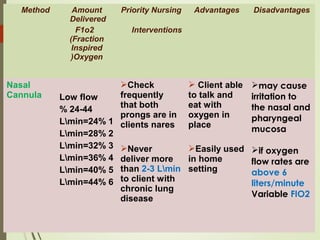
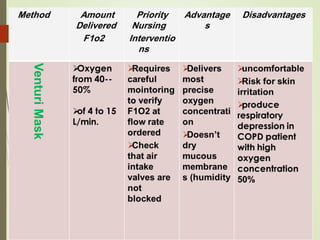
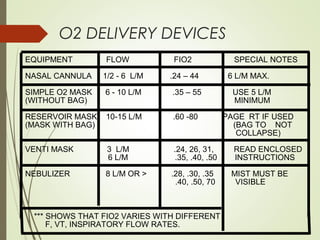
This document discusses oxygen therapy, including its definition, types, purposes, administration, and complications. Oxygen therapy delivers oxygen at concentrations greater than 21% to increase oxygen saturation in tissues. It is used to treat various respiratory conditions. Administration involves nasal cannulas, face masks, venturi masks, and other devices. Potential complications include oxygen toxicity, retrolental fibroplasia, and absorption atelectasis. Careful monitoring is needed with oxygen therapy.