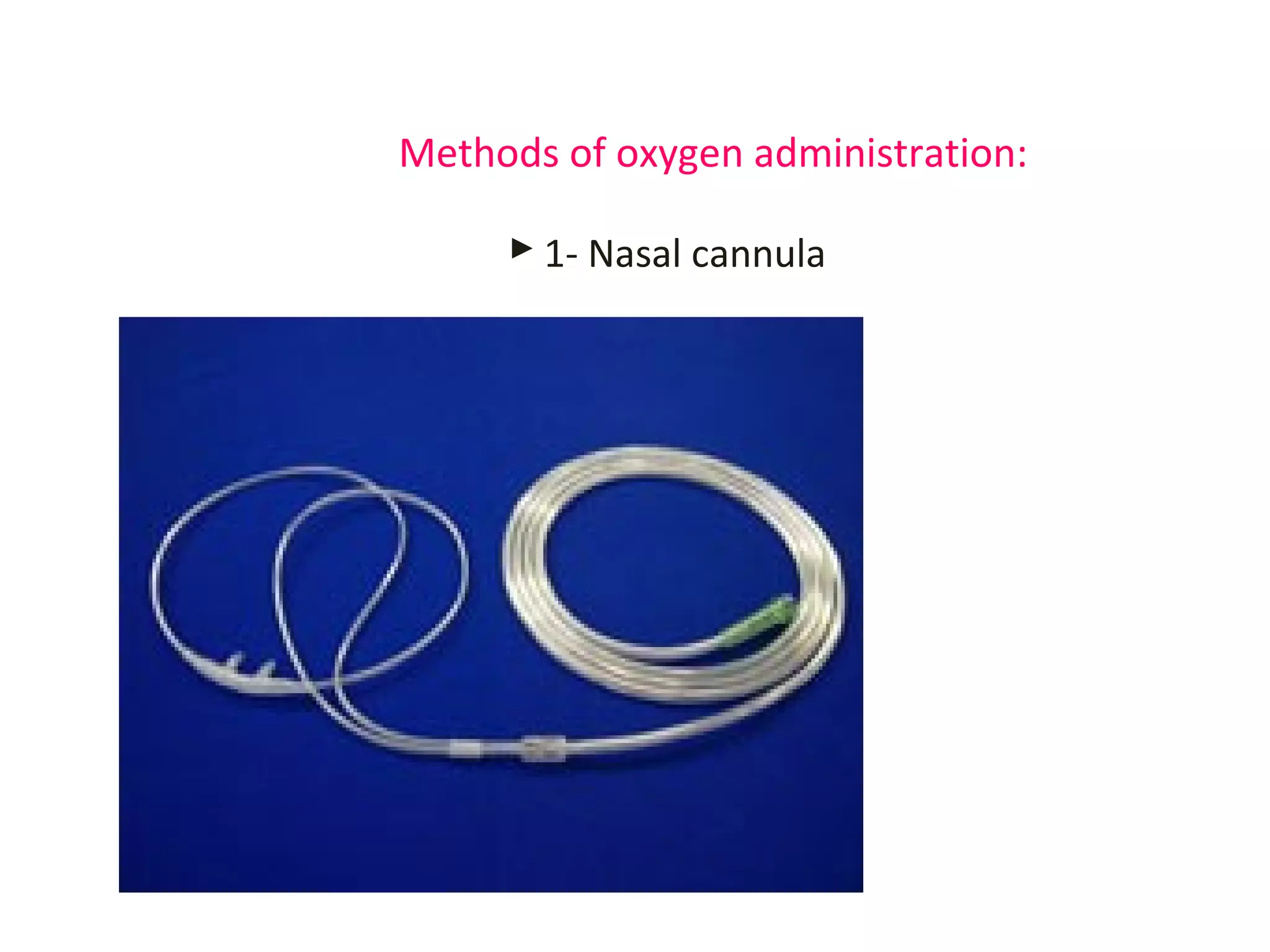
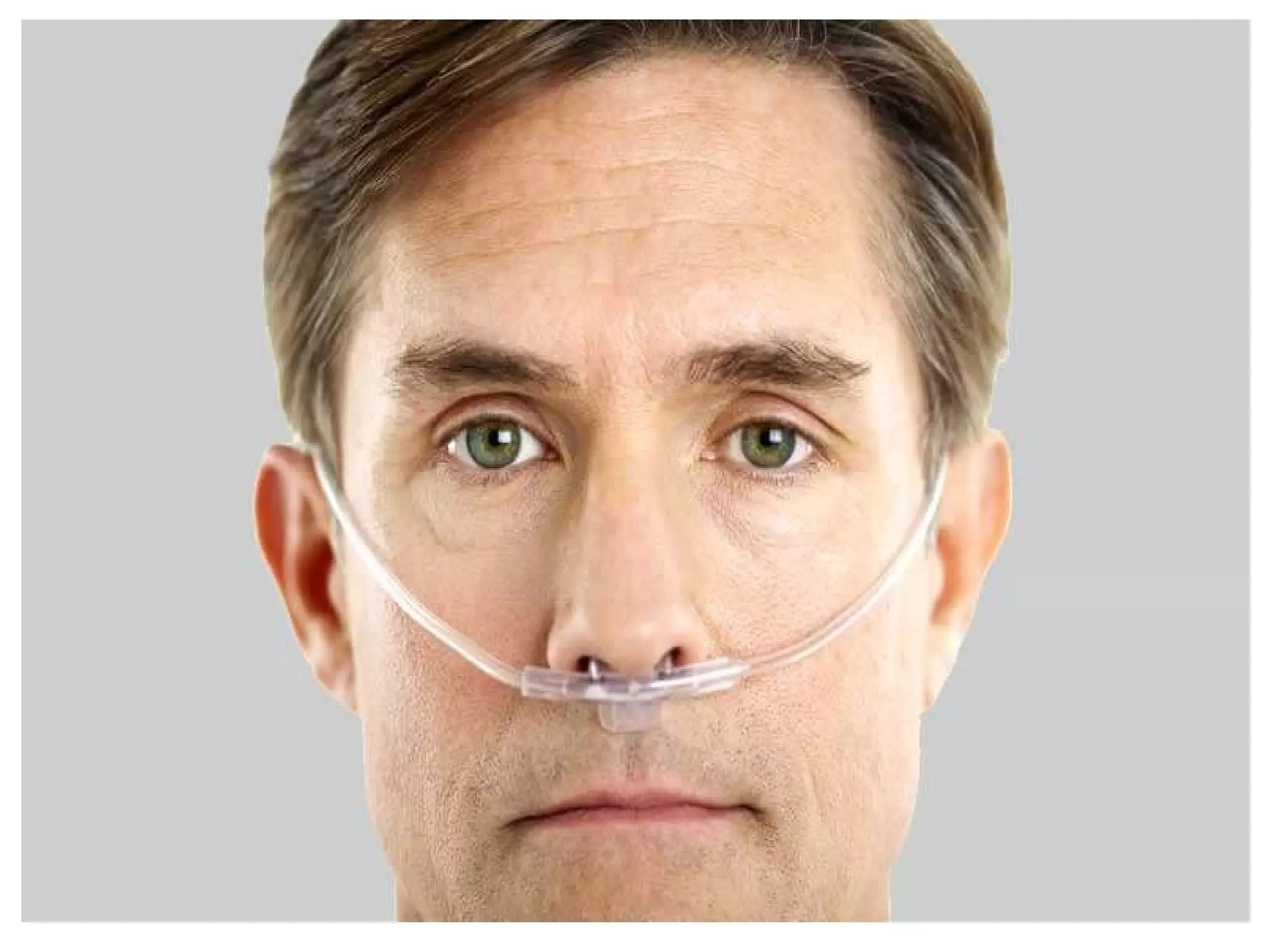
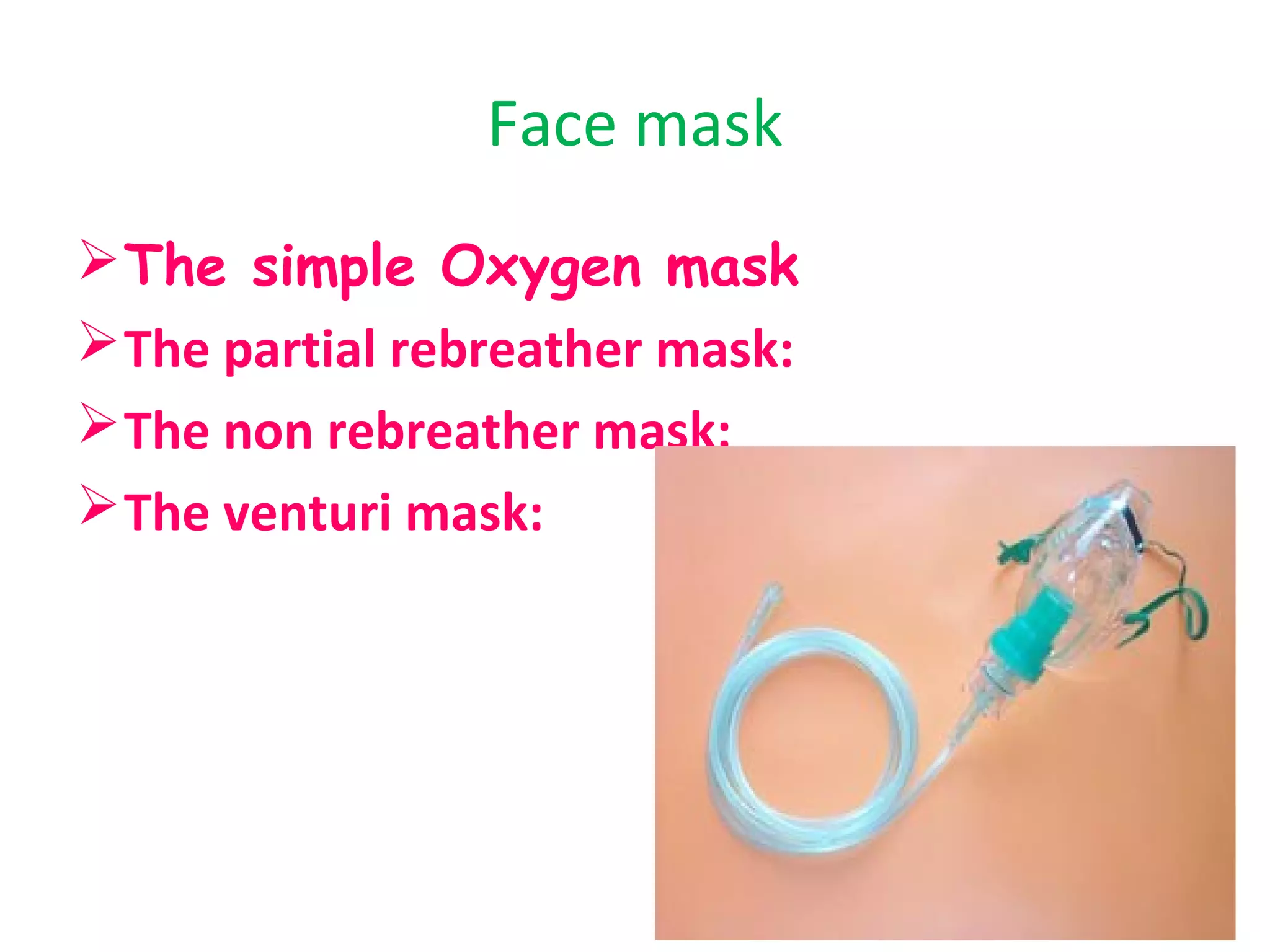
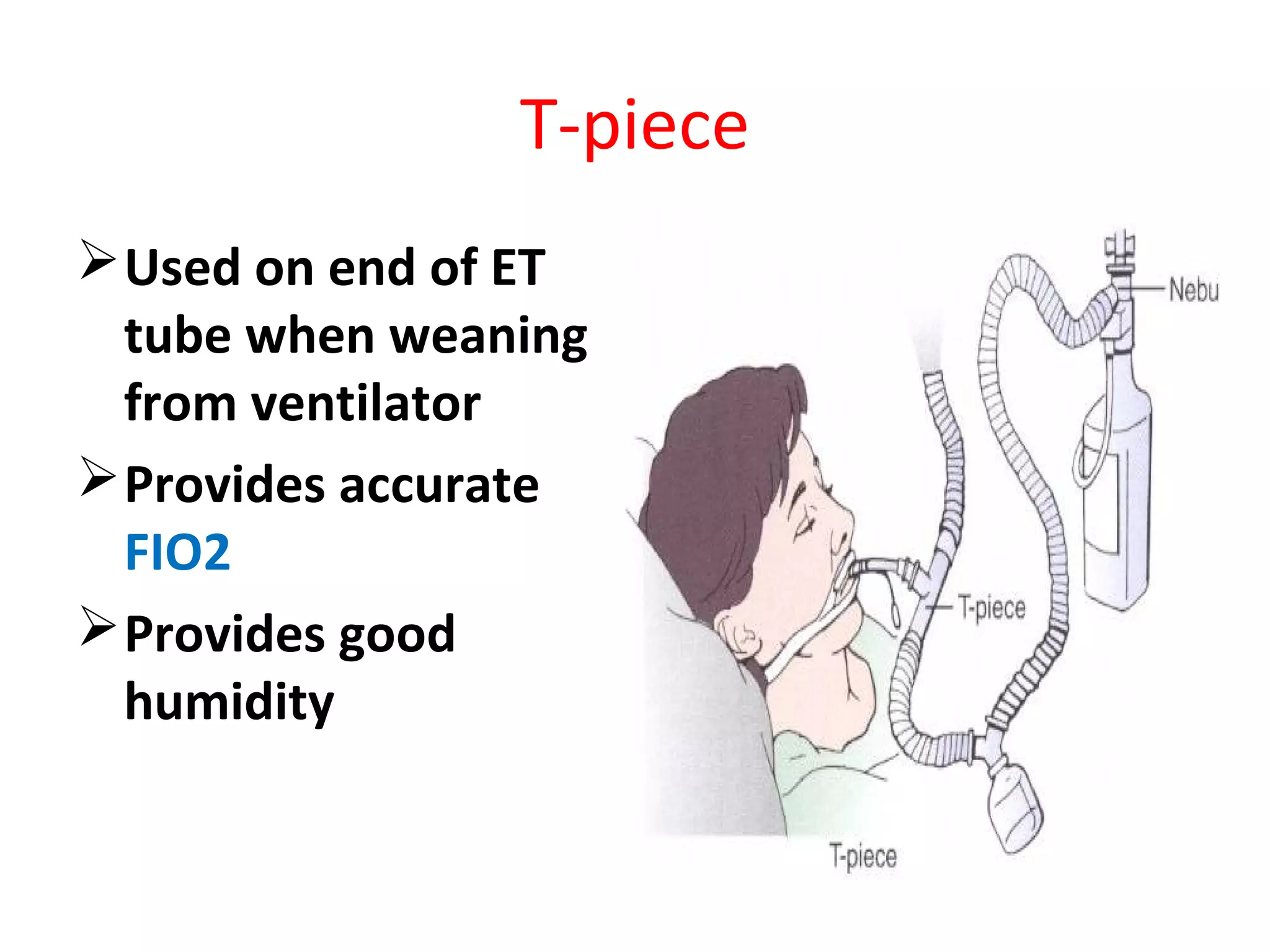
Oxygen therapy is a medical treatment that delivers oxygen to patients, increasing the oxygen levels in their lungs and blood, typically administered through various devices such as nasal cannulas and masks. It is crucial for patients with low oxygen saturation due to conditions like respiratory illnesses or heart attacks. Proper documentation and understanding of administration methods are essential for effective application and monitoring.