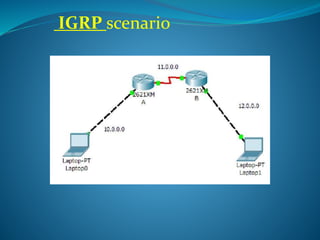
IGRP (Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) is a Cisco proprietary distance vector protocol that improves upon RIP by allowing a maximum hop count of 100, addressing the limitation of 15 hops in RIP. It utilizes four timers to regulate performance, including a 90-second route update timer and a 230-second route invalid timer. IGRP focuses on metrics such as bandwidth, load, delay, reliability, and MTU to determine the best routing paths, and it is configured by specifying directly connected networks.