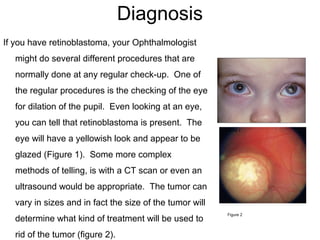
Retinoblastoma was first identified in 1597 from an autopsy finding of a cancerous tumor in a 3-year old's eye. In the 1980s, Dr. Knudson discovered the retinoblastoma gene, the first tumor suppressor gene identified. Retinoblastoma is most common in infants and young children under 6 years old. It is usually caused by a genetic mutation but can occasionally be due to a new mutation. Common signs include poor vision, a white appearance in the eye, crossed eyes, and white spots floating in the pupil. Treatment options include laser therapy, cryotherapy, chemotherapy, or eye removal, with advantages and disadvantages to each approach.