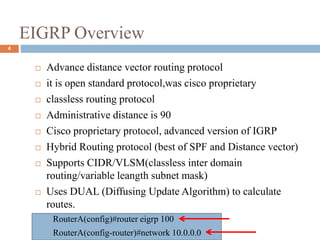
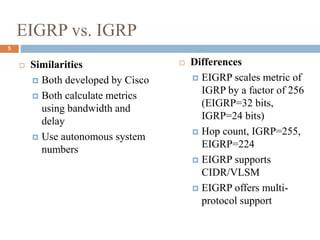
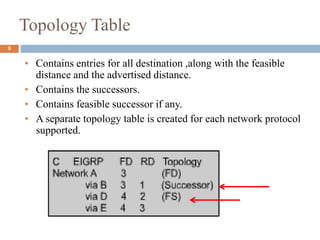
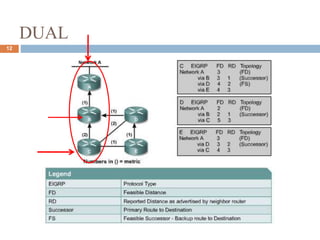
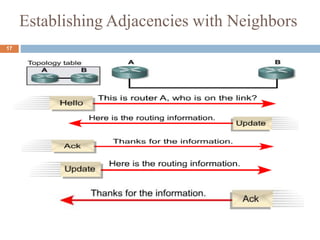
This presentation by Nutan Singh discusses Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), detailing its features, functionalities, and comparisons with IGRP. EIGRP is an advanced, classless, hybrid routing protocol that utilizes a Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) for route calculation and supports multiple protocols. Key advantages include rapid convergence, efficient bandwidth usage, and the ability to support unequal-cost load balancing.











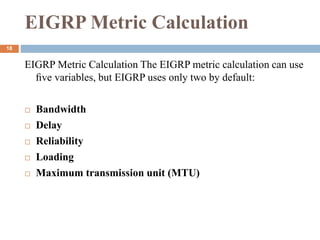
![Metric calculation
metric = (K1 * bandwidth) + [(K2 * bandwidth) / (256 –
load)] + (K3 * delay)
If these K values are equal to their defaults, the formula
becomes
K1=K3=1, K2=K4=K5=0
metric = (1 * bandwidth) + [(0 * bandwidth) / (256 – load)] +
(1 * delay) * [K5 / (reliability + K4)]
metric = bandwidth + [0] + delay
metric = bandwidth + delay
The EIGRP metric value ranges from 1 to 4,294,967,296
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eigrppptnutan-200917095351/85/Enhanced-Interior-Gateway-Routing-Protocol-EIGRP-NETWORK-PROTOCOL-19-320.jpg)







