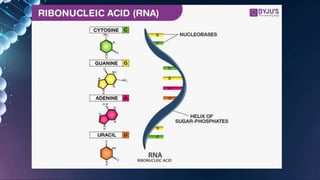
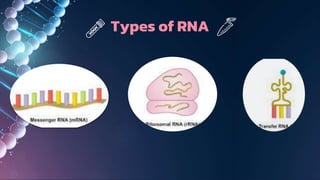
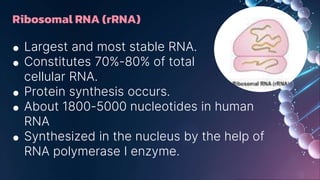
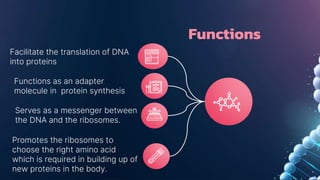
The document summarizes RNA and its functions. It discusses that RNA is a single-stranded nucleic acid that is present in all living cells and carries genetic information translated by ribosomes into proteins. It outlines the three main types of RNA involved in protein synthesis: mRNA, rRNA and tRNA. The document also provides characteristics of RNA, descriptions of the different RNA types, their functions, and differences between RNA and DNA.