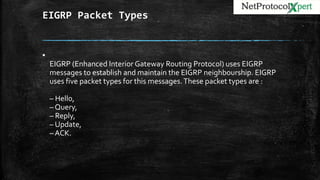
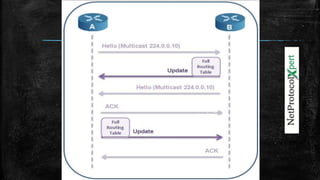
EIGRP is a proprietary routing protocol developed by Cisco that uses a composite metric and has fast convergence properties. It functions as a hybrid of distance-vector and link-state routing protocols, sending subnet mask and VLSM information in updates. EIGRP forms neighbor relationships through periodic hello messages and establishes three key tables - Neighbor, Topology, and Routing - to store neighbor, route, and best path information. It utilizes five packet types and reliable transport to efficiently share routing updates.







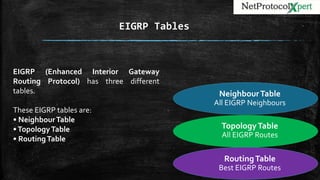



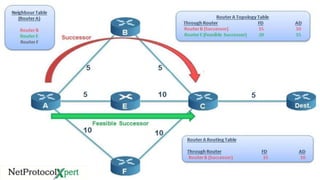
![▪ Routing Table is the table which keeps the Best Routes to any destinations.This Best Routes are
Successors
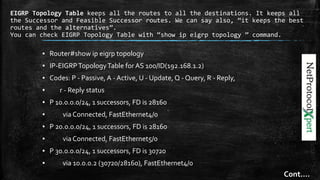
▪ You can see the RoutingTable with “show ip route eigrp” command.
▪ An example output of “show ip route eigrp” command is given below:
▪ Router#show ip route Eigrp
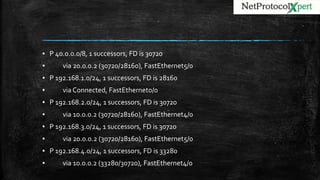
▪ 30.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
▪ D 30.0.0.0 [90/30720] via 10.0.0.2, 00:04:28, FastEthernet4/0
▪ D 40.0.0.0/8 [90/30720] via 20.0.0.2, 00:04:28, FastEthernet5/0
▪ D 192.168.2.0/24 [90/30720] via 10.0.0.2, 00:04:28, FastEthernet4/0
▪ D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/30720] via 20.0.0.2, 00:04:28, FastEthernet5/0
▪ D 192.168.4.0/24 [90/33280] via 10.0.0.2, 00:04:28, FastEthernet4/0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eigrp-161021041838/85/EIGRP-Enhanced-Interior-Gateway-Routing-Protocol-14-320.jpg)