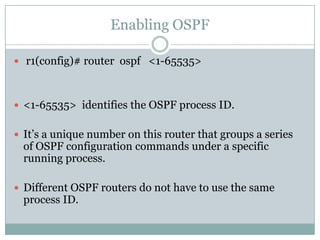
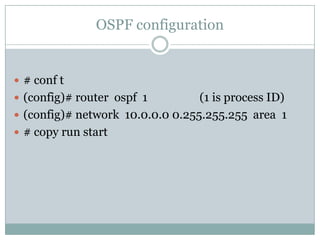
EIGRP and OSPF are hybrid and link-state routing protocols respectively. EIGRP uses the DUAL algorithm and metric system to determine the best paths, while OSPF uses the Dijkstra algorithm and link state advertisements. Both protocols form neighbor relationships to exchange routing information, but OSPF requires adjacencies and is more restrictive in sharing routes between areas.