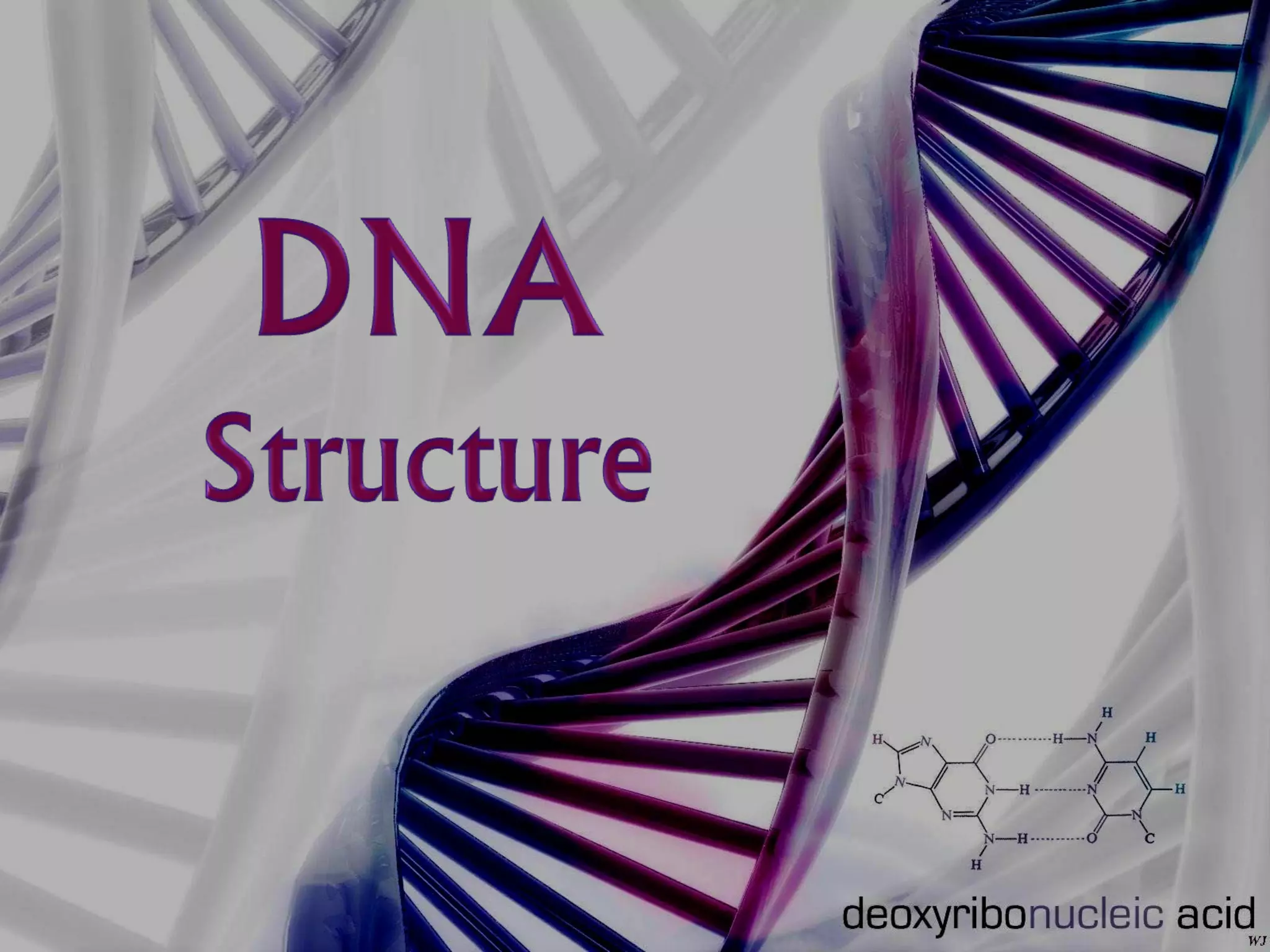
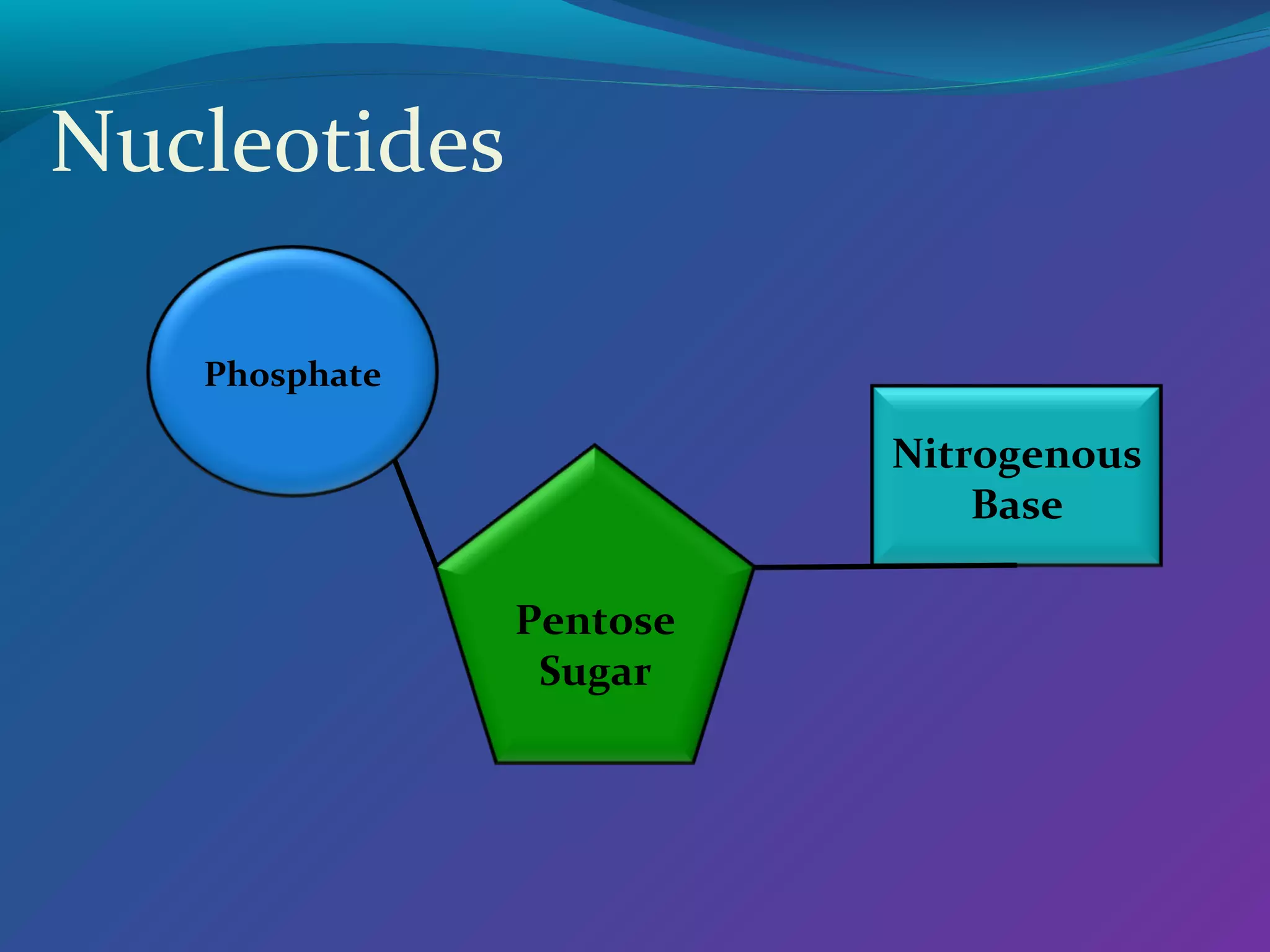
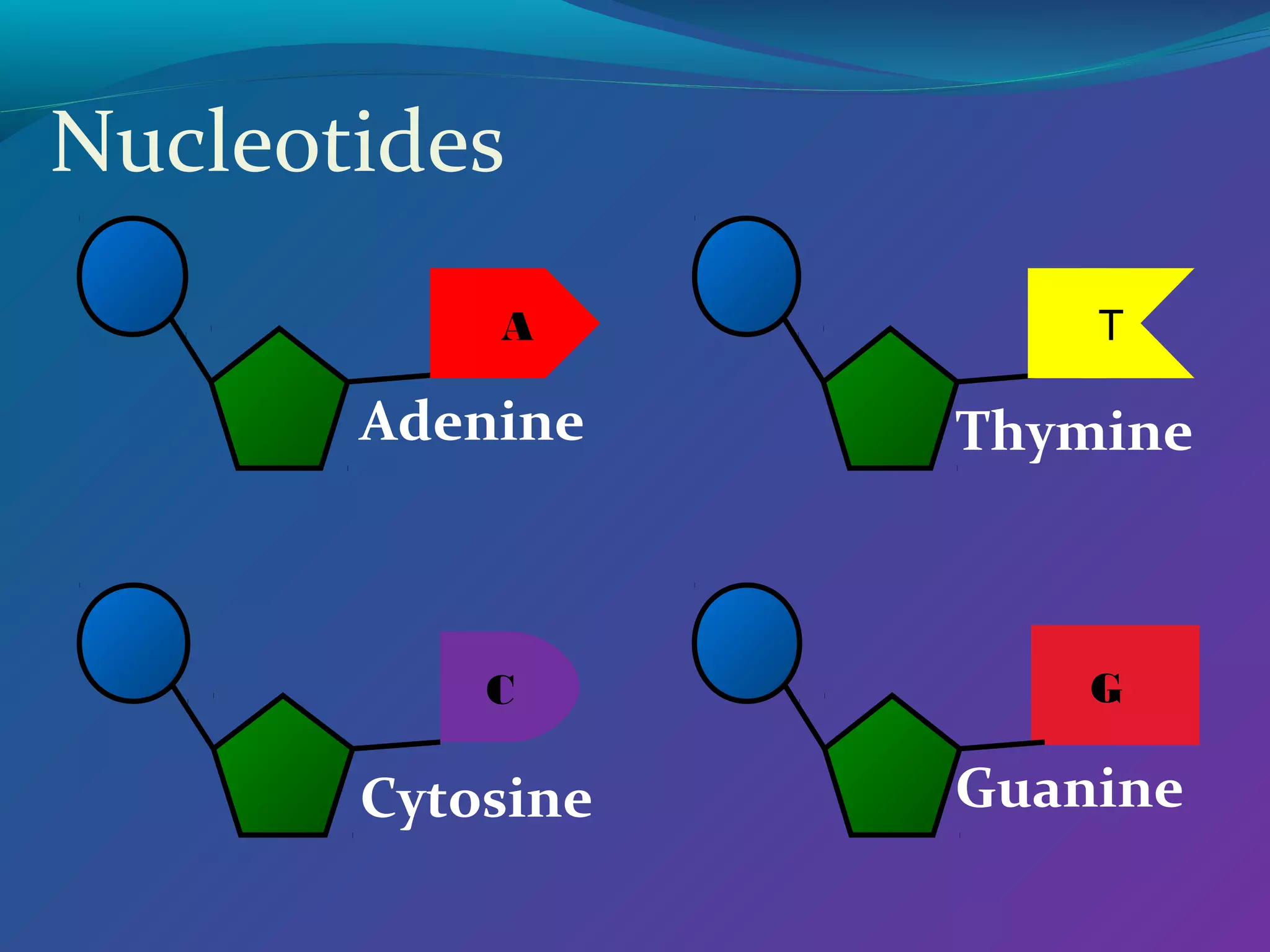
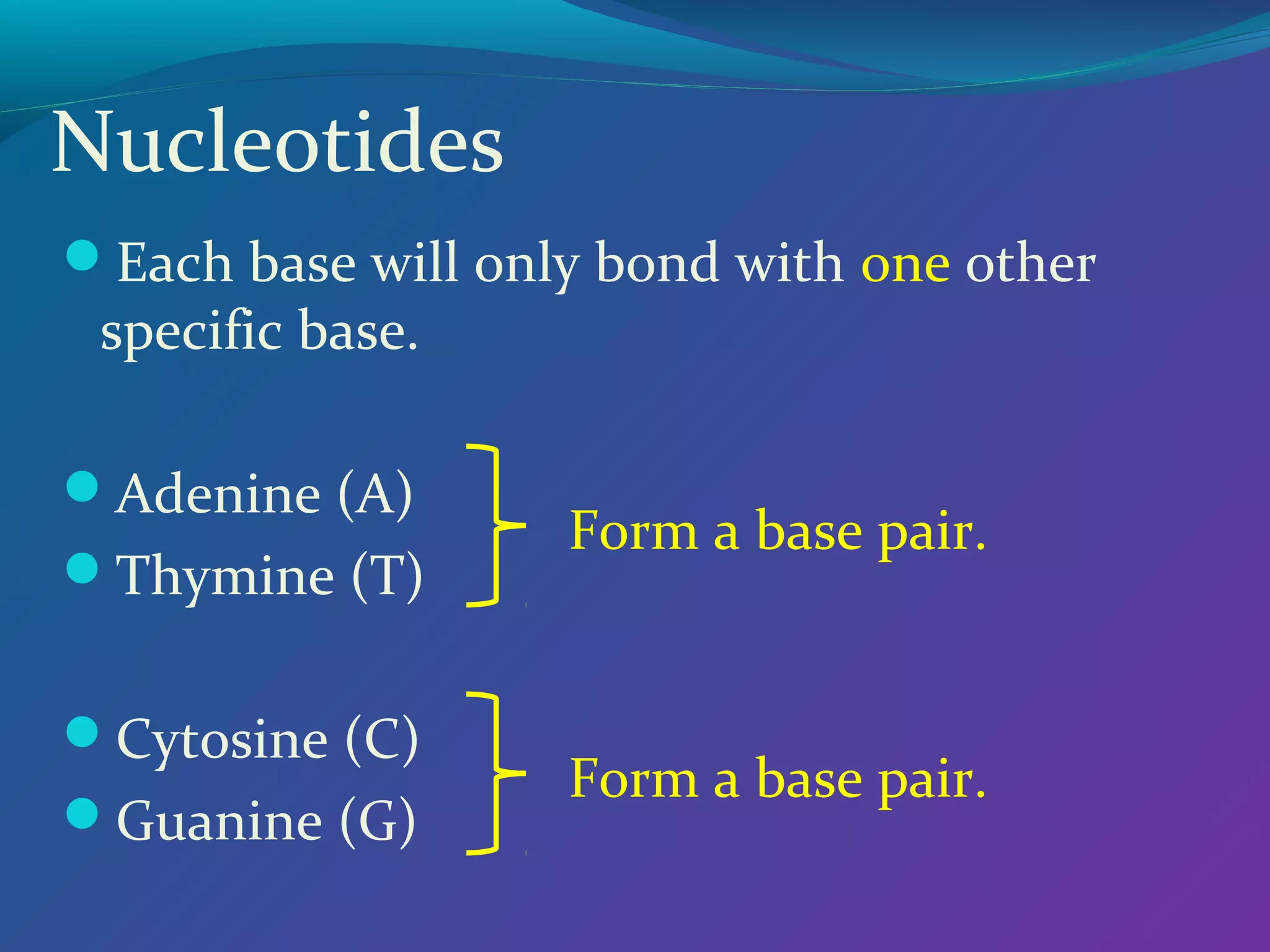
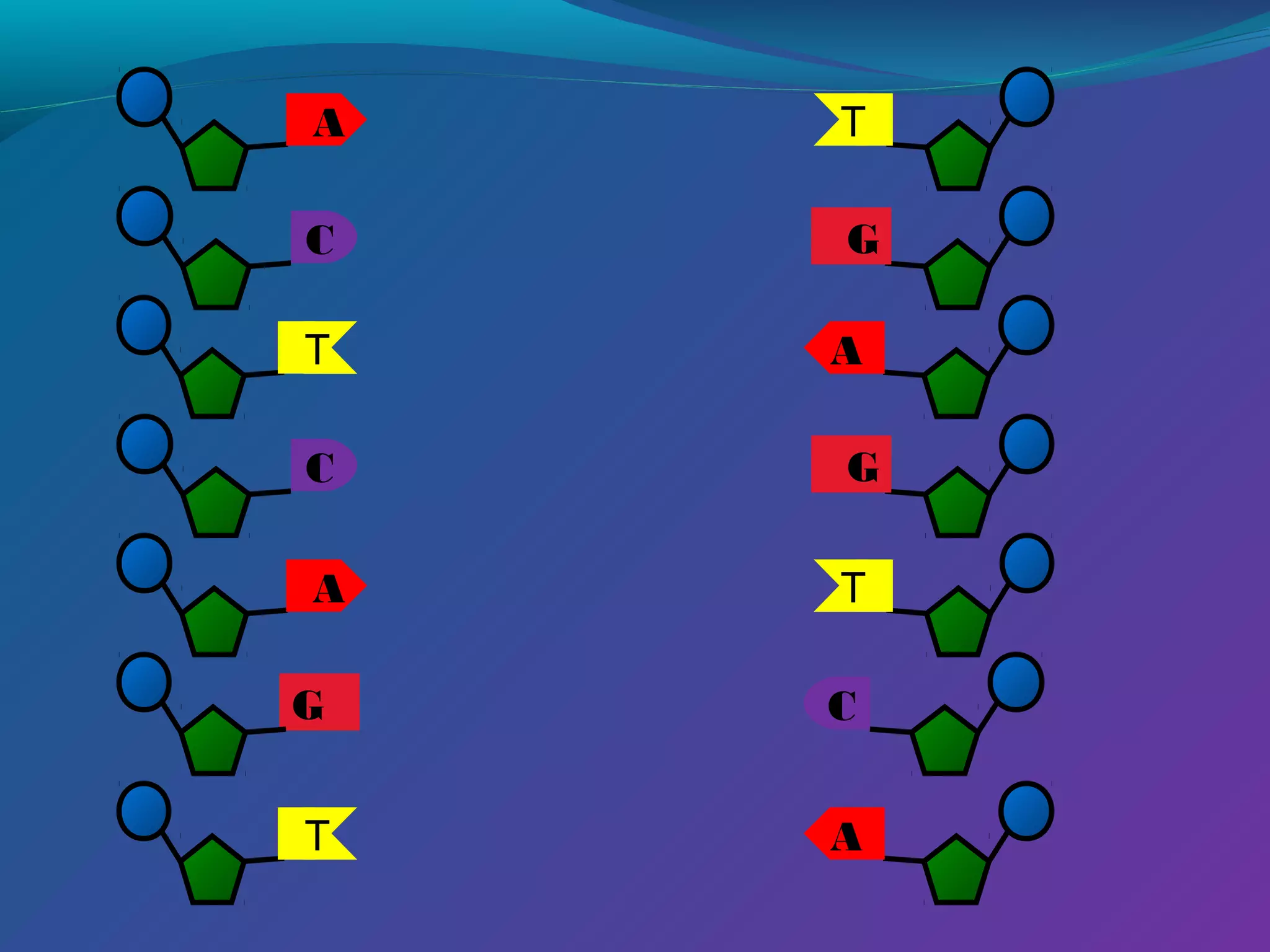
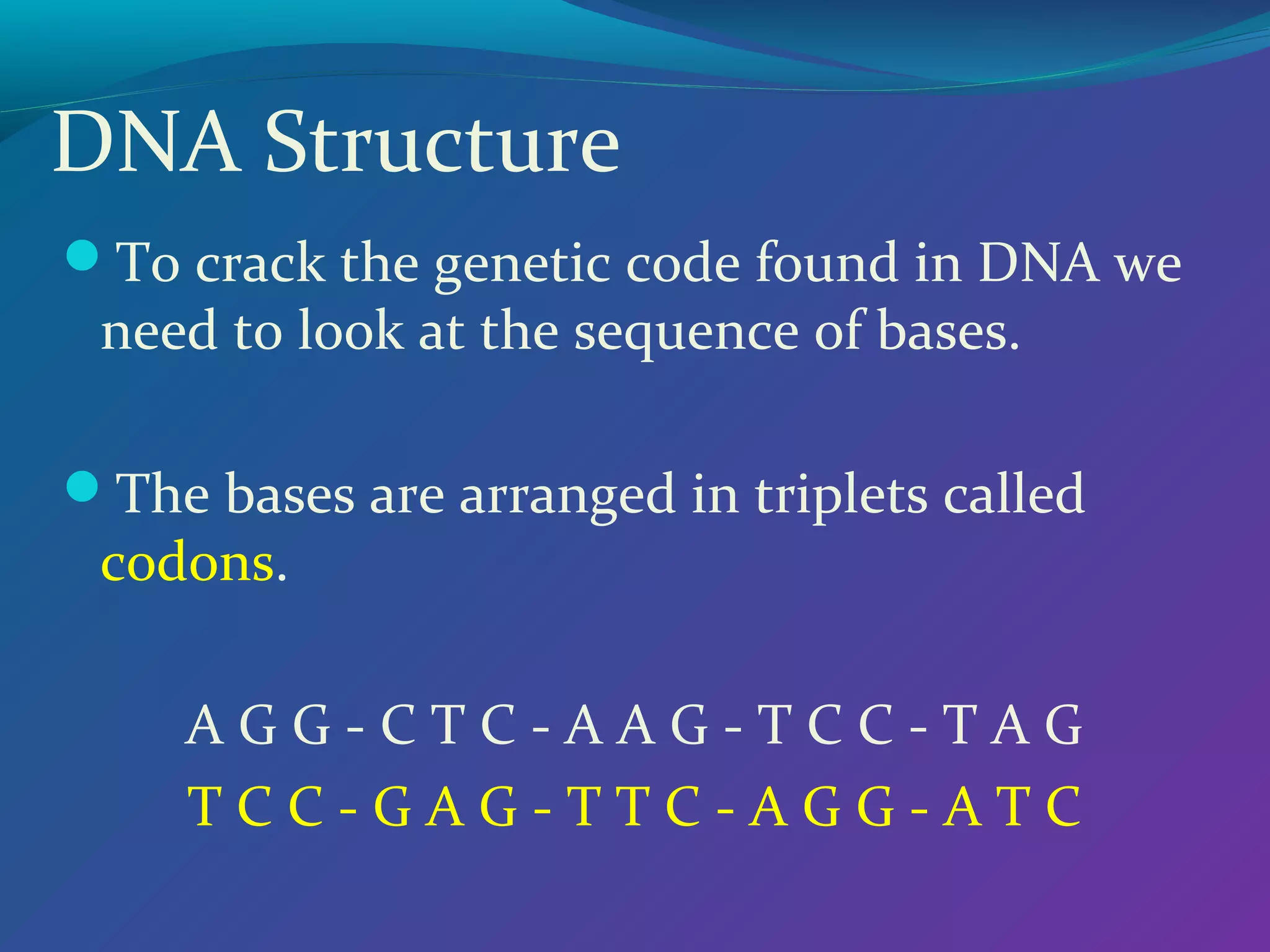
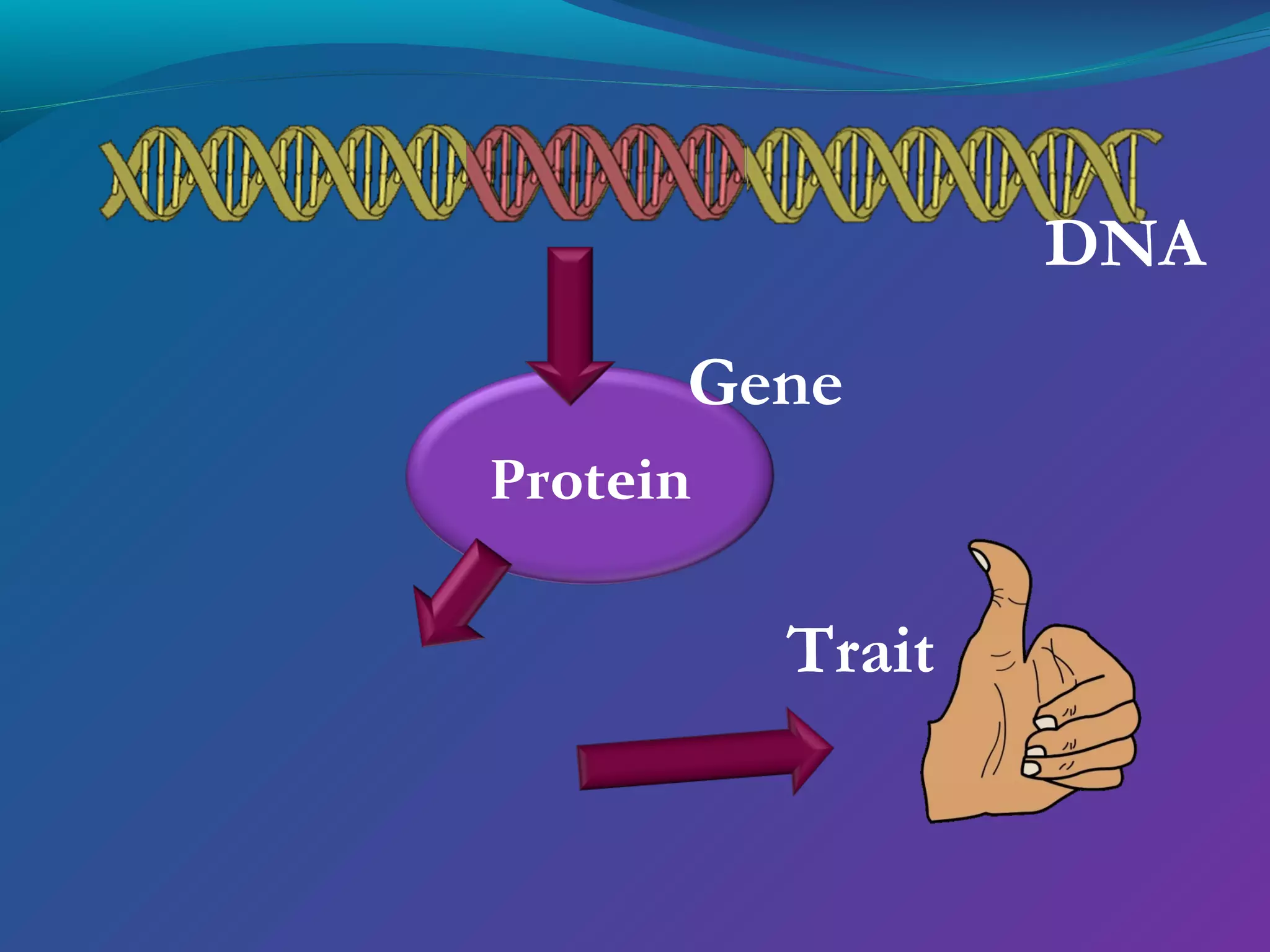
DNA consists of a double helix structure made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate, pentose sugar, and one of four nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine). The bases bond specifically with each other (A-T and C-G) to form base pairs between the two DNA strands. The sequence of these base pairs encodes genetic information and determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins.