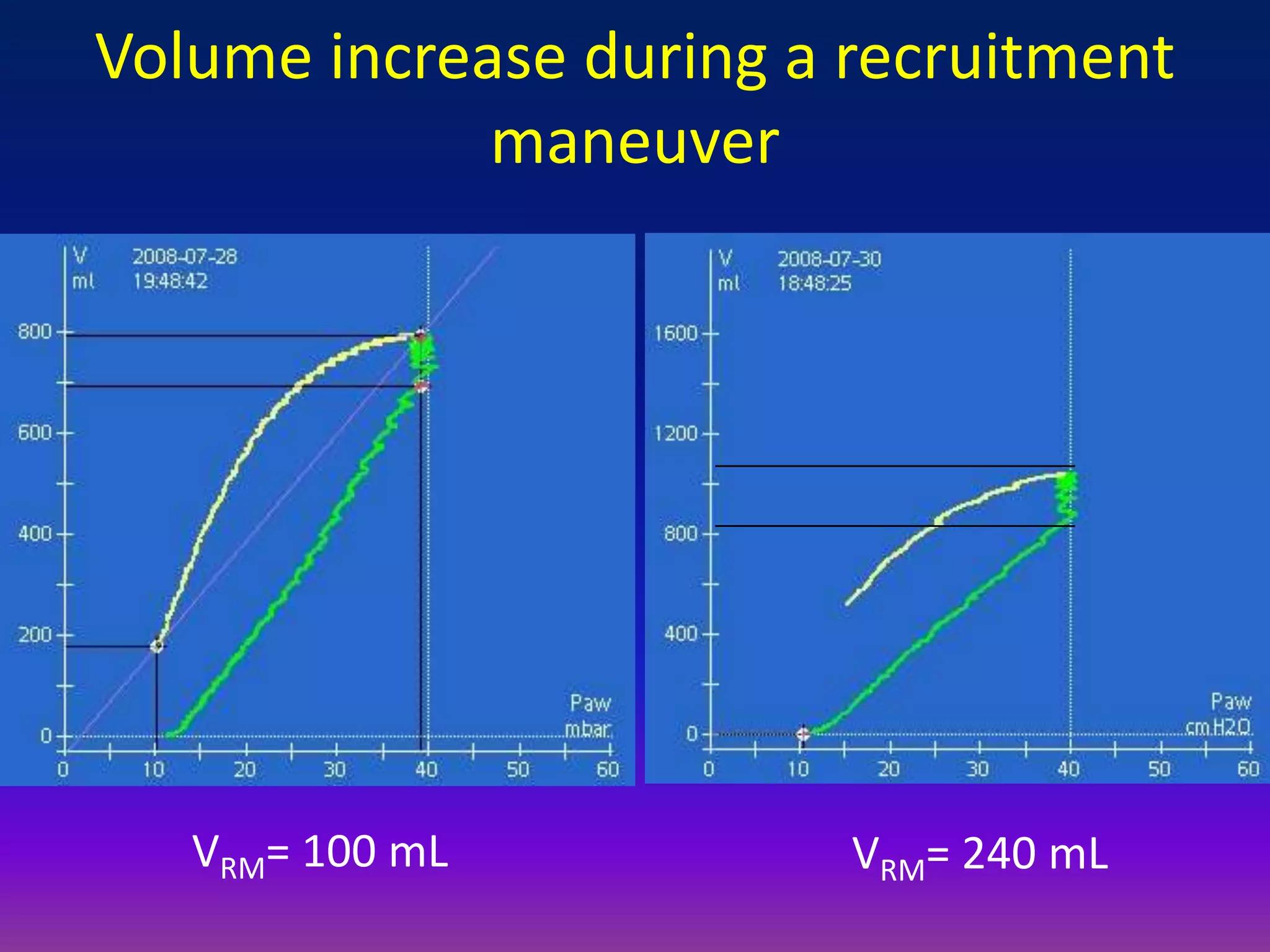
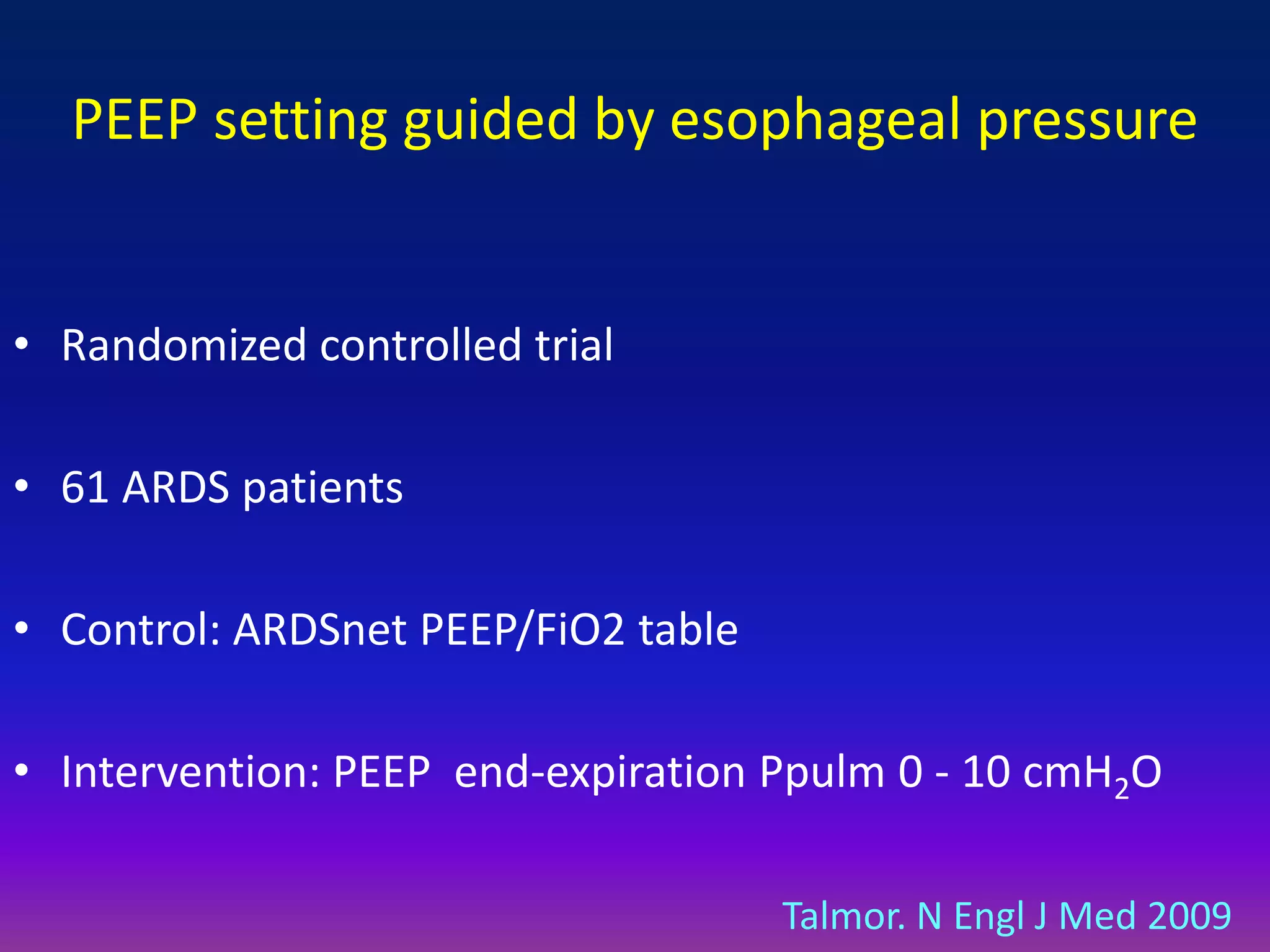
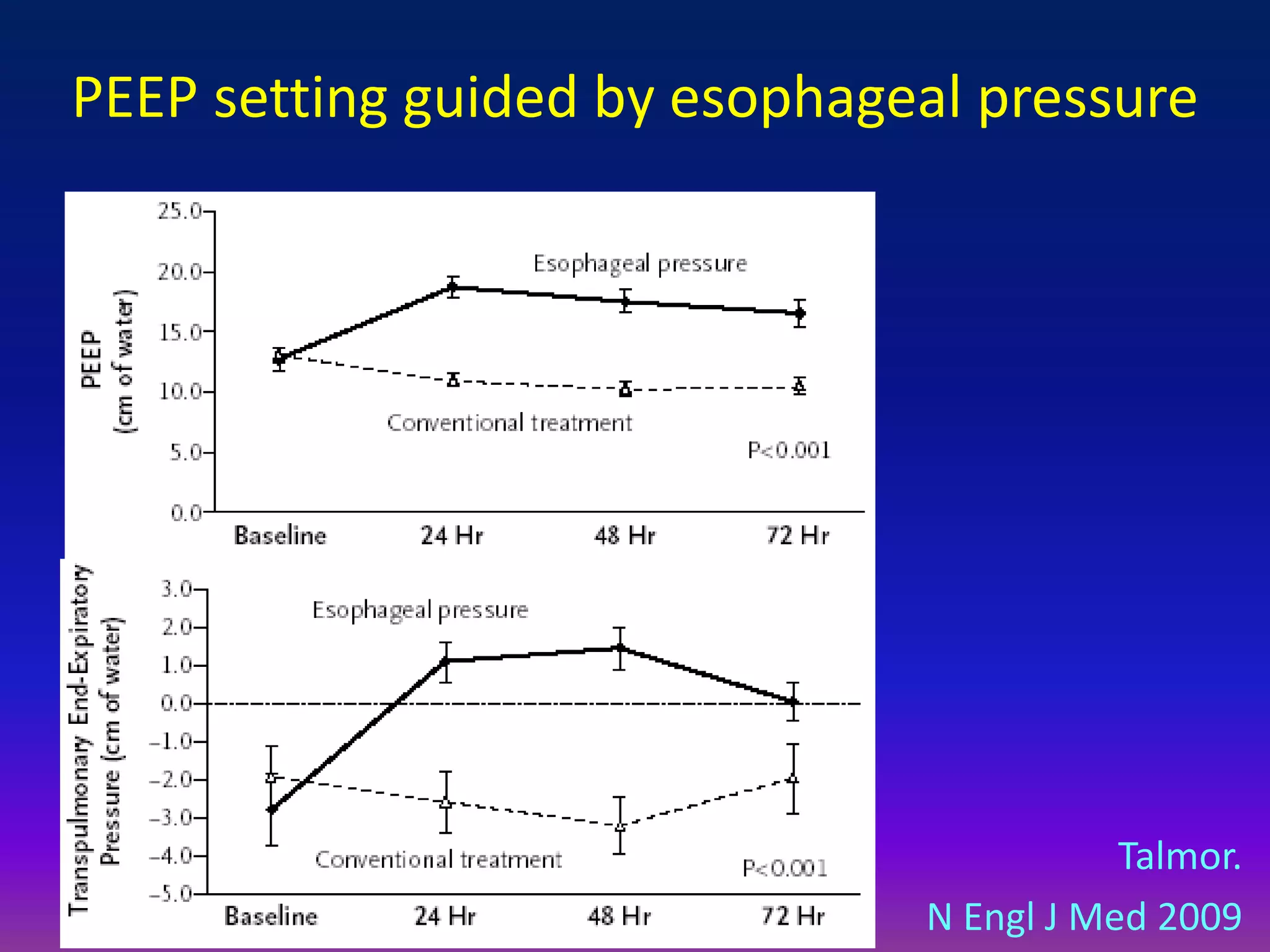
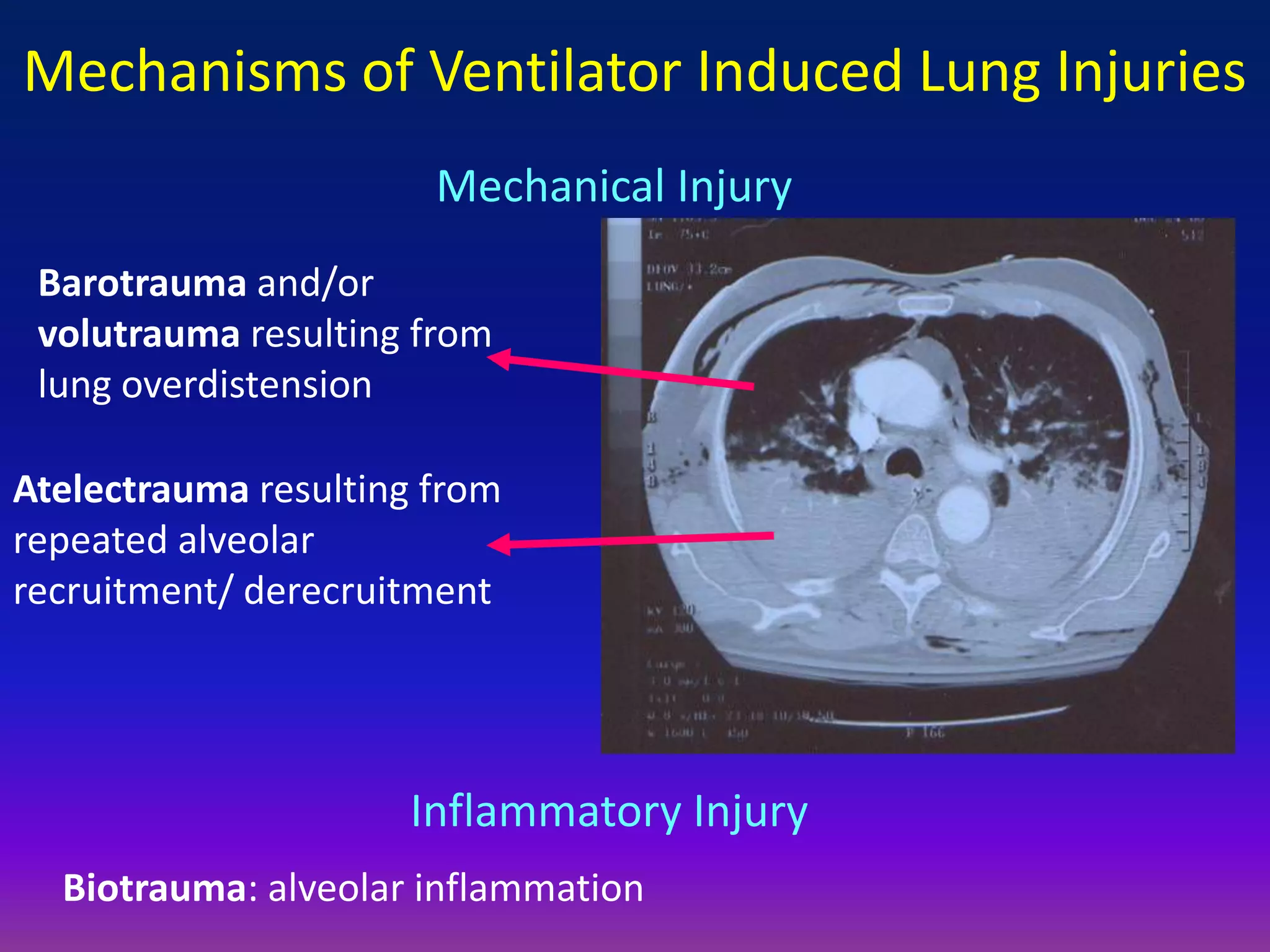
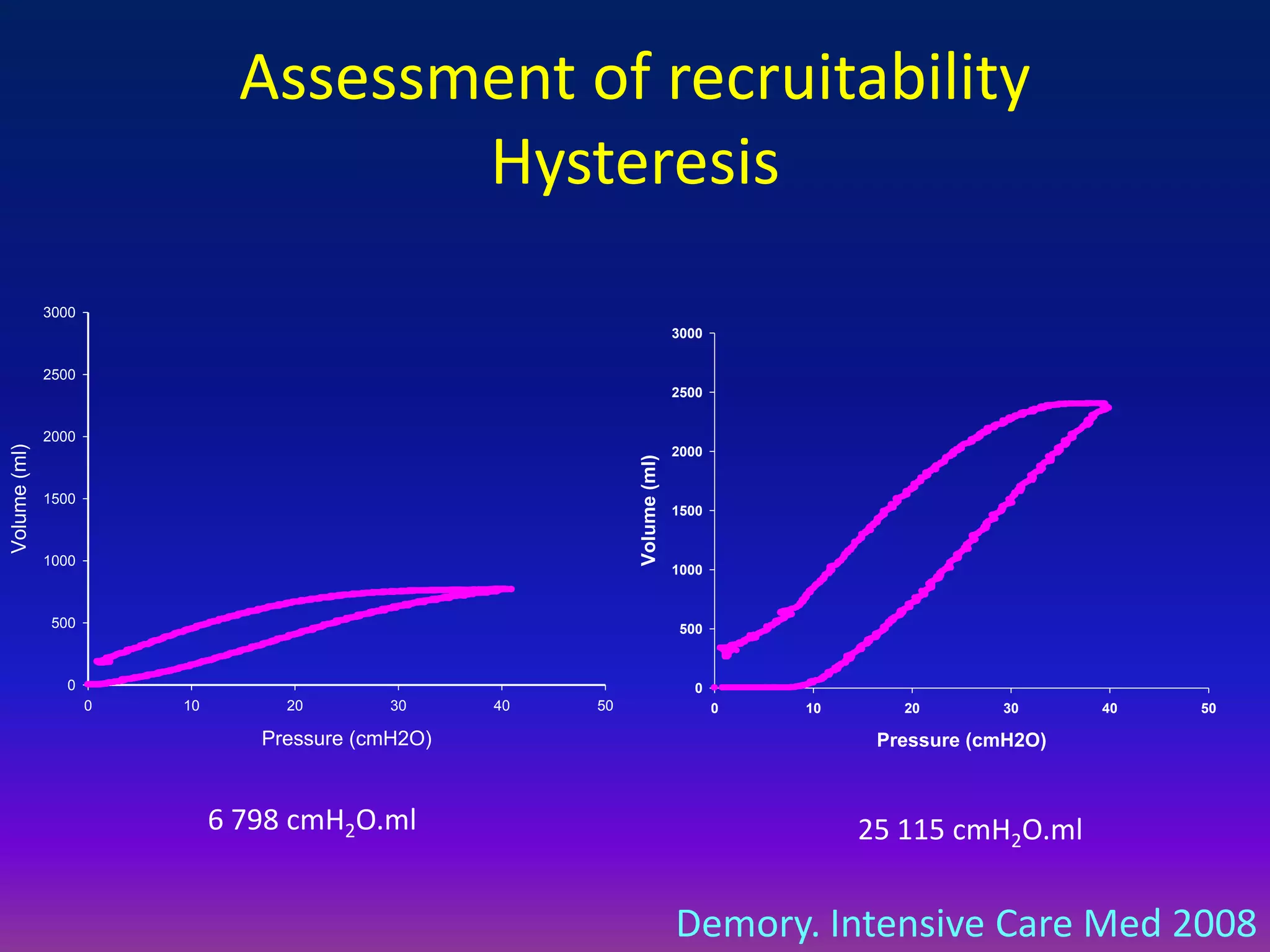
This document discusses pulmonary recruitment in ARDS patients and strategies for lung protection during mechanical ventilation. It describes how recruitment maneuvers using high airway pressures can reopen collapsed alveoli, preventing ventilator-induced lung injury from repeated opening and closing. The optimal settings for recruitment maneuvers and PEEP levels depend on a patient's recruitability, assessed via low-flow pressure-volume curves. PEEP levels are best guided by esophageal manometry or oxygen saturation to maintain alveolar stability and oxygenation without overdistension.




























![Optimal duration of the recruitment maneuver = 2,3 ± 1,3 sn = 50Arnal. Intensive Care Med [submitted]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pvcurveandlungrecruitment-110428091901-phpapp01/75/PV-Curve-and-Lung-Recruitment-31-2048.jpg)
![Optimal duration of the recruitment maneuver**Recruitment maneuvern = 50Arnal. Intensive Care Med [submitted]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pvcurveandlungrecruitment-110428091901-phpapp01/75/PV-Curve-and-Lung-Recruitment-32-2048.jpg)