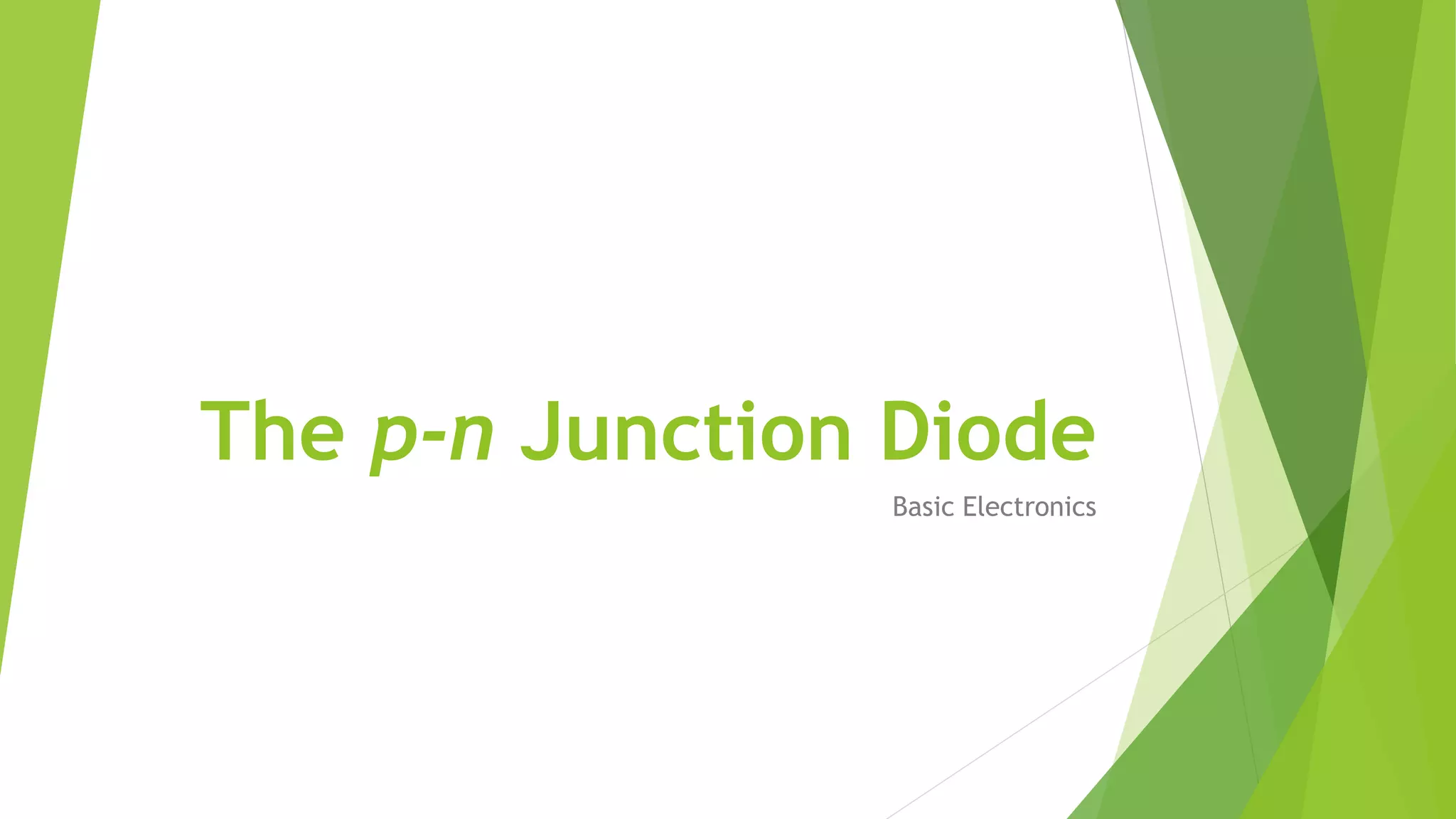
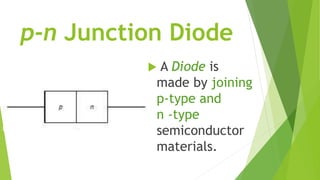
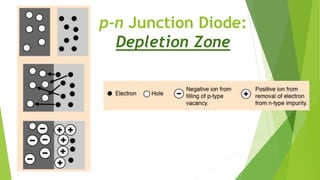
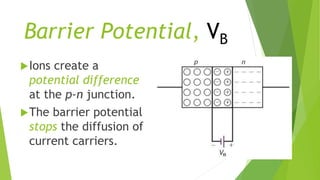
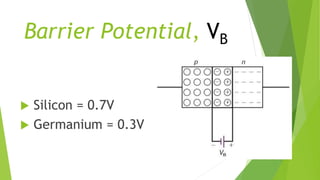
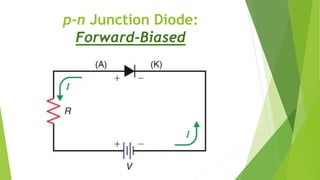
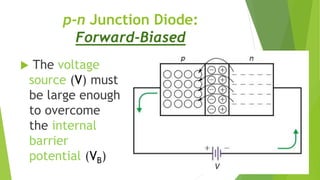
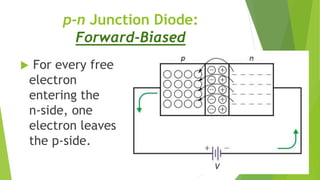
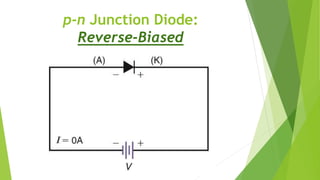
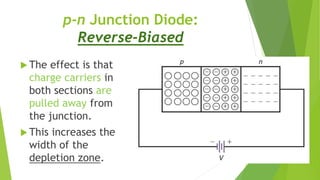
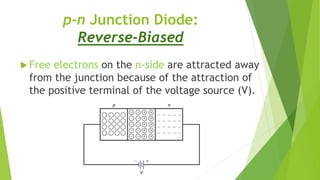
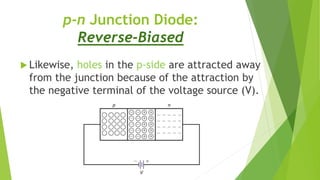
The document discusses the basics of a p-n junction diode. It explains that a diode is made by joining p-type and n-type semiconductor materials, forming a depletion zone at the junction. Current can only flow from the p-side (anode) to the n-side (cathode). Applying a forward bias lowers the potential barrier, allowing current to flow. A reverse bias widens the depletion zone, preventing current from flowing.