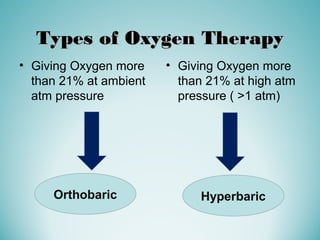
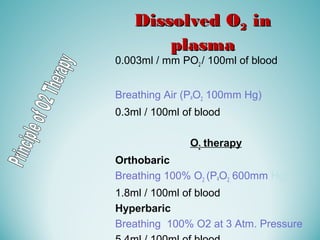
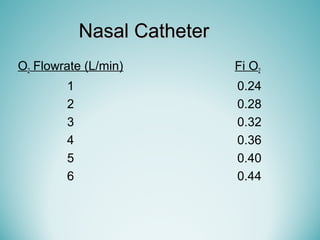
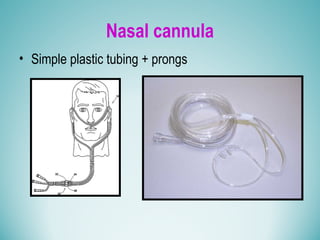
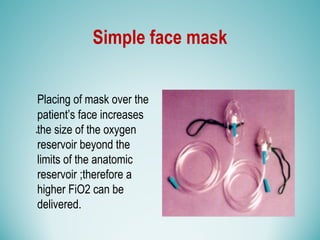
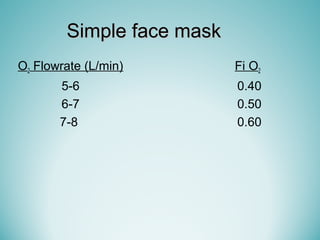
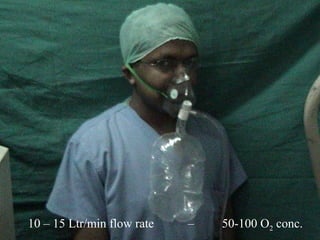
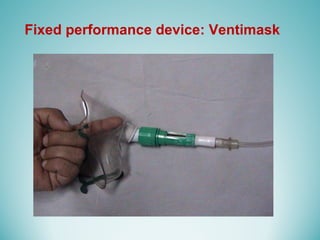
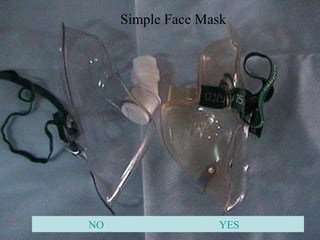
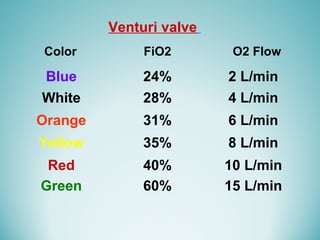
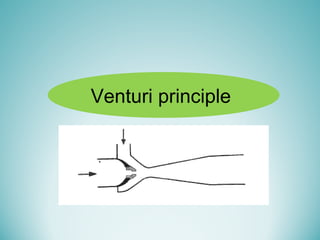
Oxygen therapy involves administering oxygen at concentrations greater than 21% to treat or prevent hypoxia. The two main types are orthobaric oxygen therapy, which delivers increased oxygen at ambient pressure, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which delivers high oxygen concentrations at increased atmospheric pressure. Orthobaric devices include nasal cannulas, face masks, and venturi masks which can provide fractional inspired oxygen concentrations from 24% to 60% depending on the device and oxygen flow rate. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is used to treat certain infections, acute injuries, and non-healing wounds by exposing the patient to 100% oxygen at pressures usually between 2 and 3 atmospheres absolute. Potential side effects of oxygen therapy include respiratory issues, central



































![Hyperbaric Oxygen therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) exposure (breathing
oxygen at increased ambient pressure, typically 2-
3 atmospheres absolute [ATA]) causes an
increase in PaO2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02oxygentherapyforug-160204024931/85/Oxygen-Therapy-56-320.jpg)