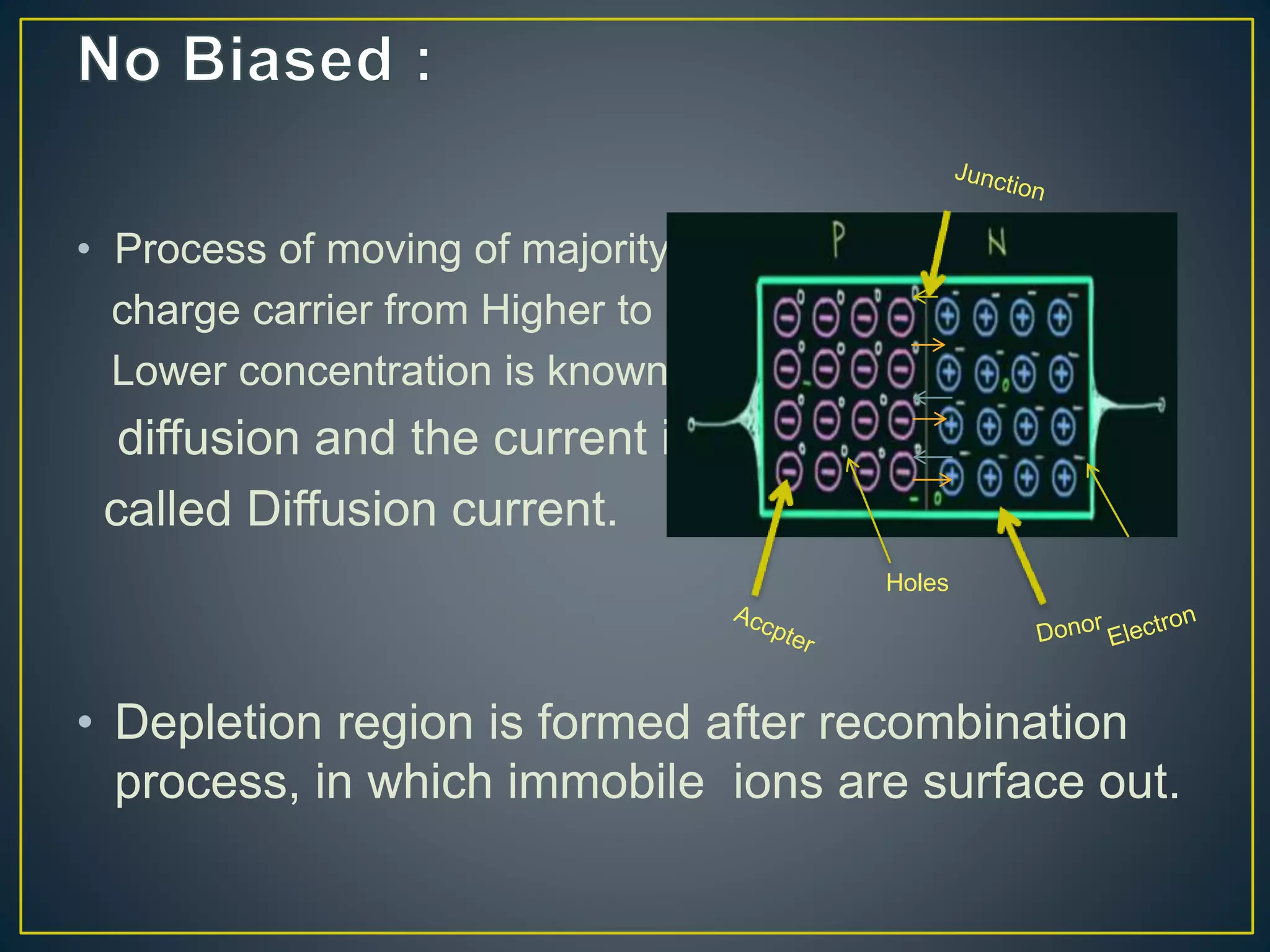
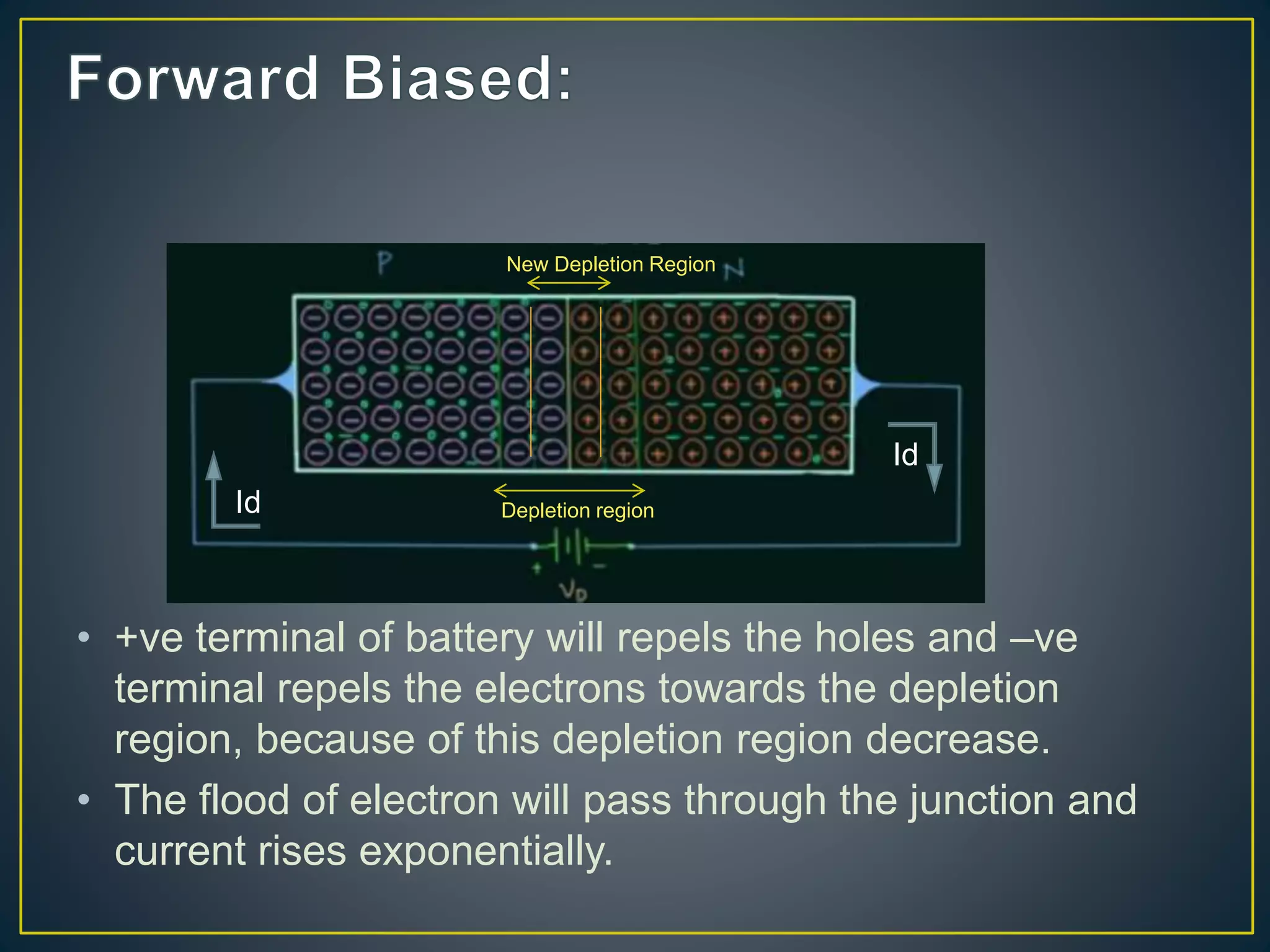
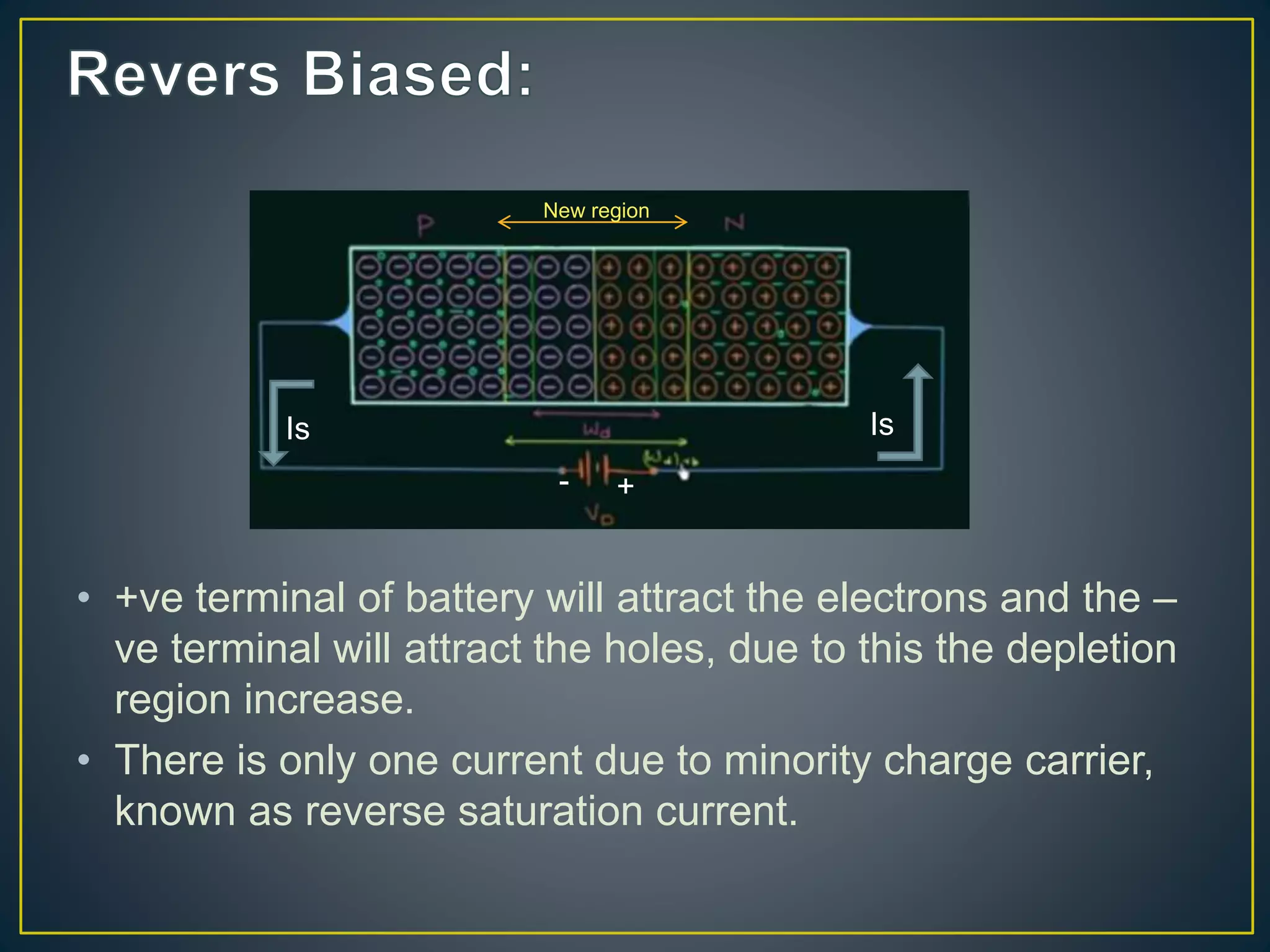
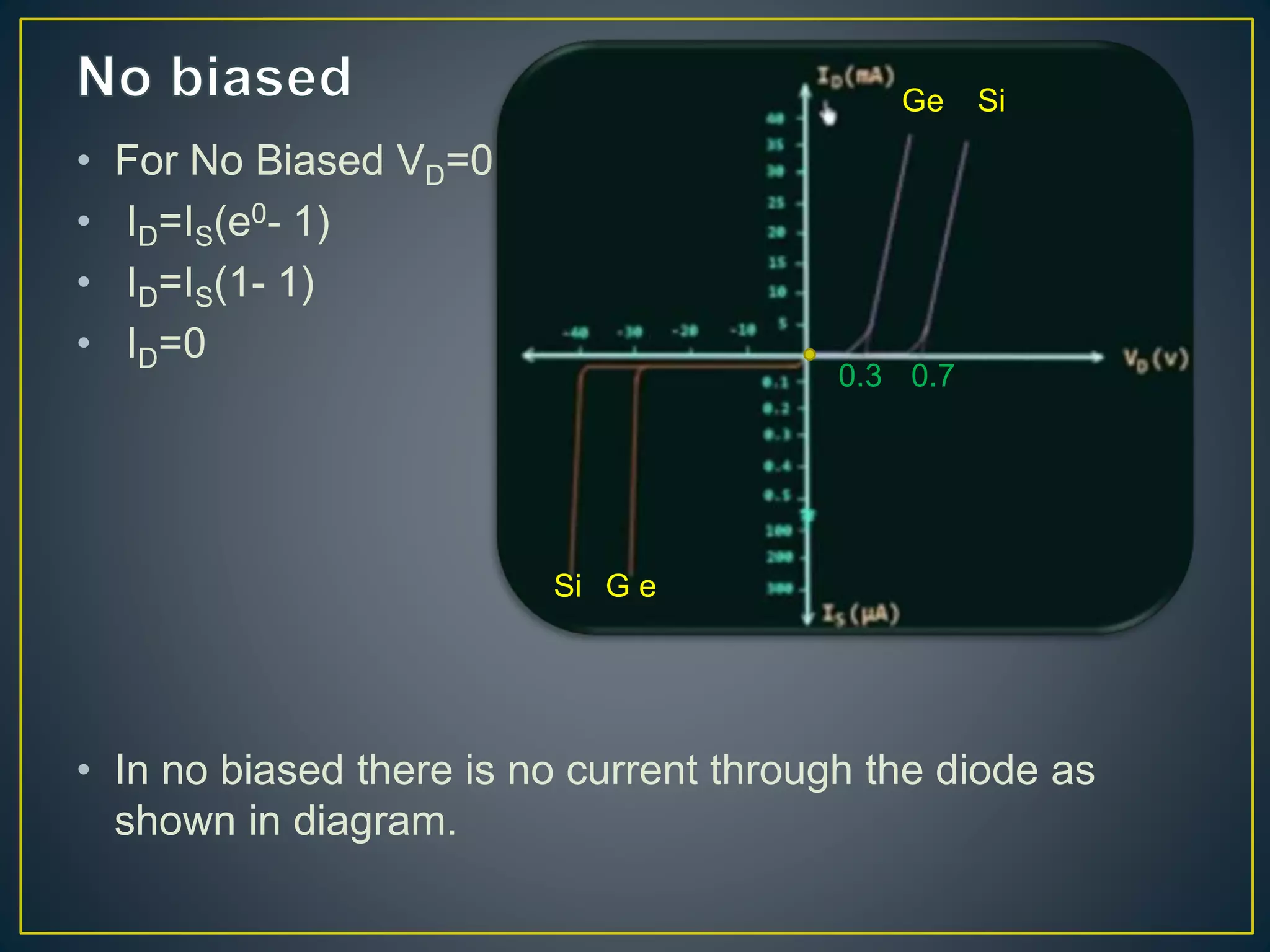
2) Under no bias, there is no current flow. Under forward bias, the depletion region decreases and current rises exponentially. Under reverse bias, there is only a small reverse saturation current.
3) The diode current-voltage relationship and how it changes under different biasing conditions. Forward bias leads to an exponential rise in current above the potential barrier voltage.