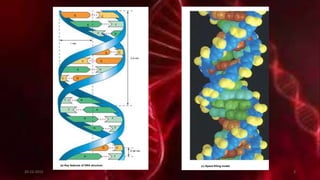
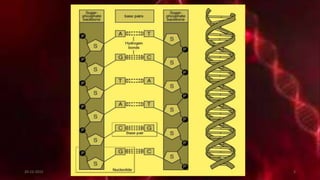
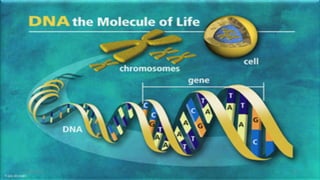
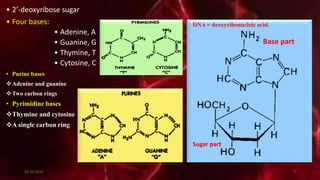
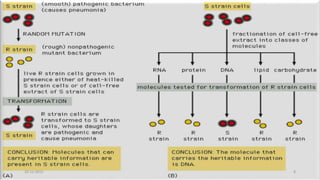
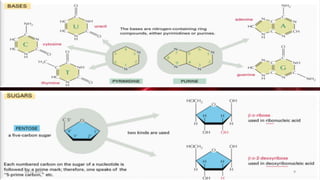
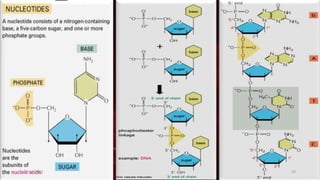
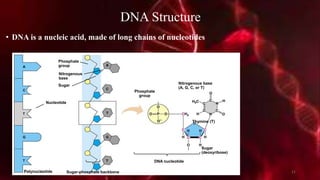
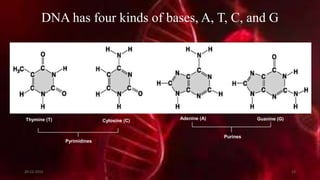
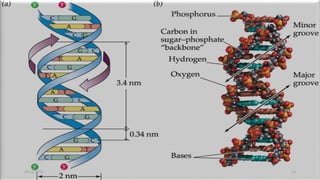
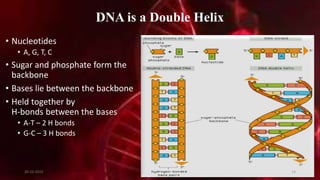
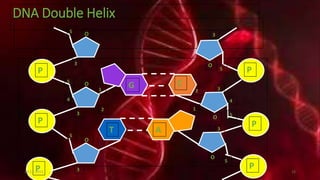
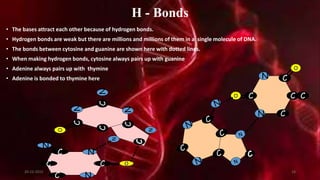
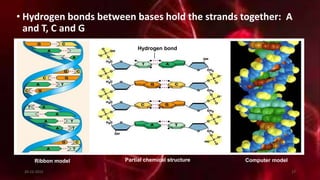
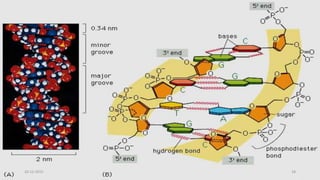
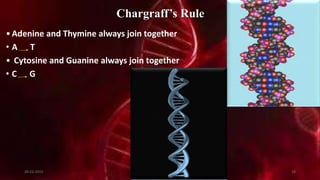
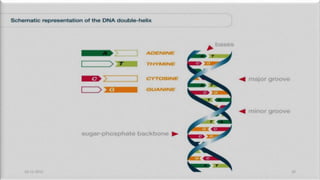
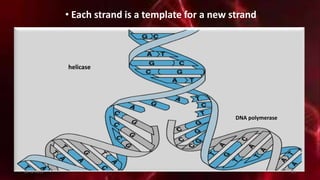
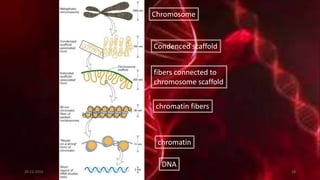
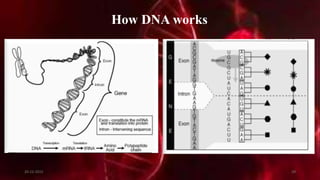
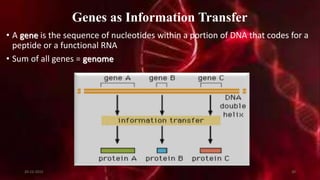
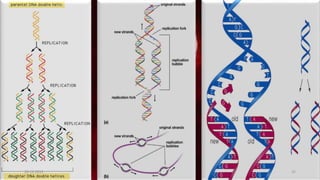
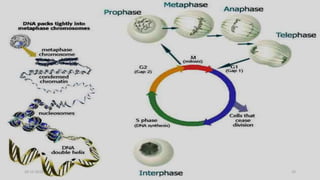
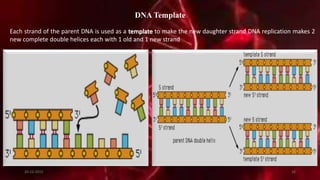
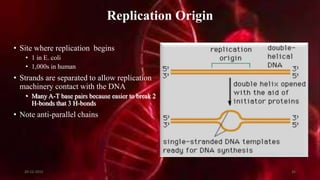
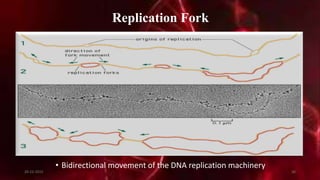
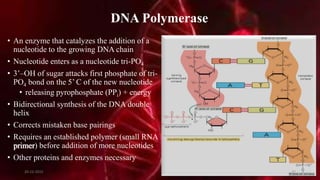
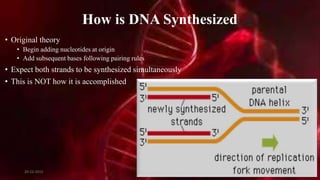
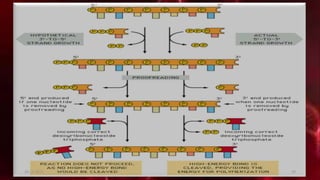
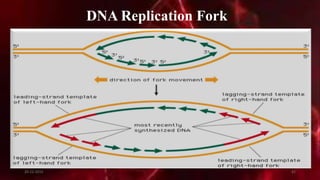
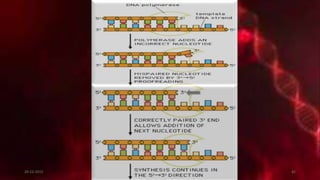
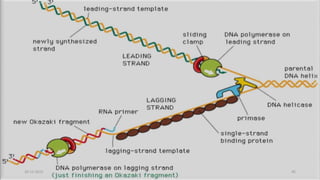
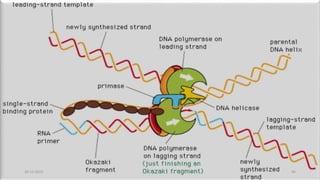
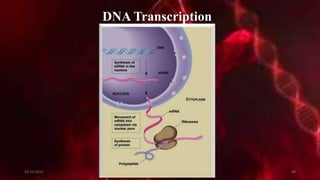
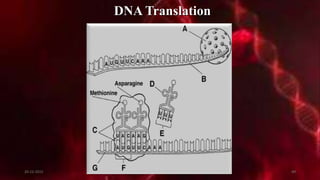
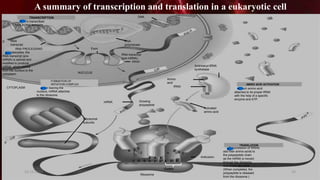
DNA carries the genetic instructions for living organisms. In 1953, Watson and Crick discovered that DNA has a double helix structure, with nucleotides on each strand connected through hydrogen bonds between complementary nucleotide base pairs (A-T, C-G). DNA replicates semi-conservatively prior to cell division, using each original strand as a template to produce two new double helices. Genes within DNA code for proteins through transcription and translation.
![DNA
(Deoxyribonucleic acid)
Mr. Sagar Kishor Savale
[Department of Pharmacy (Pharmaceutics)]
2015-016
avengersagar16@gmail.com
Department of Pharmacy (Pharmaceutics) | Sagar savale
20-12-2015 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dna-151221065015/85/DNA-Deoxyribonucleic-acid-1-320.jpg)