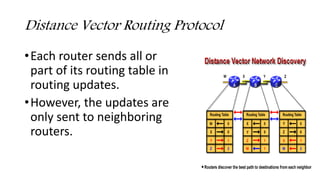
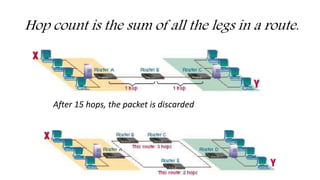
RIP is an interior gateway protocol that employs distance-vector routing and uses hop count as its routing metric. It works by periodically sharing full routing tables between neighboring routers to detect changes in network reachability. The maximum number of hops allowed in the RIP protocol is 15, which limits the size of networks it can support. There are two versions of RIP - version 1 lacks support for VLSM and authentication, while version 2 adds these features and multicasts updates. RIP has limitations such as slow convergence, count to infinity problems, and an inability to support networks larger than 15 hops without extensions.