Embed presentation
Downloaded 24 times

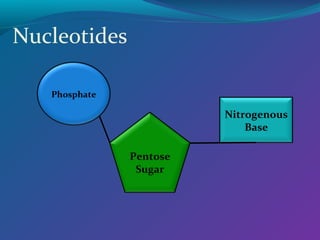

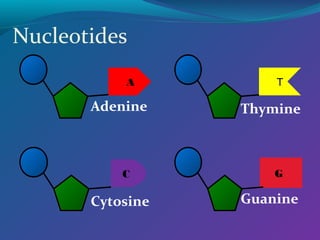


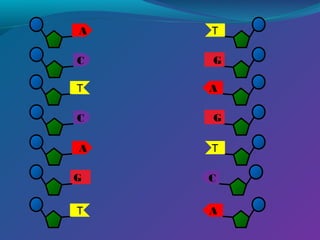


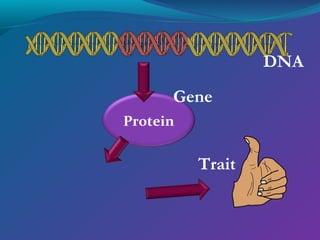

The document discusses the structure of DNA. DNA consists of two strands that form a double helix structure. DNA is made up of nucleotides, each containing a phosphate group, pentose sugar, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. The bases bond specifically with each other to form base pairs between the strands. The sequence of bases in one strand determines the sequence in the other strand. Genes are sections of DNA that code for proteins, with each gene having a unique sequence that produces a unique protein and gives organisms their traits.











