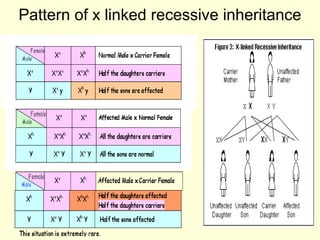
X-linked traits show different patterns of inheritance in males and females due to females having two X chromosomes and males having one X chromosome and a Y chromosome. For X-linked recessive traits, males will always be affected if they inherit the mutated gene from their mother, while females will only be affected if they inherit the mutated gene from both parents. Examples of X-linked recessive traits include hemophilia and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Fragile X syndrome is an example of an X-linked dominant trait where females can be affected by inheriting only one copy of the mutated gene.