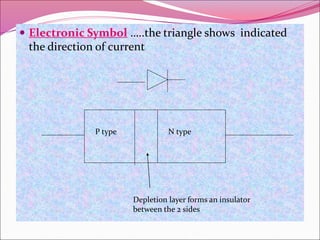
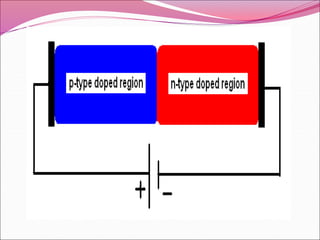
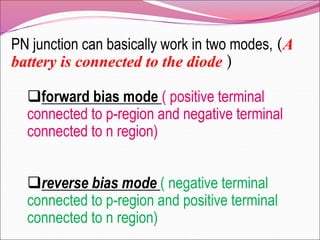
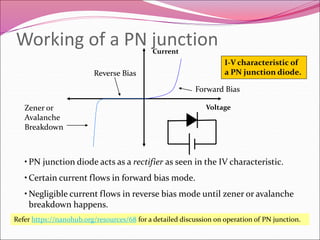
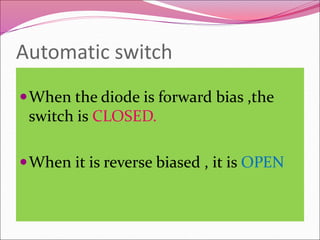
A PN junction is formed by joining a P-type semiconductor with an N-type semiconductor. When joined, majority charge carriers diffuse across the junction, creating a depletion layer empty of mobile charges. This layer acts as an insulator. When forward biased, the depletion layer narrows, allowing current to flow. When reverse biased, the layer widens, blocking nearly all current flow. The I-V characteristic of a PN junction diode shows it acts as a rectifier, allowing current in only one direction. Diodes have applications in rectification, switching, and light emission.