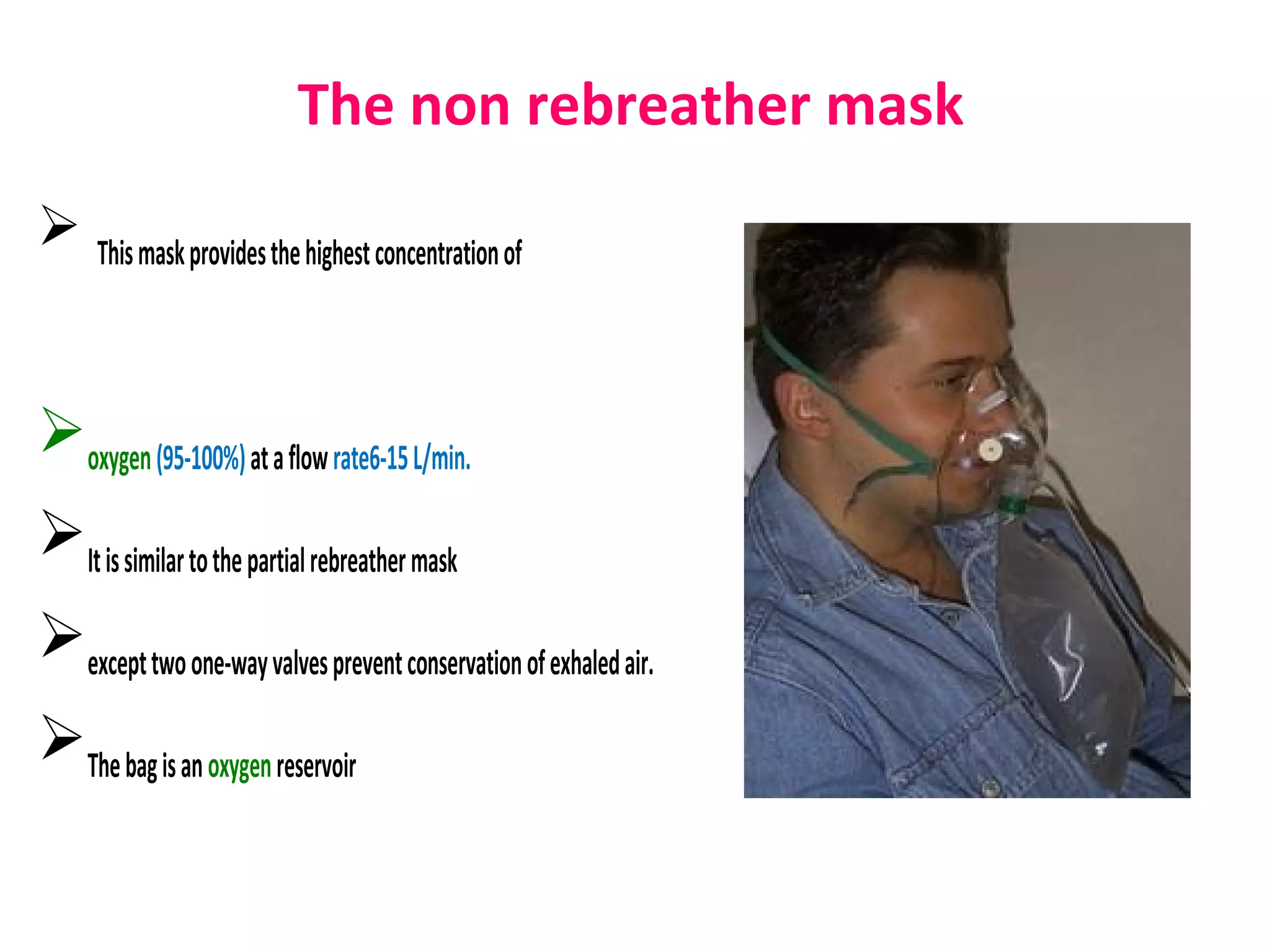
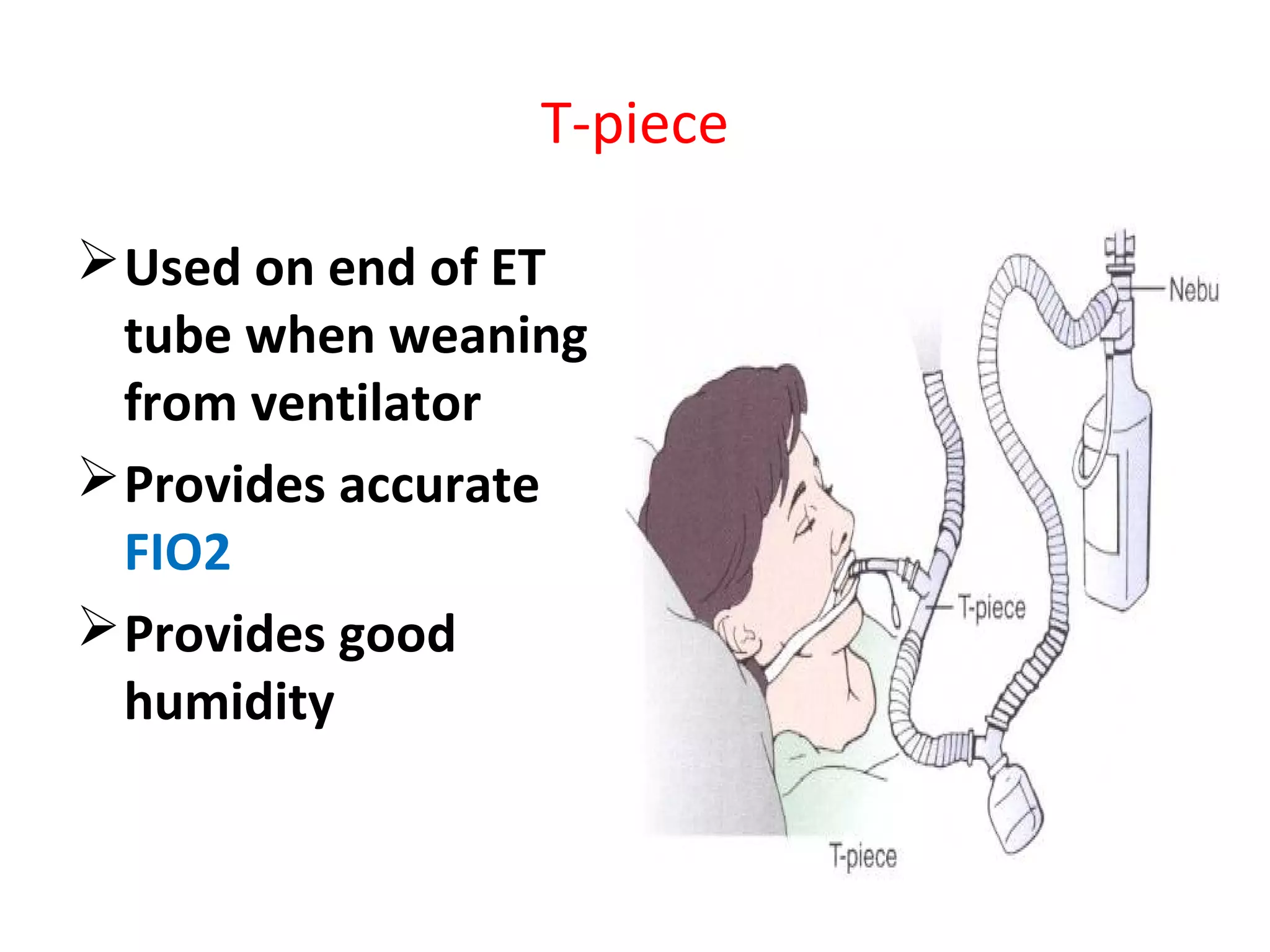
Oxygen therapy involves administering oxygen at concentrations greater than 21% found in air to treat conditions where oxygen levels in the blood are low. It works by increasing oxygen saturation in tissues. Various devices are used including nasal cannulas, face masks, tracheostomy collars, and T-pieces to deliver oxygen concentrations from 24-100% depending on the device. Oxygen therapy treats various respiratory conditions like COPD, heart attacks, and injuries where supplemental oxygen is needed to support tissue function. Side effects from long term high concentration use include cough, nausea, and nasal congestion.